This article will specifically talk about the usage of Pi in Java.
How to Use Pi in Java?
The general value of Pi is “3.14”. It is primarily utilized for calculating the Area and Circumference of a circle. It is also utilized in several mathematical formulas, functions, and constants.
In Java, Pi can be used as:
We will now check out both of the mentioned methods one by one.
Method 1: Use Pi in Java as Pre-defined Constant
Java programmers can utilize the “Math.PI” constant of the “java.lang” package. It is a static double type constant that belongs to the Java Math class:
Note: The “final” keyword is utilized for defining a constant that maintains its value and keeps it the same during the execution.
As the Pi (π) is the static variable, you can call its value by using the class name or by adding the Math library in the code and accessing the PI constant.
Syntax
The syntax for calling PI by using the Math class name is given as:
Or import Math class and call the PI constant where needed:
Have a look at the given examples to learn about the usage of Pi as a Pre-defined constant.
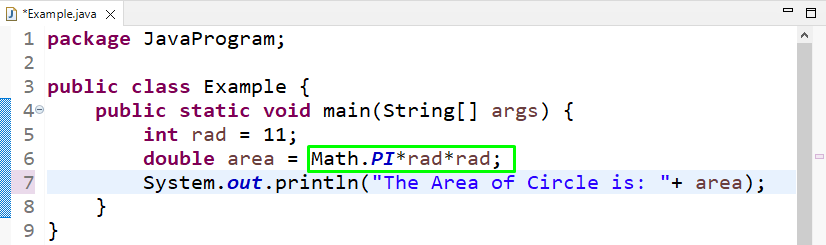
Example: Using Math.PI in Java
In this example, we will use Math.PI as a Pre-defined constant to find the area of a circle. The formula for the area of a circle is given as “πr^2”. We will specify the radius value as “11” and store it in an integer type variable named “rad”. The calculated area by using Math.PI will be stored in a double type “area” variable:
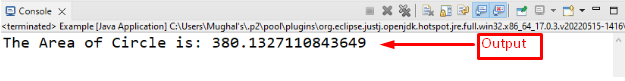
The given output indicates that we have successfully accessed the value of Math.PI and evaluated the area of the circle:
Let’s check out the other method of using the Pi Constant.
Method 2: Using Pi in Java as User-defined Constant
Pi can also be utilized in Java as a User-defined constant. In this method, you have to assign a value to the Pi variable by yourself and then use it where needed.
Example
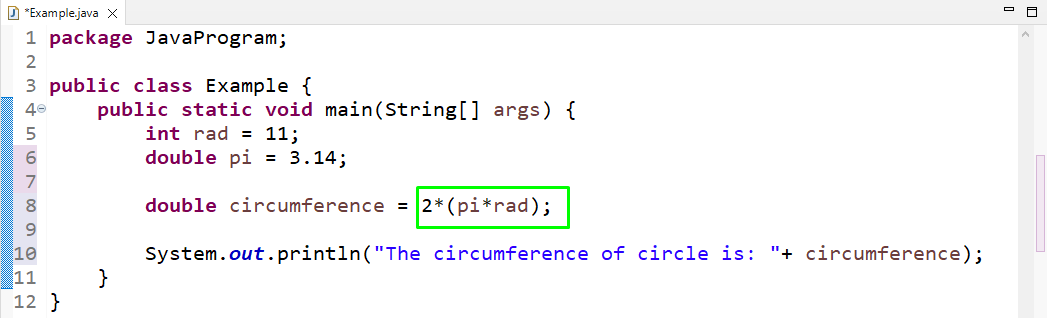
Here, we will find the circle’s circumference without calling the predefined “PI” constant. To do so, firstly, we will create two variables, “rad” of int type for storing radius and “pi” double type for the saving the value of pi as “3.14”:
double pi = 3.14;
Next, we will create another double type variable for storing results named “circumference”. The circle circumference’s formula is given as “2*(pi*r)” print it by using the “System.out.println()” method:
System.out.println("The circumference of circle is: "+ circumference);
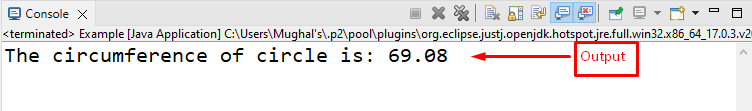
As you can see, our Java program calculated the circle circumference based on the User-defined Pi value:
We have provided all the essential instructions related to the usage of Pi in Java.
Conclusion
In Java, Pi can be used as a Pre-defined constant “Math.PI” and a User-defined constant. For using Pre-defined constants, you can either call the Math.PI constant of the Math class or import the Math class in your projects. However, in the User-defined Pi constant, you can set the value of Pi to a variable and then utilize it. This blog illustrated the use of Pi in Java with detailed examples.