The boolean value can contain two types of data. These are True or 1 and False or 0. Bash does not support Boolean values, but any bash variable can contain 0 or “true” and 1 or “false“. The logical boolean operators are supported by bash. The boolean value is required to use when the script needs to generate the output based on the True or False value of a variable. The way to declare and use boolean values in the bash script has shown in this tutorial.
Example-1: Declare Boolean variable using 0 or 1
The way to use boolean values 0 and 1 in the bash variable has shown in this example. Create a bash file with the following script that will print a message based on the value of a variable that will contain 0 or 1. Two numeric values will be taken as the MCQ and descriptive marks. If the value of the mcq variable is more than and equal to 60 and the value of the des variable is more than and equal to 50, then the value of the passed variable will be set to 1; otherwise, 0 will be set into this variable. Next, the passed variable will be checked to print the success message or the failure message.
# Using 0 or 1 for declaring boolean values
#Take an integer value for MCQ marks
echo "Enter MCQ marks:"
read mcq
#Take an integer value for descriptive marks
echo "Enter Descriptive marks:"
read des
#Check the passing marks
if [[ $mcq>=60 && $des>=50 ]]; then
#Set 1 for true
passed=1
else
#Set 0 for false
passed=0
fi
#Print message based on the value of $passed
if [ $passed -eq 1 ]; then
echo "You have passed the exam."
else
echo "You have failed the exam."
fi
Output:
According to the output, the above script has been executed two times. 70 has been given as MCQ marks, and 65 has been given as descriptive marks in the first execution. Both values return true for the conditional expression, and 1 has set to the passed variable. 40 has been given as MCQ marks, and 80 has been given as descriptive marks in the second execution. False has returned from the conditional expression for the 40, and 0 has been set to the passed variable. “You have passed the exam” has printed when the value of the passed variable is 1, and “You have failed the exam” has printed when the value of the passed variable is 0.
Example-2: Declare Boolean variable using “true” or “false”
The way to use the boolean value as a string in the bash script has shown in this example. Create a bash file with the following script to authenticate a user and identify the type of the user by using “true” and “false” values. Username and password will be taken from the user after executing the script. The value of the administrator variable has initialized to “false” and it will be set to “true” when the valid username and password will be provided, and the username is “admin”. Next, the values of the valid variable and the administrator variable will be checked to print the welcome message or error message.
# Using “true” or “false” for declaring boolean values
#Take the username
echo "Enter username:"
read username
#Take the password
echo "Enter password:"
read password
administrator="false"
#Check username and password
if [[ $username == "admin" && $password == "secret" ]]; then
#Set "true" for valid user
valid="true"
#Set "true" for administrator
administrator="true"
elif [[ $username == "fahmida" && $password == "67890" ]]; then
#Set "true" for valid user
valid="true"
else
#Set "false" for invalid user
valid="false"
fi
#Print message based on the values of $valid and $administrator variables
if [[ $valid == "true" && $administrator == "true" ]]; then
echo "Welcome Administrator."
elif [[ $valid == "true" && $administrator == "false" ]]; then
echo "Welcome $username."
else
echo "Username or Password is invalid."
fi
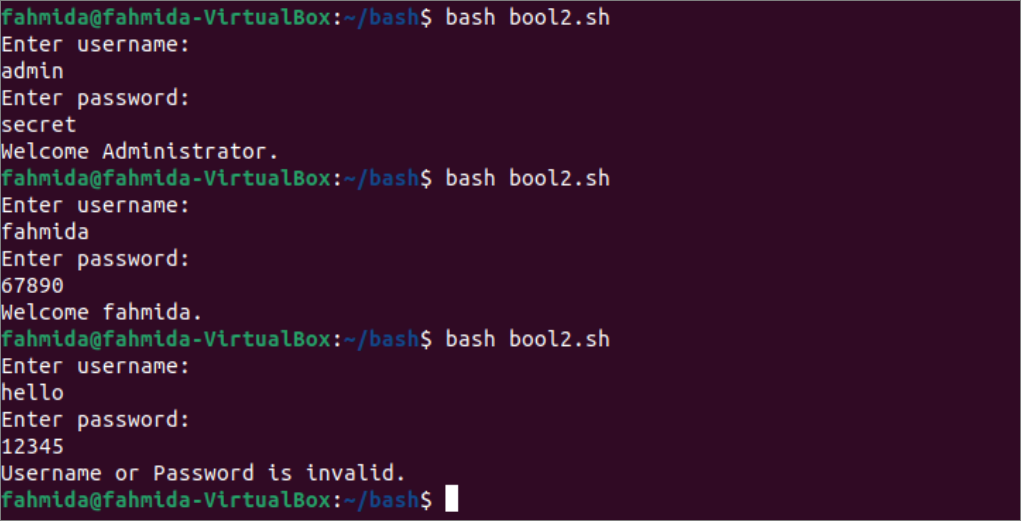
Output:
According to the output, the above script has been executed three times. In the first execution, the valid username and password of the administrator have been given, and the “Welcome Administrator” message has been printed. In the second execution, the valid username and password have been given for the username, fahmida, and the “Welcome fahmida” message has been printed. In the third execution, an invalid username and password were given, and the error message, “Username or password is invalid,” was printed.
Example-3: Declare Boolean variable using True or False
The way to use the boolean value as a string in the bash script has shown in this example. Create a bash file with the following script that will print a message based on the value of a variable that will contain the value, True or False. The value of the like variable will be set based on the user’s input after executing the script. A message will be printed based on the like variable.
# Using True or False for declaring boolean values
echo "Do you like programming?(Y/N)"
# Take input from the user
read answer
# Check the input values
if [[ $answer == 'Y' || $answer == 'y' ]]; then
#Set True for true value
like=True
elif [[ $answer == 'N' || $answer == 'n' ]]; then
#Set False for false value
like=False
else
echo "Invalid answer."
exit 1
fi
#Check the valie of $like variable
if [ $like = True ] ; then
echo 'Glad to know that you like programming.'
else
echo 'You can learn programming.'
fi
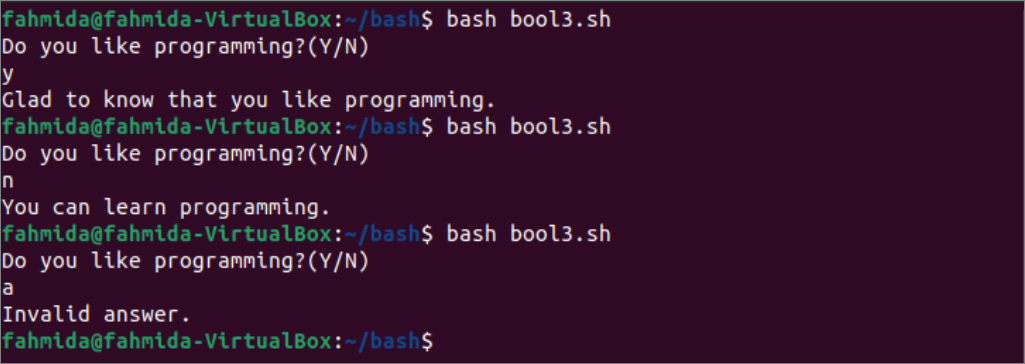
Output:
According to the output, the above script has been executed three times. In the first execution, ‘y’ has given as input value that set True value into like variable and the message, “Glad to know that you like programming.” has printed. In the second execution, ‘n’ has given as input value that set False value into like variable and the message, “You can learn programming.” has printed.
Conclusion:
The way to implement the feature of boolean variable in bash script has been explained in this tutorial by using multiple examples for helping the readers to use boolean values in their bash script.