One of the common statistical calculations that come up even in database administration is a percentile.
A percentile is a statistical measure that allows us to divide a dataset into equal parts of segments. The role of percentiles is to provide an insight into the data distribution which is how we understand how the values are spread out.
In this tutorial, we will learn how we can calculate the percentiles in SQL to divide the data into various segments.
Sample Table
Let us start by setting up a basic table that contains a sample data for demonstration purposes. This helps us to illustrate how the various methods of calculating the percentiles behave and the resulting output.
Let us create a table called “products” that contains the grocery information. The “create table” clause is as follows:
product_id INT PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT,
product_name VARCHAR(255),
category VARCHAR(255),
price DECIMAL(10, 2),
quantity INT,
expiration_date DATE,
barcode BIGINT
);
Once we created the table, we can proceed and add the sample data into the table. We can use the following “insert” statements:
into
products (product_name,
category,
price,
quantity,
expiration_date,
barcode)
values ('Chef Hat 25cm',
'bakery',
24.67,
57,
'2023-09-09',
2854509564204);
insert
into
products (product_name,
category,
price,
quantity,
expiration_date,
barcode)
values ('Quail Eggs - Canned',
'pantry',
17.99,
67,
'2023-09-29',
1708039594250);
insert
into
products (product_name,
category,
price,
quantity,
expiration_date,
barcode)
values ('Coffee - Egg Nog Capuccino',
'bakery',
92.53,
10,
'2023-09-22',
8704051853058);
insert
into
products (product_name,
category,
price,
quantity,
expiration_date,
barcode)
values ('Pear - Prickly',
'bakery',
65.29,
48,
'2023-08-23',
5174927442238);
insert
into
products (product_name,
category,
price,
quantity,
expiration_date,
barcode)
values ('Pasta - Angel Hair',
'pantry',
48.38,
59,
'2023-08-05',
8008123704782);
insert
into
products (product_name,
category,
price,
quantity,
expiration_date,
barcode)
values ('Wine - Prosecco Valdobiaddene',
'produce',
44.18,
3,
'2023-03-13',
6470981735653);
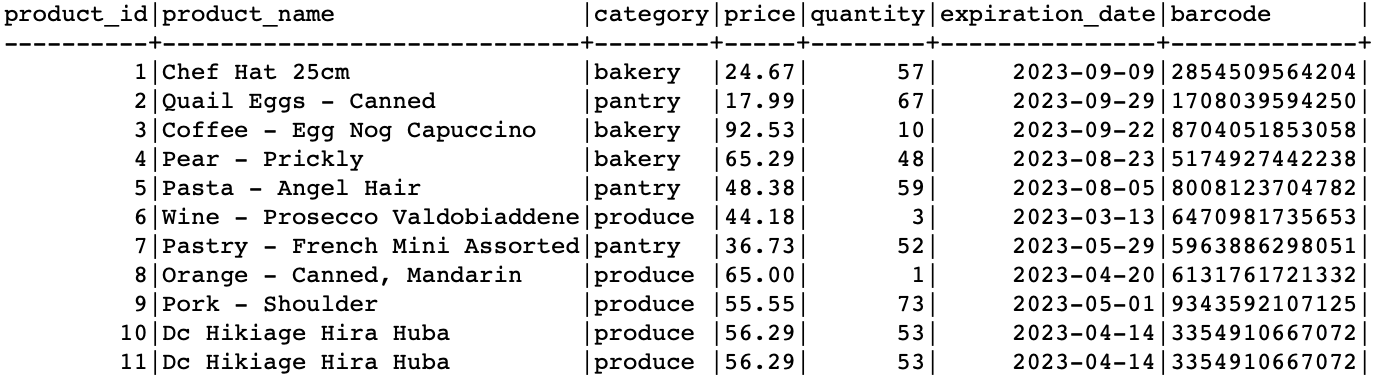
At the end, you should have a table as follows:
SQL Percentile
As you can guess, the way of calculating the percentile may differ depending on the database engine. However, the most common method is using the PERCENTILE_DISC() and PERCENTILE_CONT() functions.
These functions are part of the Standard SQL specification (2003). Hence, it is bound to be supported by PostgreSQL and Oracle.
PERCENTILE_CONT()
Let us start with the PERCENTILE_CONT() function. This function allows us to calculate the percentile values as a fraction of the dataset.
The function returns an interpolated values which might not be precise to the specific data point in your dataset.
The function syntax is as follows:
The function accepts the following parameters:
- Percentile – It specifies the desired percentile value (0.0 to 1.0).
- column_name – It denotes the column for which we wish to calculate the percentile.
- OVER () – It sets the window function to specify the entire dataset.
An example on how to use this function is as follows:
PERCENTILE_CONT(0.5) WITHIN GROUP (ORDER BY price) OVER () AS median
FROM
products;
Note: The given query only works in PostgreSQL since MySQL does not support the use of WITHIN GROUP.
This calculates the 50th percentile of the provided data.
PERCENTILE_DISC()
We can use the PERCENTILE_DISC() function to calculate the percentile value as a discrete value directly from the dataset.
The function returns a value that corresponds to an actual data point.
The function syntax is as follows (PostgreSQL):
An example output is as follows:
PERCENTILE_DISC(0.25) WITHIN GROUP (ORDER BY price) OVER () AS percentile_25
FROM
products;
This should calculate the 25th percentile of the data.
Conclusion
This tutorial covered how to use the various functions to calculate the percentiles in SQL databases.