The sed command has longlist of supported operations that can be performed to ease the process of editing text files. It allows the users to apply the expressions that are usually used in programming languages; one of the core supported expressions is Regular Expression (regex).
The regex is used to manage text inside text files, with the help of regex a pattern that consists of string and these patterns are then used to match or locate the text. The regex is widely used in programming languages such as Python, Perl, Java and its support is also available for command line programs such as grep and several text editors too like sed.
Although the simple searching and sorting can be performed using sed command, using regex with sed enables advanced level matching in text files. The regex works on the directions of characters used; these characters guide the sed command to perform the directed tasks. In this article, we will demonstrate the use of regex with sed command and followed by the examples that will show the application of regex.
How to use regex in sed
This section is the core part of the writing that contains the detailed explanation of Regular Expressions in sed context: let’s start with it
Matching the word
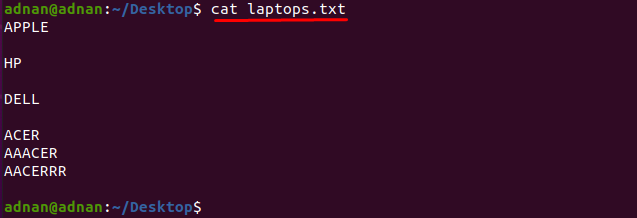
If you want to find the word that exactly matches the characters, then you must specify the exact characters that matches the word: For instance, we have a text file that contains the list of laptop manufacturers named as “laptops.txt”:
Let’s get the content of the file by using the command mentioned below:
Use the following command will help to get the “ACER” word:
Matching all words start with specific character
This regex support contains multiple actions that are described in this section:
If you want to search and match the words that starts and end with a specific character, then you must use “*” sign in between characters to do so; but it is noticed that the “*” symbol prints the words that start with single or multiple “A’s” but with single “R”: For instance, the command written below will print all the words that starts with single or multiple “A” and ends with single “R”:
To match the word that ends with specific character or that contains only specified character: the command written below will display the words with character “P” or the exact word “HP”:
Matching the words with specific character
It is noticed that you can get the words that contain any character with the help of sed command: For instance, the command mentioned below will find the words that contains one of these characters “A”, “H” or “D”:
Matching the string
You can use sed command with regular expressions to print the strings; you can either print all the strings or you can also target a specific string by using the starting or ending character of that string:
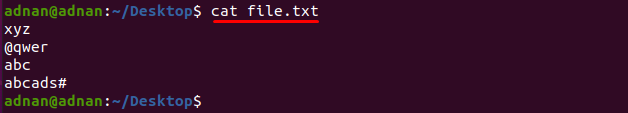
we have used “file.txt‘ to use it as an example in this section; this file contains the following content:
For instance, if you want to print all the strings; the following command will help you in this regard:
If you want to get all the strings that start with character “a” then you have to use carrot symbol (^) to indicate the starting character of the string.
The command mentioned below till print the strings that start with “@”:
Moreover, if you want to get only those strings that end with a specific character then you have to use “$” with that character. For instance, the command written here will print the strings that ends with “#”:
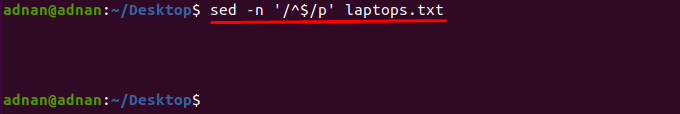
Matching the blank lines
The sed command regex support allows the user to print/delete the empty lines by using “/^$/”; the following command will print the empty lines in “laptops.txt” file:
Or you can delete by replacing “p” with “d” in the above command as displayed below:
Matching the letter case
The sed command allows users to manipulate the words with specific letter case:
For instance, you can print, delete, substitute the letter case words by using sed command:
A text file named as “test.txt” is used in this example, the content of this file is printed by using following command:
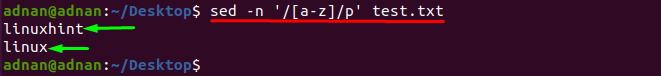
Matching the lowercase letters
The following command will print all those words that contain lower case letters in them:
Matching the uppercase letters
Or you can print the words that contains upper case letters by issuing the following command in terminal:
Conclusion
Regular Expressions(regex) are referred to as; any word or sequence of characters that is used to get the matching words from any text file. They provide extensive support for several programming languages as well as Ubuntu commands or programs. Alongside this regex, Ubuntu provides support for extensive commands that ease the process of performing tedious tasks. The sed command line utility of Ubuntu allows you to perform several tedious tasks very easily to perform several operations on text files. We have compiled this guide to enlighten the benefits of joining regex with sed; this joint venture provides advanced level matching and searching inside text files. Regular Expressions need help from characters that are used for matching to perform various tasks such as deleting, printing, substituting, or managing text inside text files.