The Hardware Clock is quite different from the clock that is managed by the Linux kernel. It runs when the system is running, and it even remains active when the machine is turned off as it is independent of the operating system you are using.
The Configuration of Hardware Clock can be modified from BIOS. User can also set and view the hardware time using the “hwclock” command:
Syntax:
Syntax of “hwclock” command is:
hwclock [function] [options]…
Getting Started with hwclock:
The “hwclock” tool performs different functionalities with various options.
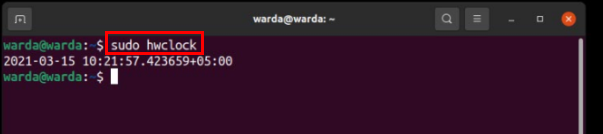
To display the hardware clock’s date and time on the terminal, type “hwclock” in the command-line. The result will be the same as the time and date are set in your BIOS:
hwclock Functions:
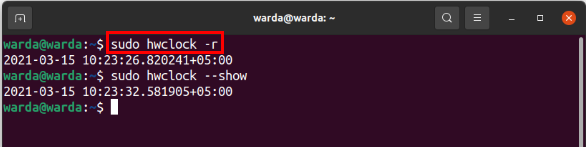
To display Real-Time Clock (RTC) on the terminal, use “-r” or “–show.” You will get the same results.
Or
Adjust Hardware Clock:
To control the adjustment of RTC when your system starts, use the “adjust” command:
There are many other functions of “hwclock” as well:
- There might be a case when your system clock is not accurate, but the Hardware Clock is. In this case, “-s” or “-hctosys” is used to copy hardware clock time to the system clock time.
- “-w” or “-systohoc” is contrary to “hctosys.” It copies system time and sets RTC. Or we can say if your hardware clock time is not accurate, then this command will set the BIOS time according to the system’s time.
- The “systz” function is used to send the configuration of the timescale to the kernel.
hwclock Options:
There are few options of the “hwclock” command:
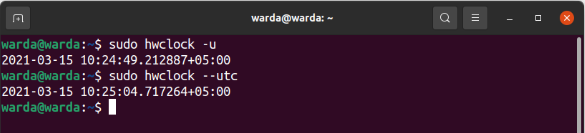
The “-u” or “–utc” option is used when you want to display that timescale of RTC is UTC.
Or
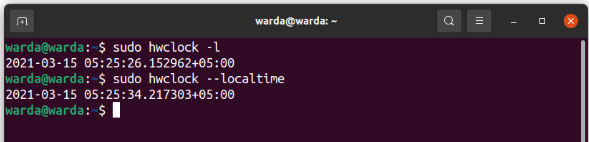
“-l” or “–localtime” option is used when you want to display that timescale of RTC is Local- time:
Or
To print the debug information, use the “debug” option in the terminal with “hwclock”:
Or
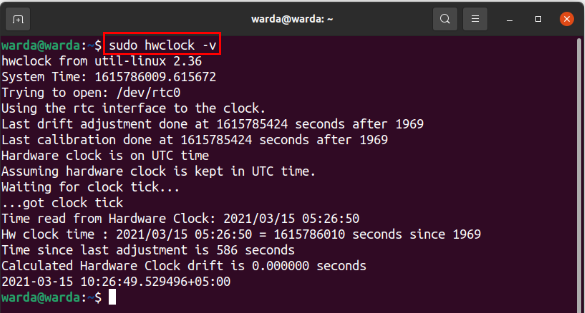
“-v” option is used to display version information of “hwclock” in the terminal:
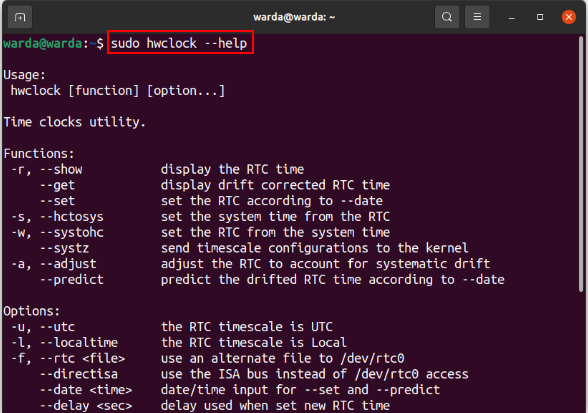
Use the “help” option to get detailed information about the “hwclock” tool in the terminal:
Conclusion:
The “hwclock” is a utility that is used to access hardware time. It is also known as RTC (Real Time Clock) and different from Linux Kernel’s clock. In this Linux command tutorial, we learned how Hardware Clockworks. We have also mentioned the usage of the “hwclock” command and its various options.