IP command is a very incredibly handy tool for network configuration. It is a replacement for the old ‘ifconfig’ command found on Linux distributions. IP command can be used to manage network interfaces, devices, tunnels, and routing aspects. Network administrators often need this tool for administering a network and troubleshooting errors.
What will we cover?
In this guide, we will see some of the actual uses of the IP command. We have performed this guide on Debian 10 (Buster) OS. You will need to have a superuser account or a user with ‘sudo’ privileges to perform some of the commands.
Getting Started with IP command
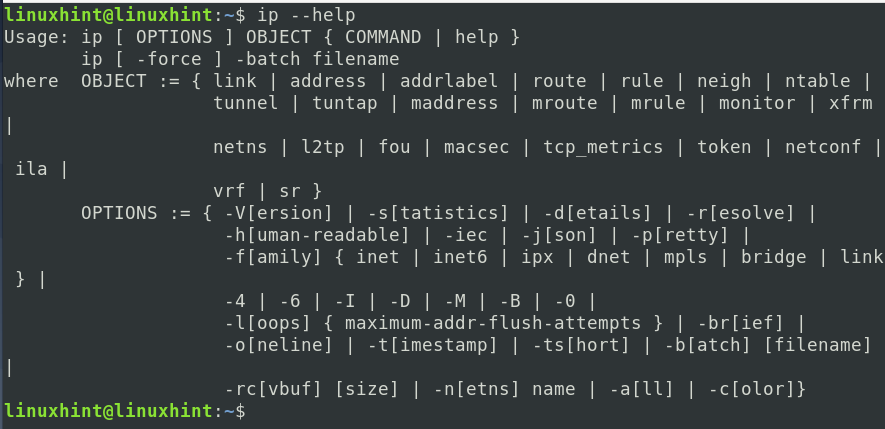
There are many possibilities with the ‘IP’ command, as we will see now. E.g., if you want to see a complete list of various options and objects that can be used with this command, then issue the following command on a Linux terminal:
‘ip link.’
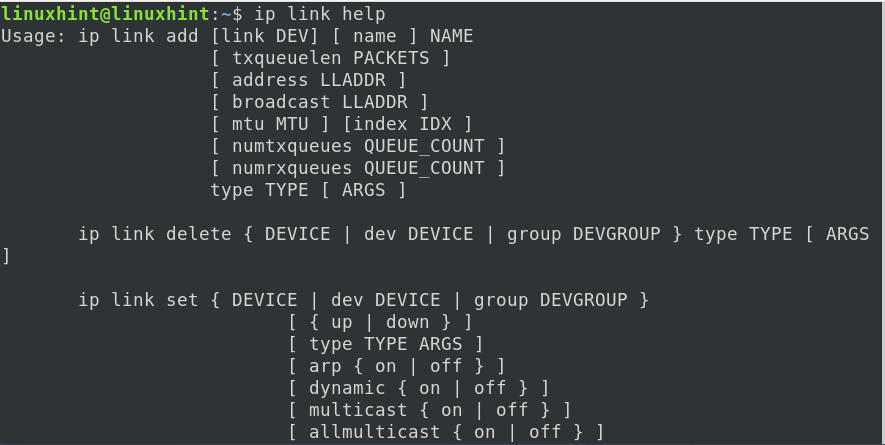
The ‘link’ object can be used to manage network interfaces. E.g., to see all the available possibilities with the ‘ip link’ object, use:
Alternatively, one can also execute the below command for more information:
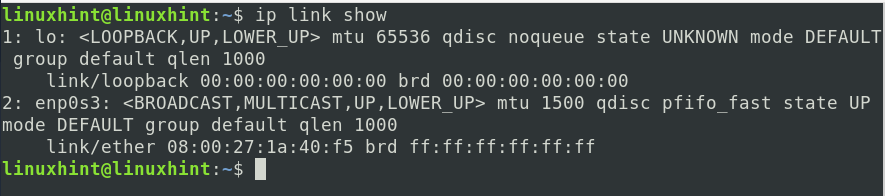
a) To list all the available interfaces on your system:
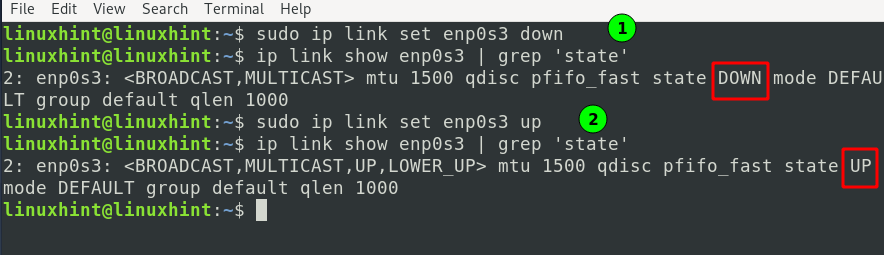
b) To bring an interface ‘down’, use:
Where ‘iface’ is the name of an interface, you can see the list of available interfaces using the ‘ip link show’ command.
c) Similarly, to bring an interface ‘up,’ we can use:
d) To check the status of a link (interface), use:
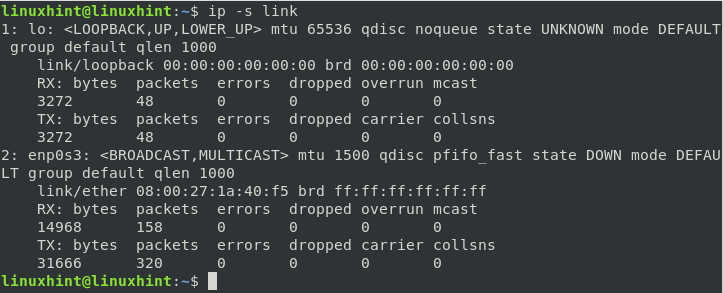
e) If you want to troubleshoot errors while establishing network connectivity, the below command can help a lot:
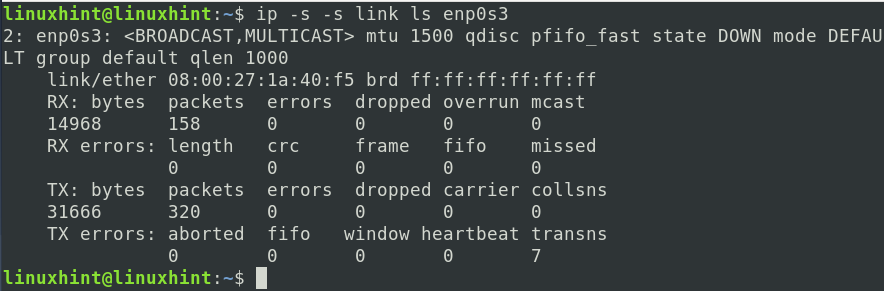
One can use the ‘-s’ option twice to see more information in the output. E.g., to see the statistics of only ‘enp0s3’ interface, use:
‘ip route’
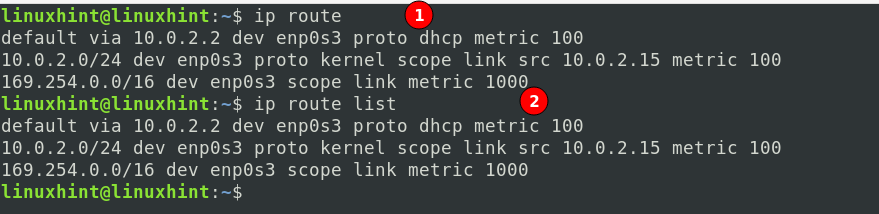
To display various options and commands used with the ‘ip-route,’ use the command:
Or, use the below one for more information:
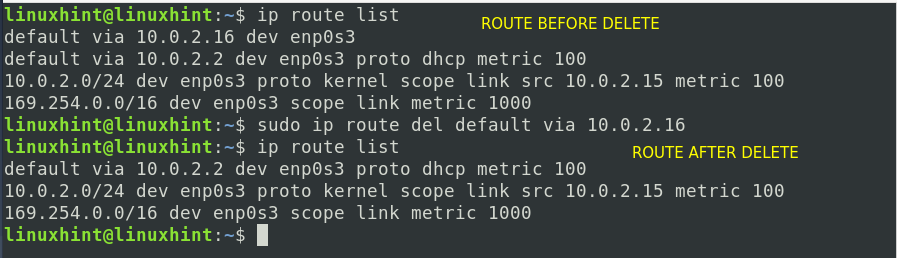
a) To display the IPv4 route table entries, use the following command:
Or
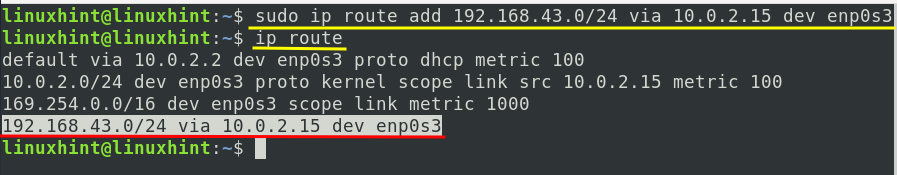
b) To add a new route, use the syntax:
E.g., to connect to a network 192.168.43.0 via 10.0.2.15 using interface enp0s3, the command will be:
c) To delete a route entry, replace the ‘add’ keyword with the ‘del’ as shown below:
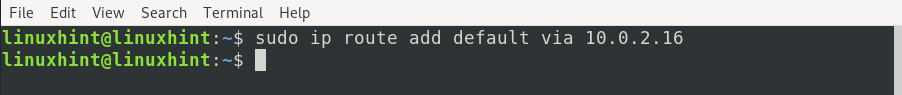
d) To add a new gateway with ‘ip route,’ use the command:
E.g., to connect to a gateway 10.0.2.0, the above command will be:
To delete this gateway, run the same command with ‘add’ replaced by ‘del’:
‘ip addr’
Again to see the complete list of options with the ‘ip addr’ command, use:
a) To see all devices/interfaces with the ‘ip’ command, use any one of the following commands:
ip addr show
ip addr
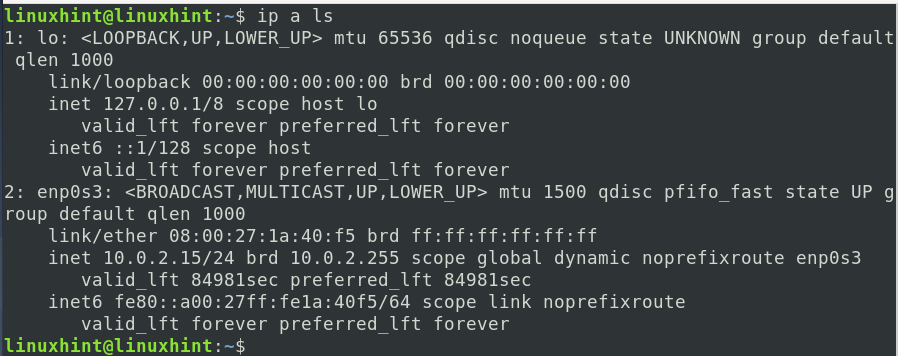
ip a
ip a ls
b) To add a temporary IP address to a given interface, we can use the format:
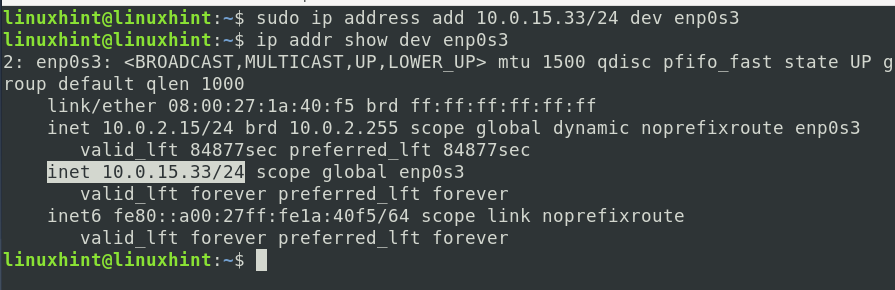
E.g., to add the address ‘10.0.15.33’ to the interface enp0s3, the command will be:
To check if the IP address is assigned on the given interface, run the command:
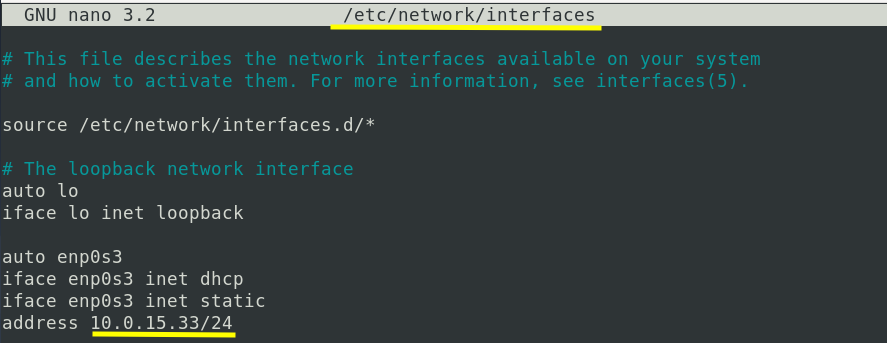
Please note that the above IP can be made permanent by editing the /etc/network/interfaces file. Open this file with any text editor like nano or vi and put the following entries into it:
iface enp0s3 inet dhcp
iface enp0s3 inet static
address 10.0.15.33/24
c) To delete the above temporary IP address of the interface, we can use the format:
E.g., to delete the above address ‘10.0.15.33’ of the interface enp0s3, the command will be:
Again check with the command:
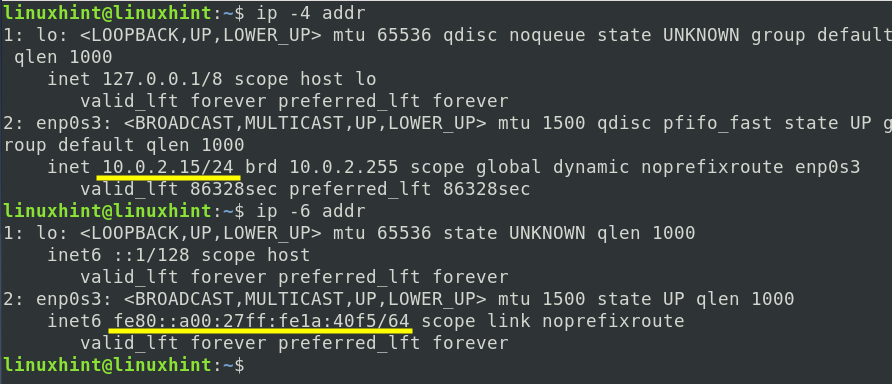
c) To display IPv4 addresses configured on your computer:
d) To display IPv6 addresses configured on your computer:
Conclusion
This guide has learned about a comprehensive list of frequently used ‘ip’ commands using Debian 10 Linux. This guide can also be tried on other Linux distributions like Ubuntu, Red RedHat-based distros, etc. To get more information regarding any ‘ip’ subcommand, you can use the man pages or the ‘help’ command.