Prerequisites
Before practicing the script shown in this tutorial, be sure to complete the following tasks.
- Install Django version 3+ on Ubuntu 20+ (preferably)
- Create a Django project
- Run the Django server to check whether the server is working properly
Set Up a Django App
Run the following command to create a Django app named socketapp:
Run the following command to install the channel:
Add the channels and app name to the INSTALLED_APP part of the settings.py file:
…..
'channels',
'socketapp'
]
Define the value of ASGI_APPLICATION in the settings.py file:
Create a folder named templates inside the socketapp folder and set the template’s location of the app in the TEMPLATES part of the settings.py file:
{
….
'DIRS': ['/home/fahmida/channel_pro/socketapp/templates'],
….
},
]
The following output will appear in the terminal after running the Django server. The output shows that ASGI/Channels version 3.0.3 is running.
Create a template file named index.html in the defined template location to display the data sent by the WebSocket. The socket object that is created using JavaScript will read the data using the JSON.parse() method, then pass the value into the content of the <h1> tag that contains the ID value, ‘msg.’
index.html
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Django Channel Tutorials</title>
<script>
socket = new WebSocket("ws://localhost:8000/msg/");
socket.onmessage = function(e) {
var data = JSON.parse(e.data);
document.querySelector('#msg').innerText = data.timeValue;
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<center>
<h1 style="color:blue" id ="msg">{{ text }}</h1>
</center>
</body>
</html>
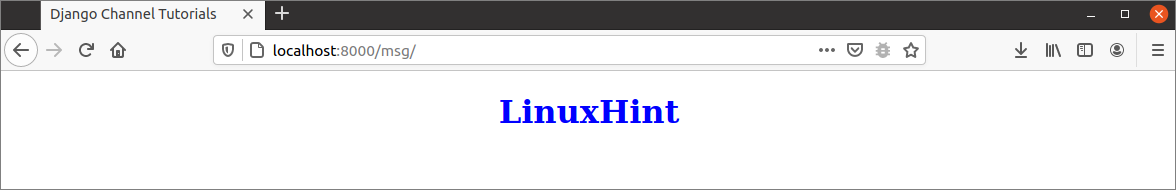
Modify the views.py file of the socketapp with the following content. The index.html template file will be displayed in the browser with the text variable when the index() method of this script is called from the urls.py file. If no message is transmitted from the socket, then the text ‘LinuxHint’ will be displayed in the browser.
views.py
from django.shortcuts import render
# Create index function to display the HTML file into the browser
def index(request):
return render(request, "index.html", context={'text': 'LinuxHint'})
Modify the urls.py file of the socketapp with the following content. Two paths are defined in the script: the ‘admin/’ path is used to open the Django Administration Dashboard, and the ‘msg/‘ path is used to read the WebSocket message.
urls.py
from django.urls import path
from socketapp import views
urlpatterns = [
path('admin/', admin.site.urls),
path('msg/', views.index)
]
When the following URL is executed without defining the consumer and routing files, the HTTP protocol will work and the following output will appear.
Now, create a consumers.py file inside the socketapp folder with the following script. The connect() method of ws_consumer will be used to accept the socket connection, read the current time value every second, and send the current time in JSON format via WebSocket when this method is called from the routing file.
consumers.py
import json
# Import WebsocketConsumer
from channels.generic.websocket import WebsocketConsumer
# Import datetime module
from datetime import datetime
# Import sleep module
from time import sleep
# Define the consumer class to send the data through WebsocketConsumer
class ws_consumer(WebsocketConsumer):
def connect(self):
self.accept()
while(True):
now = datetime.now()
self.send(json.dumps({'timeValue': now.strftime("%H:%M:%S")}))
sleep(1)
Create the routing.py inside the socketapp folder with the following script. The ‘msg/’ path is defined in the script to call the consumer for sending the data to the socket.
routing.py
from .consumers import ws_consumer
# Set the path to call the consumer
ws_urlpatterns = [
path('msg/', ws_consumer.as_asgi())
]
Modify the asgi.py file with the following script. The modules that are required to handle HTTP and WebSocket requests are imported in the script.
asgi.py
import os
# Import get_asgi_application to handle http protocol
from django.core.asgi import get_asgi_application
# Import ProtocolTypeRouter and URLRouter to set the websocket routing
from channels.routing import ProtocolTypeRouter, URLRouter
# Import AuthMiddlewareStack to handle websocket
from channels.auth import AuthMiddlewareStack
# Import websocket routing
from socketapp.routing import ws_urlpatterns
# Assign value for DJANGO_SETTINGS_MODULE
os.environ.setdefault('DJANGO_SETTINGS_MODULE', 'channel_pro.settings')
# Define application variable to handle http and websocket
application = ProtocolTypeRouter({
'http': get_asgi_application(),
'websocket': AuthMiddlewareStack(URLRouter(ws_urlpatterns))
})
Now, run the following URL from the browser again to read the data from the WebSocket.
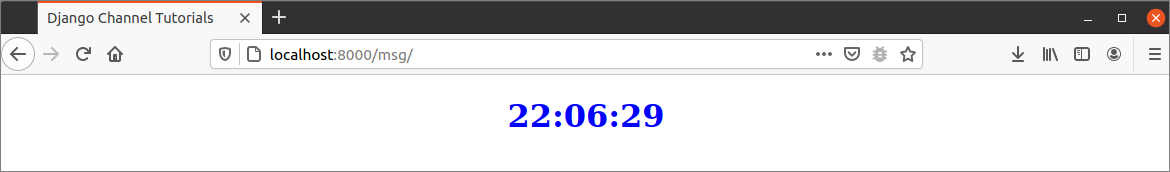
If the consumer and router are working properly, then the following digital clock will be displayed in the browser. Here, the router has sent the WebSocket request using the ‘msg/‘ path to the consumer that has accepted the request and sent the data to the template to show the digital clock in the browser where the second value of the current time is updating every second.
Conclusion
This tutorial showed you how to implement a real-time application using the Django framework and channels by creating a simple digital clock. Other types of real-time applications can also be implemented using Django and channels, such as online chatting systems. The scripts used in this tutorial work for Django versions 3+ and Channel versions 3+ only. So, if you are using an earlier Django or Channel version, then you will need to upgrade the version before testing the script provided in this tutorial.