Though storing the data on the RAM improves the speed of the system, in case of a sudden crash of the system there is a risk of losing the important data stored in the form of cache. It is better to synchronize the data on the permanent memory so, in case of any crash, there is no loss of data.
In this write-up, we will discuss the sync command used in Linux to synchronize the data of the RAM in the permanent storage.
How to use the sync command in Linux
The sync command is used for synchronizing the cache data to the hard disk, the general syntax of using the sync command:
The sync command is used with options and then the file name of which the data has to be stored, the options used with the sync command are:
| Options | Explanation |
| -d, –data | It is used to synchronize the file data of the file |
| -f, –file-system | It is used to synchronize all the files which are linked to a given file |
| –help | It displays the help options |
| –version | It displays the version details of the command |
To understand the usage of the sync command, we will perform some practical examples. First, we will sync all the data of the current user using the command:
It has synced all the cached files to the permanent memory which belongs to the current user, likewise, we have a text file in /home/hammad/mytestfile1.txt, we can sync its cache data using the command:
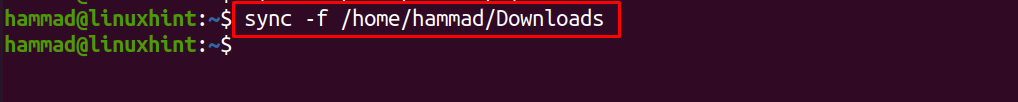
To sync the files systems, we use the “-f” option in the command:
In the above command, we have synced all the files related to the /home/hammad/Downloads, we can also sync the cache data of the mounted partition (in our case it is sda1) using the command:
The data of the mounted partition has been synced, likewise, we can also sync the log data of the /var/log/syslog using the command:
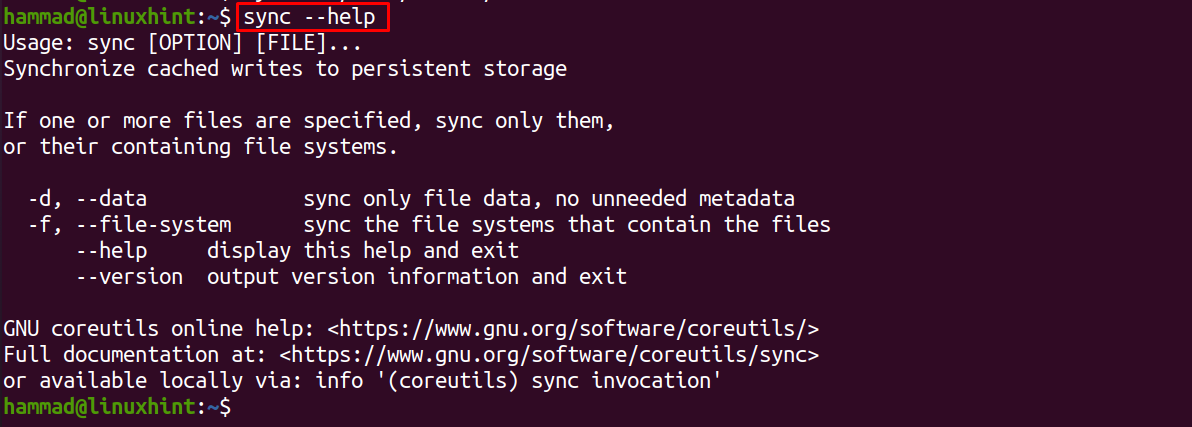
To check more details of the sync command we can use the “–help” option:
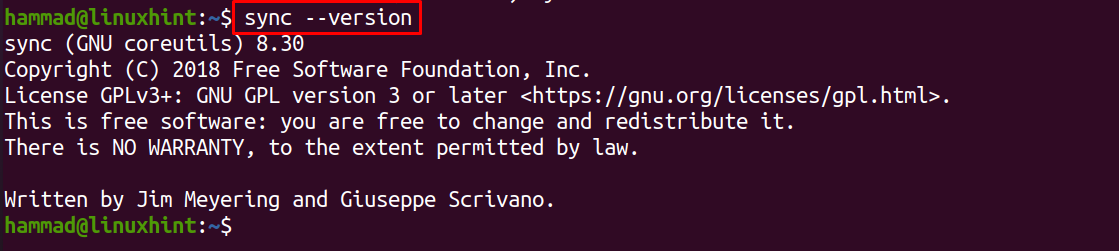
Similarly, the “version” option is used to check the version of the sync command:
Conclusion
The sync command is used in Linux to copy the data from the volatile memory which is in the form of cache to the permanent storage memory. The system saves all the data on the temporary memory because of its better speed as compared to the permanent storage devices, it is helpful but sometimes in case of unexpected shutdown of the system, a great risk is present of losing the data. To avoid this risk, it is recommended to sync the useful data from the temporary memory to the permanent memory. In this write-up, we have discussed the usage of the sync command in Linux with the help of examples for better understanding.