This article will exemplify the method to find/compute the transpose of various tensors in PyTorch.
How to Transpose a Tensor in PyTorch?
To transpose a particular tensor in PyTorch, first, import the PyTorch library. Then, create a desired 2D or 3D tensor. After that, find/compute the transpose of the tensor using the “transpose()” method. Lastly, display transposed tensor.
The basic syntax of “transpose()” method is:
Here, “0” is the first dimension, and “1” is the second dimension to be transposed.
Go through the next provided examples for a better understanding.
Example 1: Find Transpose of 2D Tensor
In the first example, we will create a 2D tensor and find its transpose. Let’s follow the below step-by-step procedure:
Step 1: Import PyTorch Library
First, import the “torch” library to compute the transpose of the tensor:
Step 2: Create 2D Tensor
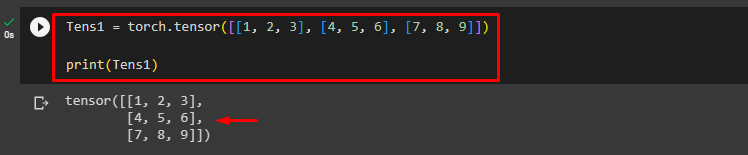
Then, create a 2D tensor using the “torch.tensor()” function and print its elements. Here, we are creating the following “Tens1” 2D tensor:
print(Tens1)
The tensor has been created successfully:
Step 3: Find Transpose of Tensor
Now, use the “transpose()” method to find the transpose of the above-created tensor:
Step 4: Display Transposed Tensor
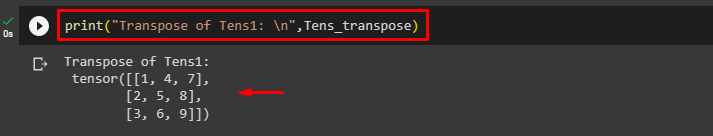
Finally, print the transposed tensor and view its elements:
The below output shows the transpose of the “Tens1” tensor:
Example 2: Find Transpose of 3D Tensor
In the second example, we will create a 3D tensor and find out its transpose. Let’s follow the provided steps:
Step 1: Define 3D Tensor
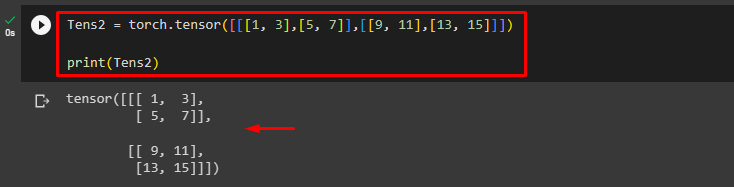
First, utilize the “torch.tensor()” function to create a 3D tensor and print its elements. Here, we are creating the following “Tens2” 3D tensor:
print(Tens2)
This has created a 3D tensor as seen below:
Step 2: Find Transpose of Tensor
Then, find the transpose of the above-created 3D tensor using the “transpose()” method:
Step 3: Display Transposed Tensor
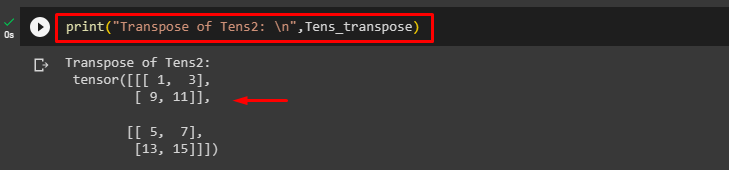
Lastly, print the transposed tensor and view its elements:
According to the below output, the transpose of the “Tens2” tensor has been computed:
We have efficiently explained the method to compute a transpose of 2D or 3D tensors in PyTorch.
Note: You can access our Google Colab Notebook at this link.
Conclusion
To transpose a tensor in PyTorch, first, import the “torch” library. Then, create the desired 2D or 3D tensor and view its elements. Next, use the “transpose()” method to find/compute the transpose of the input tensor. Lastly, print the transposed tensor and view its elements. This blog has exemplified the method to find/compute the transpose of different tensors in PyTorch.