Their flexible nature, as well as out of the box performance, has led to their increasing popularity. Since they are considered the backbone of a developer, it is thus imperative to choose the one which offers the best features while allowing work to be done efficiently.
Emacs is one such text editor that offers some of the best features to its users. It is an open-source, cross-platform editor that is highly customizable and provides a user-friendly interface to its users. Providing features like multiple editing modes, full Unicode support for scripts, text manipulation tools, and integration with numerous external tools like the shell and git clearly gives an indication of how powerful it is.
In addition to this, it not only acts as a text editor but can also be set up to provide other functionalities such as project planner, debugger, email client, etc. Hence, in this article, we will be looking at how you can download and install Emacs on your Ubuntu system.
Installing Emacs in Ubuntu
Ubuntu offers multiple ways for users to install Emacs on their computers. Let us look at some of them:
Installing Emacs using Snap
Snaps are Canonical developed applications that can be installed on almost all Linux distributions. A considerable advantage of using Snaps over using Ubuntu repositories is that it provides users with the most up-to-date software without sacrificing the reliability of your working environment. Installing applications through Snap is extremely easy. Users can install Emacs by running the following command in the command line:
Once this is done, you can find Emacs in your list of installed applications.
Installing Emacs using the PPA Repository
Some users, however, have found the snap versions of Emacs to be less stable and buggier. Thus, a better alternative for installing Emacs is by using the PPA repository.
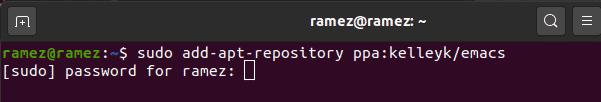
To do this, open the terminal via Ctrl+Alt+T or by searching terminal in the Ubuntu Dash. Once the Terminal is opened, enter the following command:
It is a stable PPA repository maintained by Kevin Kelley that contains the support for the latest Emacs packages. It also has support for the packages: mailutils, systemd, and xwidgets, which are dependencies required by Emacs.
After entering the command, you will be asked to enter your password (as shown in the image below). Do so, and it will then add the PPA repository to your system.
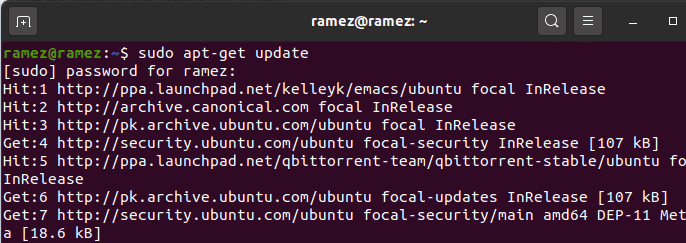
Next, we want to update our system’s apt-cache and packages to the latest versions so that no issues arise during installation. This can be done by running the following command into the terminal:
Finally, Emacs can be installed by running the following command:
Over here, the Version refers to the version number of Emacs that you want to install. In my case, it would be 26.
Users can also check the version of their installed Emacs by entering the following command into the terminal:
Build and Compiling Emacs
Another painless way of installing Emacs is by building and compiling ourselves. To do this, we need to install some dependencies first. For installing the build dependency, enter the following command into the terminal:
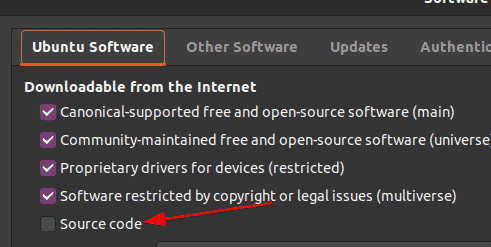
Next, for downloading the Emacs dependencies, we first have to enable the Source Code download option. To do this, go to Software & Updates and activate Source Code found under the Ubuntu Software heading.
Now enter the following command to download the Emacs dependencies:
After installing the dependencies, we now have to download the source distribution of Emacs. To do this, go to the website of Emacs and click on GNU/Linux.
Now click on the hyperlink with the name nearby GNU mirror provided under the GNU/Linux heading.
You will then be directed to a website where all the releases of Emacs will be present. Choose and download the one which you want to install in your system. In my case, I will be downloading the emacs-26.3 tar.gz file.
When the tar file has been downloaded, go to the folder where it was downloaded and extract it using the command:
Over here, the Version refers to the version number of Emacs that you downloaded. In my case, it would be 26.3 (See the image below for better understanding)
If you’re not interested in seeing the files being extracted, you can instead enter the command:
Now enter the directory of your installed Emacs (emacs-VERSION would be the directory name) and compile Emacs by running the following commands into the terminal:
$ ./configure
$ make
In my case, this would be:
$ ./configure
$ make
Finally, Emacs can be installed by running the command:
Why use Emacs?
Emacs is one of the most powerful text editors out there, known for its dynamicity and customizable nature. It is highly flexible and extensible, as users can easily customize and set it up according to their preferences. In addition to this, it offers some extremely useful editing tools that make the work of developers much easier and faster. Emacs is undoubtedly a must editor to have.