In this tutorial, we will show you the use of Tar CVF and Tar XVF in Linux with examples
Use Tar CVF and Tar XVF in Linux Explained with Example Commands
The Tar CVF is used to create archive files in Linux. If you use only the tar command, the files are not archived, they are only compressed into a single file. The Tar CVF in the command has three arguments:
- C is used to create archive files
- V provides the progress output
- F points to the filename
Let’s look at the general syntax for using the tar cvf command:
Note: You can use the * to add all the files of the current directory to the archive file.
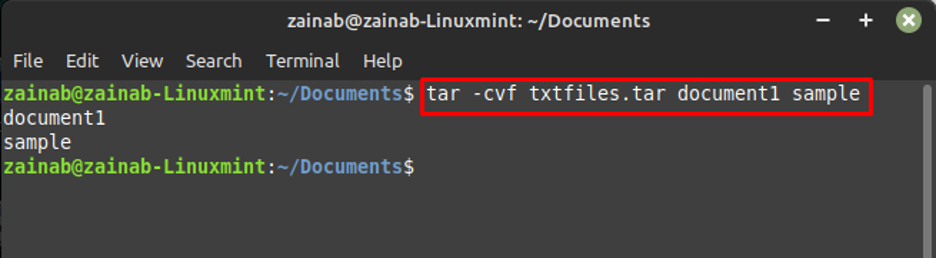
In the example written below, we are creating an archive file with the name txtfiles.tar and adding two files in it including document1 and sample.
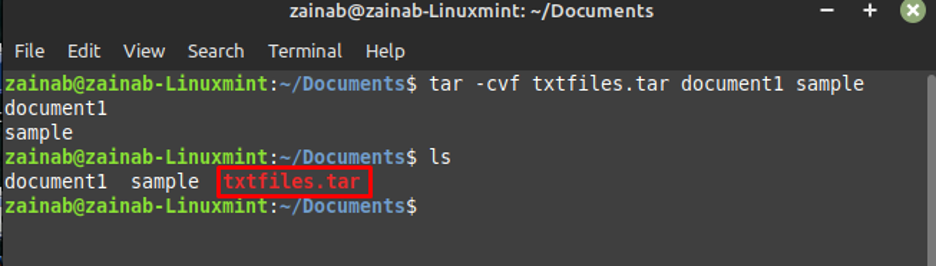
Use the ls command to check the created archive file:
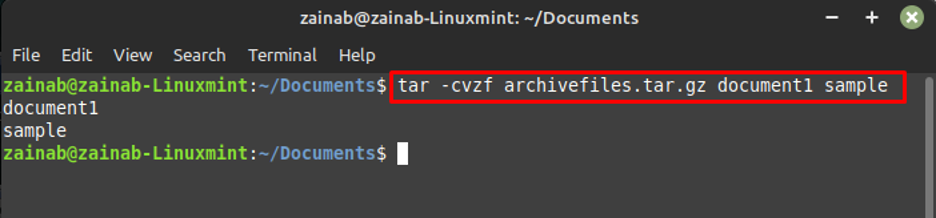
To create a gzipped archive file, use the -z option with the CVF, the file will be created in the current directory with tar.gz extension:
The gzipped is the archive file of the text files, here we are creating the archive file of document1 and sample:
Verify the formation of the file with the ls command:
Linux Tar XVF With Example Commands
The Tar XVF is used to extract files from the existing archive files. In the command, the XVF has three arguments, so what do they mean? The X is used to extract the files, V is used to display the progress and F refers to the files.
The syntax of the Tar XVF command is:
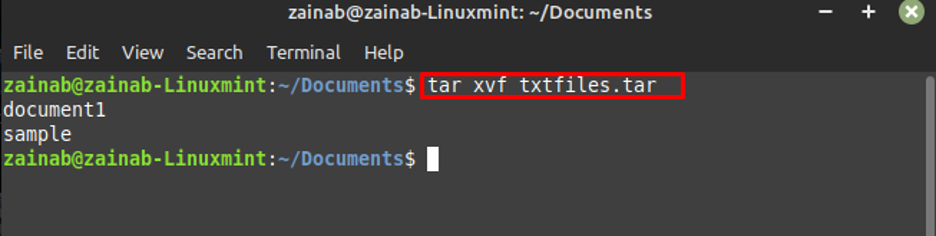
In our case, we are extracting the txtfiles.tar in the documents. When you execute the command, it will display the names of the files present in the archive file.
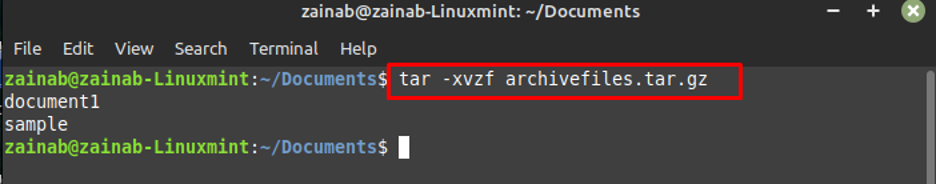
To un-compress the gzipped file, use the xvzf with the file name:
Bottom Line
The tar command is used to create an archive file in Linux that can be moved and shared with other users. This utility has many helpful functionalities including managing backups, extracting installation files, and compressing files that can be extracted using the different options. The cvf is used to create an archive file and when the file is created, xvf is used to extract the archive files.