In this tutorial, we will learn about a common multiplication operation that involves dividing two mathematical table columns.
Sample Table
For demonstration purposes, let us create a table that contains a metric data and use it to illustrate how to multiply two columns in SQL.
id INT AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY NOT NULL,
country_name VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL,
population INT NOT NULL,
distance FLOAT NOT NULL,
gdp DECIMAL(15,
2) NOT NULL DEFAULT(0)
);
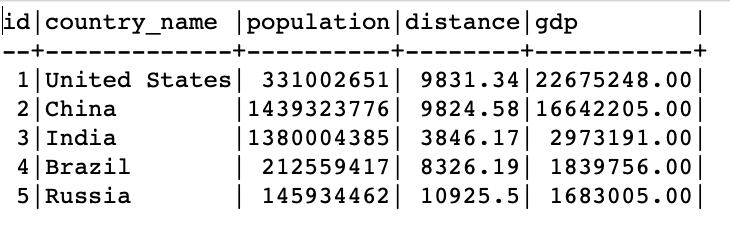
This should create a table called “country_data” and contains a country information such as the country name, population, total distance, and gdp.
We can then insert the records into the table as follows:
INTO
country_data (country_name,
population,
distance,
gdp)
VALUES
('United States',
331002651,
9831.34,
22675248.00),
('China',
1439323776,
9824.58,
16642205.00),
('India',
1380004385,
3846.17,
2973191.00),
('Brazil',
212559417,
8326.19,
1839756.00),
('Russia',
145934462,
10925.55,
1683005.00);
The resulting output is as follows:
Multiply Two Columns in SQL
Suppose we want to calculate the product of the population and distance columns. We can multiply the total population by the distance of the country.
In SQL, to multiply two columns, we use the “*” operator followed by the columns in which we wish to divide.
For example:
country_name,
population,
distance,
gdp,
(population * distance) AS prod
FROM
country_data;
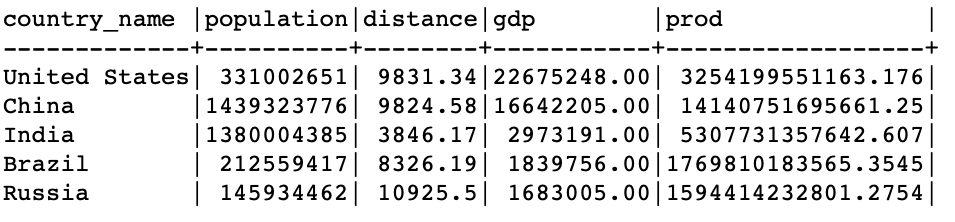
In this case, we multiply the population column by the distance column and assign the resulting column with the alias of prod.
The resulting set is as follows:
This shows the average population of a country per square units.
Conclusion
In this tutorial, we learned how we can perform the mathematical multiplication in SQL by multiplying two table columns to fetch the results for each corresponding value.