This tutorial will demonstrate:
What is the “git rev-list” Command in Git?
The “git rev-list” command lists and traverses the commit objects in a repository. It will permit Git users to filter and display commits based on criteria such as commit ranges, branches, tags, dates, authors, and more.
Syntax
The general syntax of the above-discussed command is provided below:
In the above syntax:
- “<options<” is an optional parameter that can be replaced with the desired option/flag.
- “<commit range>” parameter determines the range of commits that users want to set. It can take various forms, such as commit SHA hashes, branch names, tags, or even relative references like HEAD~3 which means 3 commits before the current commit.
Multiple options/flags can be used along with the above-stated command. Some of them are described below:
- “–all”: List all commits in the entire repository.
- “–since”, “–until”: Filter out the commits according to the commit date, and allow users to specify a range.
- “–author”: Filter the commits based on the author’s name or email address.
- “–grep”: Search for commits that match a specified pattern.
- “–max-count”: Limits the number of commits displayed.
- “–merges”, “–no-merges”: Filter the commits to include or exclude merge commits.
- “–first-parent”: Only display the first parent of merge commits.
How to Utilize the “git rev-list” Command in Git?
To use the “git rev-list” command in Git, check out the provided examples:
- Example 1: List All Commits Between Two Commits
- Example 2: List Particular Branch Commits
- Example 3: List Commits Before Current Commit
Example 1: List All Commits Between Two Commits
To list all the commits between two commits, follow the below-stated steps:
- Go to the Git local directory.
- View Git log history by executing the “git log –oneline” command.
- List all available commits between the two commits by executing the “git rev-list” command.
Step 1: Redirect to Git Local Directory
First of all, go toward the Git local directory with the help of the “cd” command:
Step 2: View Git Log History
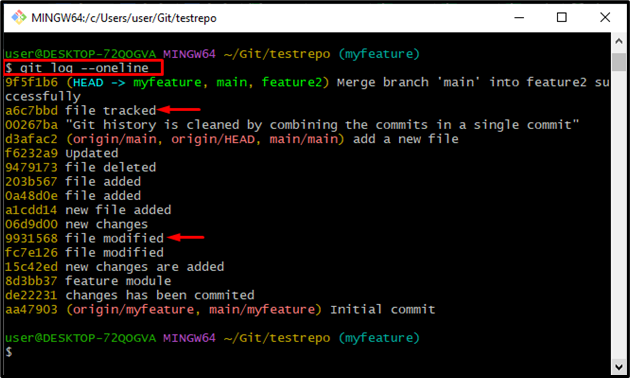
Execute the below-given command to show each commit within a single line:
From the provided output, we have selected “a6c7bbd” and “9931568” SHA hashes for further use:
Step 3: List Commit Object
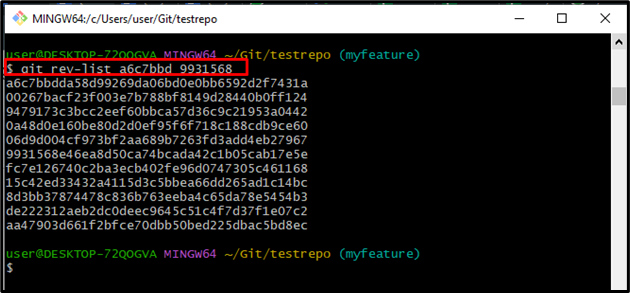
To list commit objects, execute the “git rev-list” command along with the selected hashes:
The resultant output shows that all the available commits between the mentioned commits have been listed successfully:
Example 2: List Particular Branch Commit Objects
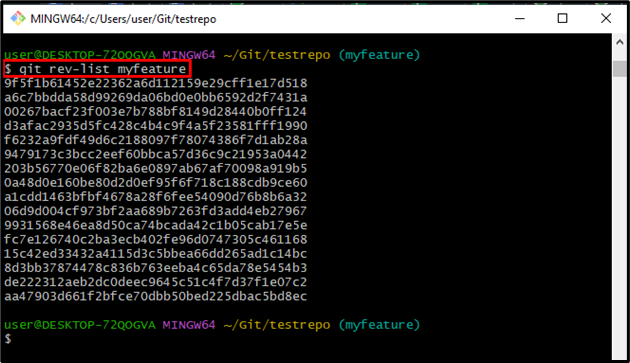
List all commit objects of a particular branch by executing the “git rev-list” along with the branch name:
It can be noticed that all the commit objects have been listed successfully:
Example 3: List Commits Before Desired Commit
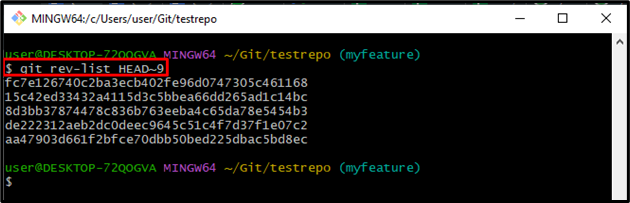
Users can also list the commit objects by providing the commit range. For instance, in the below command, we specified “HEAD~9” which will show all commit objects before the “9th” commit:
As you can see, all the commit objects before the provided HEAD pointer have been listed successfully:
That’s all about the “git rev-list” command in Git.
Conclusion
The “git rev-list” command lists and traverses the commit objects in a repository. To do so, go to the local Git directory and view its log history using the “git log –oneline” command. Then, execute the “git rev-list” command along with the options according to your preferences to list the commit objects. This tutorial explained the “git rev-list” command in Git.