Pre-requisites
Install GitHub Desktop
GitHub Desktop helps the git user to perform the git-related tasks graphically. You can easily download the installer of the latest version of this application for Ubuntu from github.com. You have to install and configure this application after download to use it. You can also check the tutorial for installing GitHub Desktop on Ubuntu to know the installation process properly.
Create a GitHub account
You will require to create a GitHub account to publish any local repository.
Create a Local Repository
You have to create a local repository with one or more files and folders to check the commands used in this tutorial to stash the untracked files.
Initialize the git Repository
Go to the local repository folder from the terminal and run the following command to initialize the local repository.
Add a File in the Repository
Run the following command to add the basic.py in the repository.
Check the Tracked and Untracked File
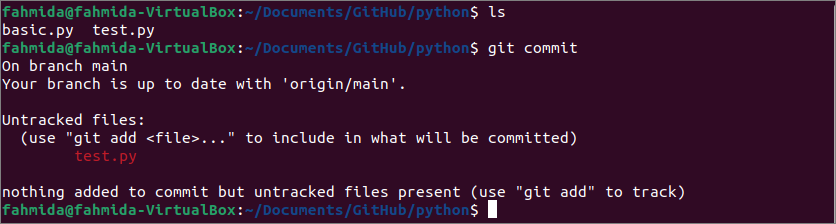
Run the “ls” command to check the list of all files and folders of the local repository folder.
Run the “git commit” command to check the tracked and untracked files:
The following output shows that the repository folder contains two files. These are basic.py and test.py. The basic.py is added to the repository before. So, basic.py is a tracked file and test.py is an untracked file, respectively.
Stash Untracked Files Using “git stash”
The modified untracked files can be saved using the “git stash” command in two different ways. One way is to use the –include-untracked option with the “git stash” command. Another way is to use the -u option with the “git stash” command. The use of these options has been shown below.
A) Using –include-untracked Option
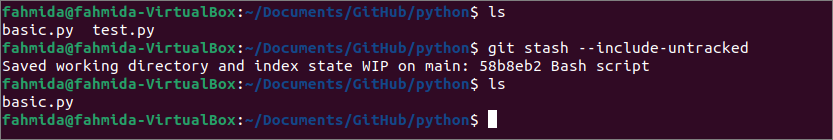
Run the following commands to check the file and folder list of the repository folder. Save the untracked files and check the file and folder list of the repository folder again. Here, the “ls” command is used to show the list of files and folder of the repository folder, and the “git stash –include-untracked” command is used to save the untracked files.
$ git stash --include-untracked
$ ls
The following output shows that the repository folder contains two files, named basic.py and test.py, before executing the “git stash” command. Here, basic.py is tracked file and test.py is an untracked file. The untracked file is removed from the repository folder after executing the “git stash” command.
B) Using -u Option
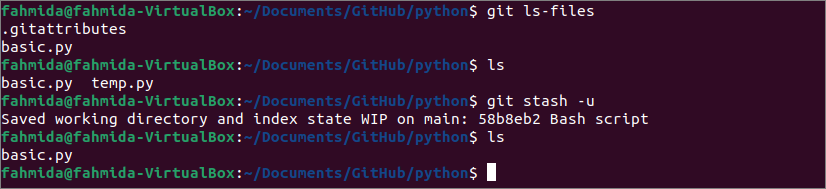
Run the following commands to check the tracked and untracked files of the repository. Save the untracked files and check the file and folder list of the repository folder again. Here, the “git ls-files” command is used to show the list of tracked files, the “ls” command is used to show the list of files and folder of the repository folder, and the “git stash -u” command is used to save the untracked files.
$ ls
$ git stash –u
$ ls
The following output shows that the repository folder contains two files, named basic.py and test.py, before executing the “git stash” command. Here, basic.py is tracked file and test.py is an untracked file. The untracked file is removed from the repository folder after executing the “git stash -u” command.
Stash Untracked Files Using “git add”
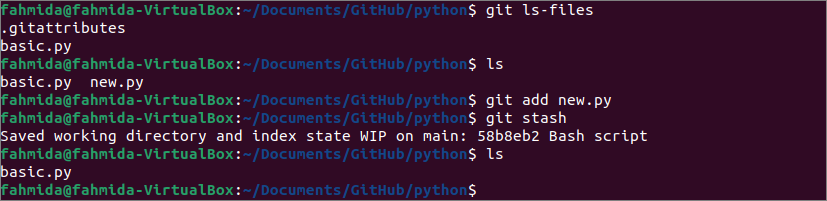
The untracked files of the repository can be saved without using the –include-untracked or -u option of the “git stash” command. You have to add the untracked files of the repository by using the “git add” command and run the “git stash” command to save the untracked file and clean the current directory for working by removing the untracked file from the repository folder.
$ ls
$ git add new.py
$ git slash
$ ls
The following output shows that the list of tracked and untracked files of the current repository is like the previous commands of stashing the unstacked file. The untracked file is removed from the repository folder after executing the “git stash” command.
Retrieve the Stashed File
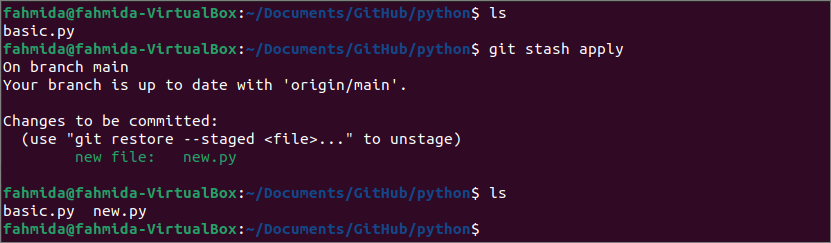
There is another git command to restore the saved untracked files in the repository folder when needed. Run the following command to check the list of files and folders of the current repository folder and restore the previously stashed untracked files in the repository folder. Here, the “ls” command is used to show the list of files and folder of the repository folder, and the “git stash apply” command is used to restore the untracked files.
$ git slash apply
$ ls
The following output shows that the repository has one tracked file and after executing the “git stash apply” command, the untracked file that is stashed before is restored in the repository folder.
Conclusion
Different ways of stashing untracked files and cleaning the current repository directory have been described in this tutorial using the “git stash” command. How the untracked files can be restored using the “git stash” command was also shown here. The concept of the tracked and untracked files and the way to stash the untracked files in git will be cleared for the git users after reading this tutorial.