Replace the last occurrence of the text in a string:
This section shows how the last occurrence of the searching pattern in a string can be replaced by using the `sed` command.
Example-1: Replace the last occurrence of a word based on pattern
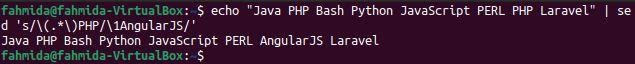
The following `sed` command will search the word ‘PHP’ in the string and replace the searching word with the word ‘AngularJS’ if the word exists in the string.
sed 's/\(.*\)PHP/\1AngularJS/'
The following output will appear after running the command. Here, the word ‘PHP’ exists two times in the string, and the last occurrence has been replaced by the word’ AngularJS‘.
Example-2: Replace the last occurrence of digit based pattern
The following `sed` command will search any digit in the string and replace the last digit with the number 9.
sed 's/\(.*\)[0-9])*/\19/'
The following output will appear after running the command. Here, the digit appears two times in the string, and the last digit, 4, has been replaced by the number 9.
Example-3: Replace the last digit of a number based on pattern
The following `sed` command will replace the last digit that exists in the string value by the value by double zero (0 0).
The following output will appear after running the command. Here, 500 exists in the string value. So, according to the replacement command, the last zero of 500 has been replaced by two double zero, and the replaced value is 5000.
Example-4: Replace the last occurrence of a word with another word
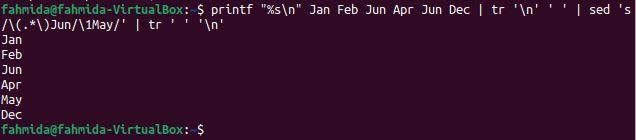
The following `sed` command will search the word ‘Jun’ in the string and replace the last occurrence of the word with the value, ‘May’.
sed 's/\(.*\)Jun/\1May/' | tr ' ' '\n'
The following output will appear after running the command. Here, the word ‘Jun’ exists two times in the string, and the last occurrence has been replaced by the word ‘May’.
Replace the last occurrence of a text in a file:
Create a text file named Sales.txt with the following content to test the `sed` command used in this part of the tutorial for replacing the last occurrence of a text-based on the pattern.
Sales.txt
January 2018 $ 200000
March 2019 $ 300000
April 2019 $ 150000
March 2020 $ 350000
May 2019 $ 210000
January 2020 $ 240000
Example-5: Replace the last occurrence of a word with another word
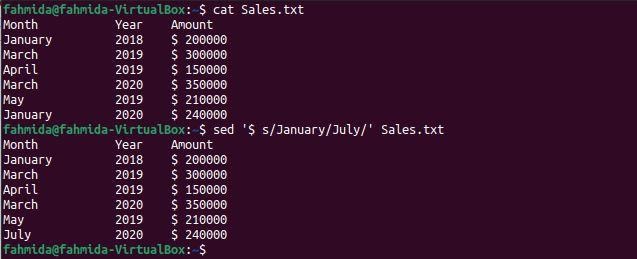
The following `sed` command will search the word ‘January‘ in the file and replace the last occurrence of this word with the word, ‘July‘.
$ sed '$ s/January/July/' Sales.txt
The following output will appear after running the commands. The word ‘January’ appears two times in the file. The last occurrence that exists in the 7th line of the file has been replaced by the word ‘July‘ in the output.
Example-6: Replace the last occurrence of a number with another number
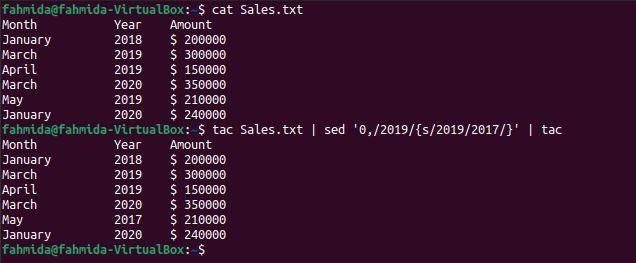
`tac` command is used to reverse the content of the file. `tac` command is used with the `sed` command in the following command to replace the last occurrence of ‘2019‘ with the word, ‘2017’.
$ tac Sales.txt | sed '0,/2019/{s/2019/2017/}' | tac
The following output will appear after running the commands. Here, the year value, ‘2019‘ appears three times in the file. The first, ‘tac’ command has reversed the content of the file and sent the output into the `sed` command to replace the first occurrence of ‘2019’ which is the last occurrence in the file by the year value, ‘2017’. After the replacement, the output has been sent to the `tac` command to reverse the output again. In this way, the last occurrence of ‘2019‘ has been replaced by the value, ‘2017‘.
Example-7: Replace everything of a line based on the last occurrence of a word
The following `sed` command will replace the line with a tab (\t) delimited text where the line starts with the string ‘Mar’ for the last time in the file.
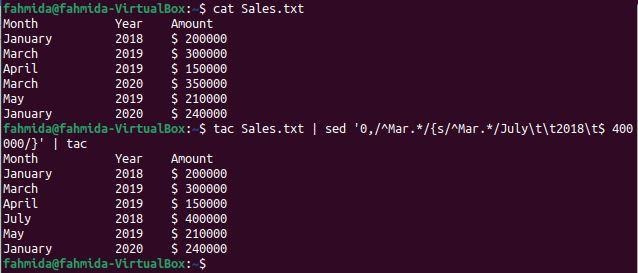
$ tac Sales.txt | sed '0,/^Mar.*/{s/^Mar.*/July\t\t2018\t$ 400000/}' | tac
The following output will appear after running the commands. Two lines in the file start with the string, ‘Mar’, and the last occurrence of this string appears in the 5th line. The first `tac` command has been used to reverse the content of the file and sent the output to the `sed` command. `sed` command has replaced the line with a text, ‘Jully 2018 $ 400000‘ where the searching string found for the first time. The output of the `sed` command has been sent to the `tac` command again to reverse the output that is the main content of the file.
Conclusion:
`sed` command can be used to replace any part of a string or a line of the file in different ways by using regular expression patterns. This tutorial showed the ways to replace the last occurrence of the searching text in a string or a file by using multiple `sed` commands. How the `tac` command can be used with the `sed` command to replace the last occurrence of the searching text has also been shown in this tutorial. But all the commands used here will generate the output temporarily. You have to use the ‘-i’ option with the `sed` command to change the content of the file permanently based on the pattern.