It is pretty simple and straightforward if you know exactly how to do it. Are you a beginner and worried? No need! Just follow the article and find out the way. This guide will find how to enable WSL on Windows and transfer files from WSL to Windows.
The Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL) is an environment with compatible features that allows the user to execute Linux commands natively on Windows.
You can execute command-line tools or utilities such as grep or ELEF-64 binaries and many others. Moreover, you can install additional packages, including languages and services, and run bash script commands using WSL.
It was first released in 2016 that provides a Linux Kernel interface for ease of the user. But at that time, developers didn’t use Linux Kernel code in the development of WSL. Later on, the latest version has introduced, “WSL 2,” in May 2019, with the advanced and robust features of creating a connection between Windows 10 and the Linux system.
The architecture of WSL 2 has made with a Linux kernel to accomplish the primary goals like increase the performance of the file system.
After introducing the WSL, it seems easy to share data and files with Windows.
How to enable WSL on Windows
(I am working on Windows 10)
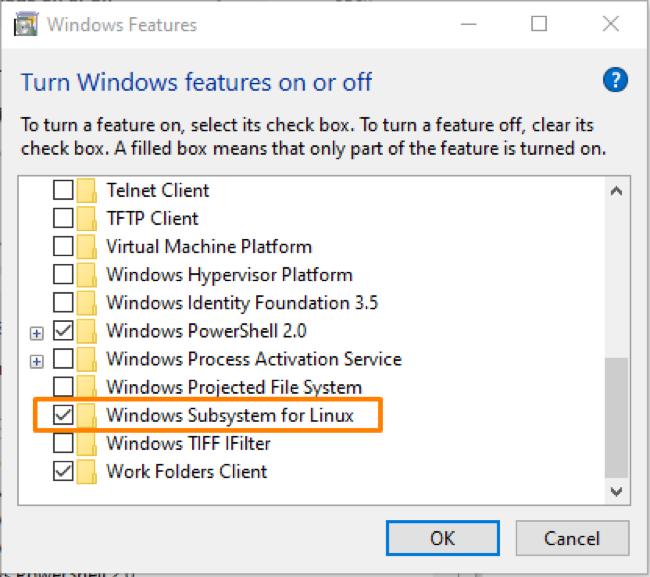
Open up the application manager and search for the “Turn Windows Features on or off.”
When you get it, hit “Enter”:
In the “Turn Windows Features on or off” window, scroll down until you get “Windows Subsystem for Linux” features. Check it and navigate to the “Ok” button to save changes.
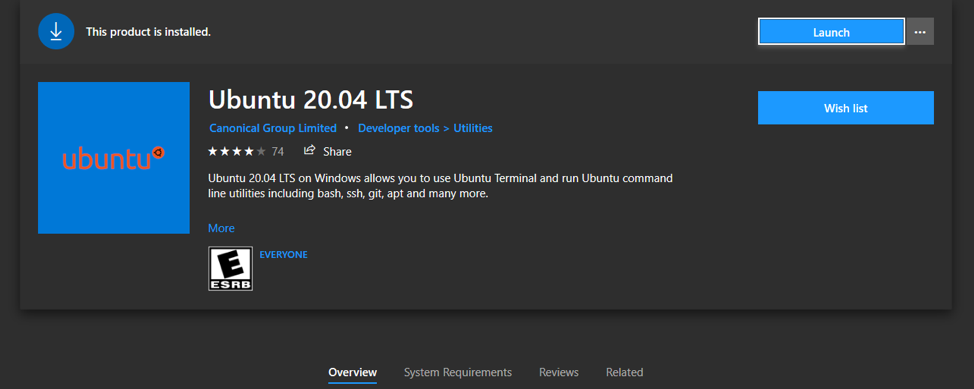
Now, restart the system and after getting back the Desktop, open the “Microsoft Store” from the application manager.
Search here Ubuntu and select “Ubuntu 20.04 LTS” from the multiple displayed options:
You will get an “Install” button, select it to begin installation and once it is done, click on the “Launch” button to open it.
Set the username and password for the command-line prompt and run the Linux commands here.
How Do I Transfer Files from WSL to Windows
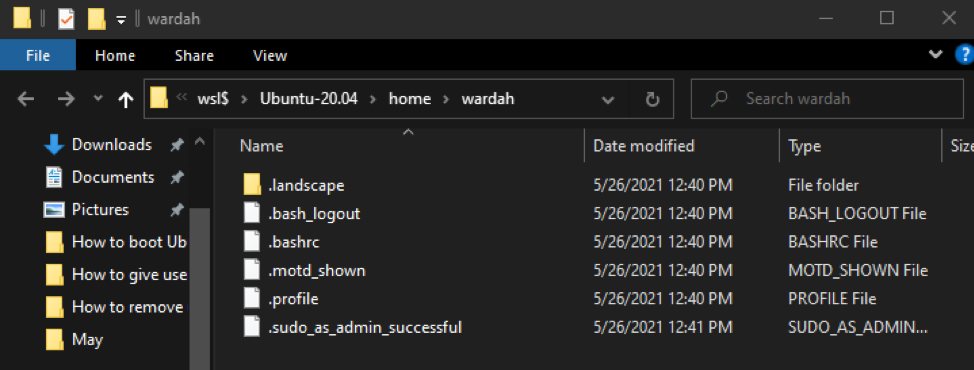
To launch the Linux directory in WSL File Explorer, execute the command in the WSL terminal:
It will open the current Linux directory file from where you can browse anything.
You can also transfer the files from WSL to Windows by copying them.
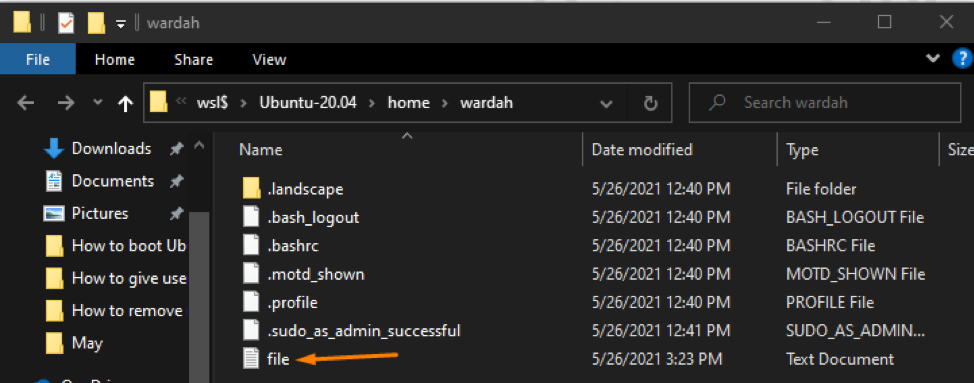
Suppose, create a text file using the “touch” command:
Open the File Explorer again to check if the file is created:
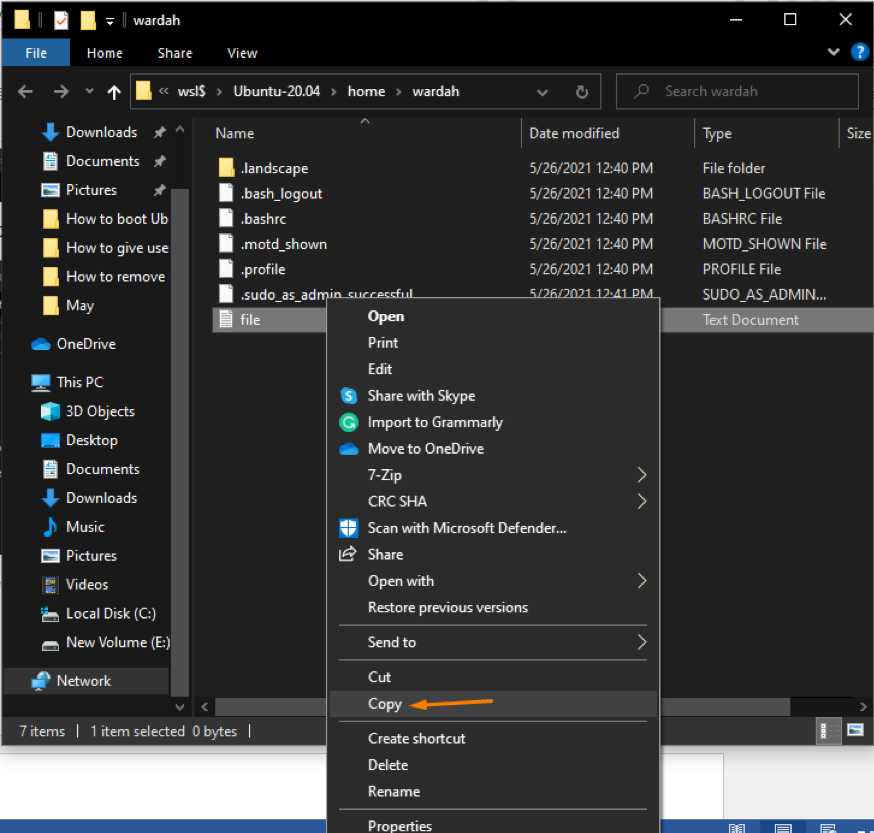
To copy the file in Windows, right-click on it and select copy:
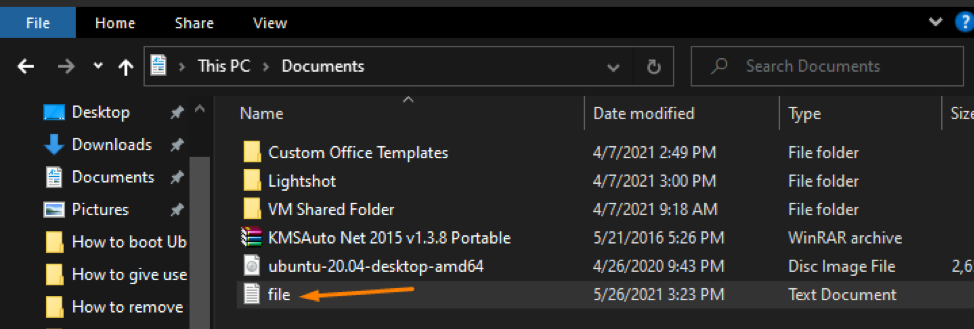
Paste it in the Windows directory where you want to transfer the file.
(I have pasted it into the “Documents” directory of Windows.
Conclusion
The Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL) is an environment with compatible features that allows the user to execute Linux commands natively on Windows. In addition, the WSL 2 comes up with advanced and compatible features to create a connection between Windows and Linux systems.
To Enable WSL on Windows, open the application manager and mark check on the “Windows Subsystem for Linux” option. Then, install the Ubuntu 20.04 system on WSL and run the command mentioned above to work on it.