The string is among the most utilized data types in the C++ programming language. It is a variable that is used to hold a collection of elements or letters. To construct a string, we would first define it, then save data in it, like most of the other datasets. Let’s discuss how to transform a string into a binary representation in C++ using several techniques.
Use the bitset<N> class to transform the string to a binary format:
We would transform every character in an arbitrary string series to its appropriate binary form. We’ll utilize the bitset<N> class to construct a predefined binary code for every character because ASCII codes are correlated with integral values and the character values could be considered an integer.
Although a few of the constructors of the bitset<N> give a possibility to build the binary code using character values, the character will be converted to the integral number regardless. Even though the integer is required. This strategy involves traversing the entire string. The ‘if’ statement can be applied within the for loop to specify the formatting of the displayed data.
At the start of the program, we have to include three header files. <iostream> for input and output functionalities. <Vector> contains elements of a specific format in a linear order and provides efficient retrieval to any member. <Bitset> is a definite N-bit series that holds only 0 or 1 as outputs.
Now, we have been using some standard functions. ‘std::cout’ is called for getting the output. ‘std::endl’ is used to shift the cursor to the next line of the code. ‘std::string’ function is used to handle different strings. The elements having the two alternative values 1 and 0 are stored by using the ‘std::bitset’. We have called the main() function.
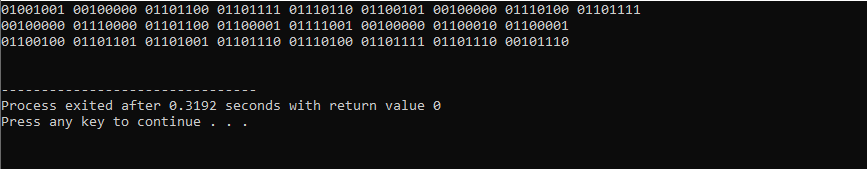
Here, we declare the string of our own choice. The entered string is “I love to play badminton”. ‘For’ loop is applied to iterate on the strings. Within the ‘for’ loop we have used the length() function to acquire the length of the defined string. In the ‘for’ loop, we just initialize the loop variable ‘j’. The next part shows the condition that the value of the variable must be less than the length of the string. We employ the ‘bitset’ function. The ‘cout’ command is used to show the outcome.
Within the ‘if’ statement, we define the condition that the variable ‘j’ will be divided by 8 and ‘j’ would not be equal to 0. We have utilized the ‘modulus’ operator (%) which shows the remainder must be 0 after dividing the variable ‘j’ by 8. In the end, we have entered ‘EXIT_SUCCESS’ to terminate the program.
Use a custom function to transform a string into a binary code:
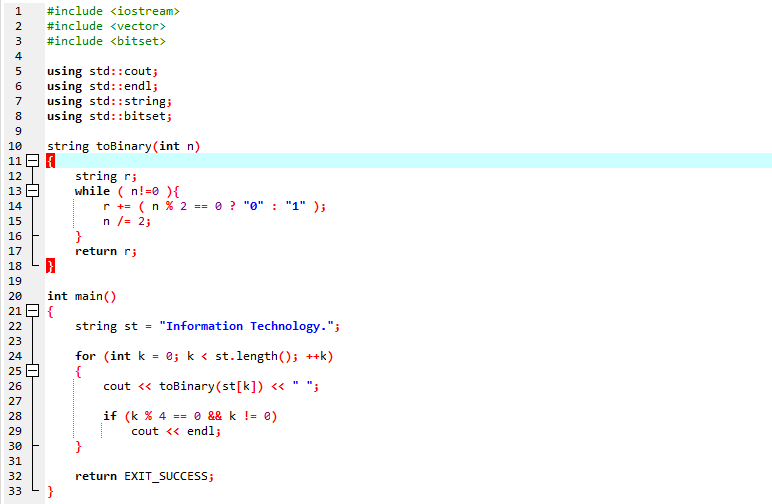
We can define a method that gets an integer value and returns the binary code of the string. This variant usually involves iteration until the specified character value is divided by 2 and truncated to 0. The previous methodology creates the particularly large representation, and that’s what we mostly use in printed numbers. The following template provides the little-endian expressions, and that’s how the core machine keeps them.
First, we introduce three libraries. <iostream>, <vector> and <bitset> along with different standard functions. We used the string toBinary() function to convert the string into its binary style. We declare the string variable ‘r’. Here we employ the ‘while’ loop. While loops continue to execute the same piece of code over and over. It has only one control condition that runs as much as it becomes true.
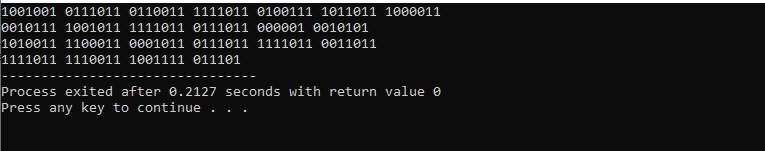
The main() function has been invoked. We specify the string of our preference here. The entered string is retained in the ‘st’ variable. “Information Technology” is the provided string in this program. To traverse over the strings, a ‘for’ loop is being used.’ We included the length() method within the ‘for’ loop to get the length of the provided string. We just initialize the loop variable ‘k’.
Then, we define the condition that demonstrates that the variable’s value is below the length of the string. The value of variable ‘k’ continues to increase. The ‘toBinary()’ method will be used. The ‘if’ statement can be used to specify that the result will be 0 after dividing the variable ‘k’ by 4 with the help of the modulus operator and that the value of ‘k’ is other than 0. The output is displayed using the ‘cout’ command. Lastly, we have been using the command ‘EXIT SUCCESS’ to exit the program.
Use the utility method to convert a string into a binary format:
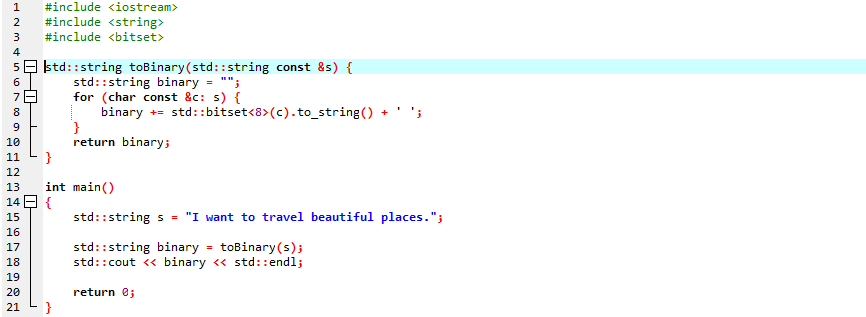
There are various utility methods used for different conversions in the standard function. To generate a particular string, we would implement a utility method. The essence will be to iterate through the entire string and create a bitset object to every character’s bit value. To convert a string to binary by using the utility method, we have been using the following example:
Here, we are going to integrate three required header files. We define the standard toBinary() method. This function holds another function ‘string const’ as an argument. We will apply the utility method to make a new string. ‘For’ loop is applied here. We define a character string here.
We have utilized the to_string() function along with the ‘std::bitset’ method and provided the specified string. This ‘for’ loop has returned the string in a binary form. Within the body of the main() function, we have declared a string. The function toBinary() is included to convert the string to binary form. We will provide the defined string as a parameter to this function. Before entering the command ‘return 0’ the ‘cout’ statement is utilized to print the output.
Conclusion:
We have talked about three methodologies used to convert the strings to binary format in this article. The aim is to determine the string’s length and then we execute a loop until the condition is fulfilled. Every cycle saves the ASCII code of the character in the string, transforms it to a binary representation, and returns the data in an array, before presenting the string in the opposite order.