If you have installed Debian 12 or other version of Debian system, you can read this guide to learn:
- How to Update Debian
- How to Update Debian from a Single Command
- How to Update a Single Package in Debian
- How to Update Debian Using apt-get Command
- How to Automate the Process to Update Debian
- How to Update Debian to Debian 12
- Conclusion
How to Update Debian
On Linux systems including Debian 12 as well, the packages are mostly installed through the apt package repository. This repository is an official source for Linux systems as it installs the packages that are compatible with your system. These packages include applications, security patches, fixes and other related software.
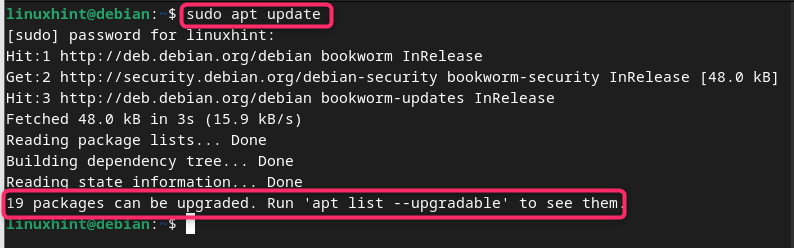
To update these packages and Debian repository, you first need to check for the packages so that you will be informed whether there is any package update available. This can be done by running the following update command:
If there is any update available, you will see the information that the packages need to be upgraded:
You can see the list of packages that are ready to be updated on Debian by running the following command:
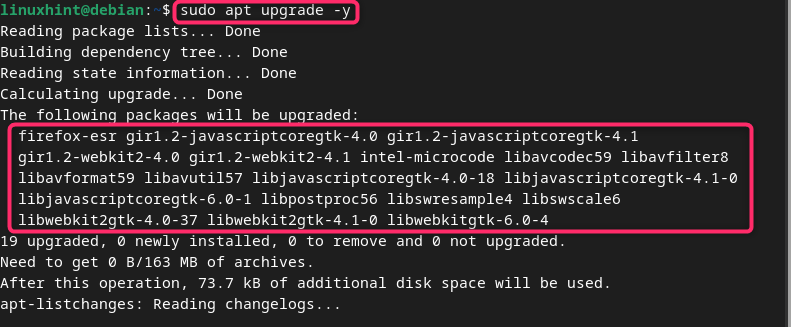
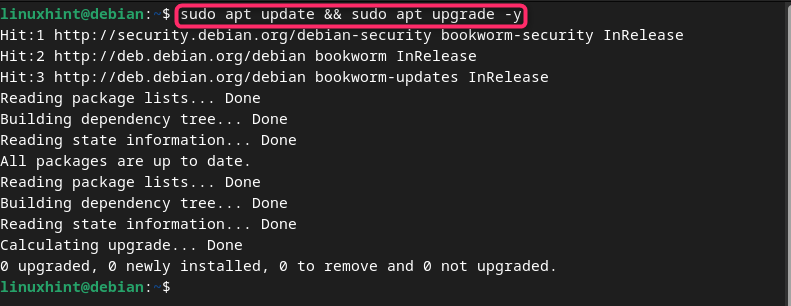
After ensuring packages are ready to be updated on Debian, you can simply run the upgrade command with -y flag to allow the system to upgrade the packages without an approval:
After the execution of the above command, all the packages are upgraded on your Debian system.
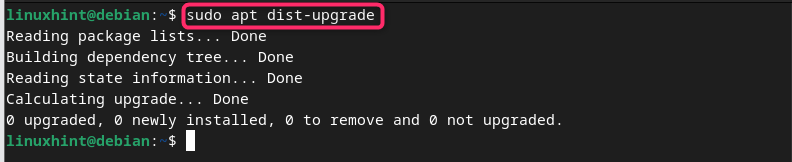
Besides using the upgrade command, you can also use the dist-upgrade command to upgrade the packages on Debian:
The dist-upgrade command is a more aggressive command compared to the upgrade command since it handles the dependencies on your system more efficiently. The dist-upgrade command not only updates the installed packages but it also removes or installs new packages that are needed to resolve dependency conflicts.
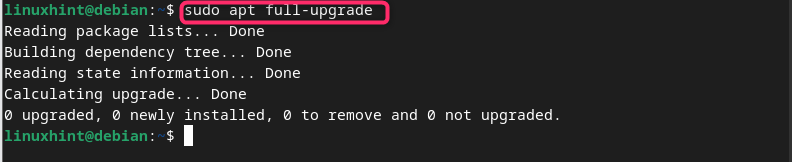
Further, you can also use the full-upgrade command given below to update Debian:
Note: The full-upgrade command will work similar to the dist-upgrade command so they can be interchanged.
How to Update Debian from a Single Command
Besides running each command separately, you can also update Debian from a single command. This can be possible if you add & between the two independent update commands, as given below:
How to Update a Single Package in Debian
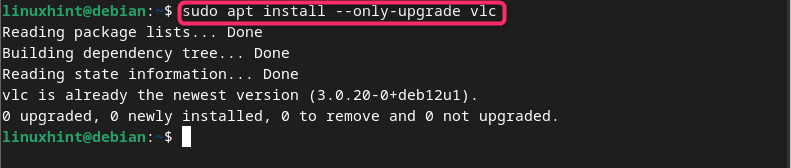
If you want to install a single package in Debian besides updating all packages, you can simply run the following command with the package name:
Here, you should name the package in place of package_name to install the package update on Debian:
In the below-given screenshot, I am updating VLC media player on Debian:
How to Update Debian Using apt-get Command
Besides using the apt command, you can also use the apt-get command to update Debian. The apt-get command works similar to apt update command as you only have to replace apt with apt-get to update Debian. However, using apt command to update Debian is better because the command not only updates packages but it also updates the dependencies that are installed with those packages. On the other hand, the apt-get command will only update packages that exist in the system. For a complete guide about what is the difference between apt and apt-get commands, read here.
How to Automate the Process to Update Debian
If you want to avoid the headache of updating Debian again and again, you can enable the unattended-upgrades on Debian. The unattended-upgrades allows you to automatically update the system once there is any update available. Thus, save your time executing the update commands again and again on the system. To learn how to configure unattended-upgrades on Debian, you can read here.
How to Update Debian to Debian 12
Besides updating the packages on Debian, you can upgrade your system to the latest version. At the time of writing this article, the latest version of Debian is Debian 12, which can easily be upgraded from the terminal. A complete step-by-step tutorial to upgrade Debian 11 to the latest Debian 12 Bookworm is provided here.
Note: For upgrading the system to Debian 12, you must ensure you are using Debian operating system except Debian 12.
Conclusion
Debian 12 is the latest version of Debian based systems that includes an updated Kernel version and advanced security updates. To protect the security of the Debian system, you must ensure updating the packages on the system. These packages are installed from the official Raspberry repository, thus using the apt update and upgrade command will quickly update these packages on the system. Besides that, you can also automate the process of updating the Debian system by enabling the unattended-upgrades option. You can also perform a complete system upgrade from the older Debian version to the latest Debian 12 system using the guidelines provided in the above section of this guide.