The SQL GROUP BY clause is a powerful tool for grouping and aggregating the data. It provides an excellent way of grouping the data based on specific criteria and then performing an action on the resulting groups.
One common use case for GROUP BY is grouping by dates. In this tutorial, we will learn the fundamentals of working with the GROUP BY clause and discuss how to use it to group the data by dates in SQL.
NOTE: We assume that you have a basic understanding of SQL. For demonstration purposes, we use the examples in this tutorial with MySQL 8. However, you can freely port the concepts of this tutorial to the other SQL-based database engines.
Sample Table:
The first step is to set up a basic table and sample data for demonstration. If you have an existing table that you wish to work with, feel free to skip this section.
To create the table, use the following query:
id int not null auto_increment primary key,
date DATE,
amount DECIMAL(10, 2)
);
Once you create the table, insert the sample data as shown in the following:
VALUES
('2023-01-01', 100.00),
('2023-01-02', 50.00),
('2023-01-03', 75.00),
('2023-01-04', 200.00),
('2023-01-05', 150.00),
('2023-01-06', 175.00),
('2023-01-07', 50.00),
('2023-01-08', 100.00),
('2023-01-09', 25.00),
('2023-01-10', 75.00),
('2023-01-11', 150.00),
('2023-01-12', 200.00),
('2023-01-13', 250.00),
('2023-01-14', 175.00),
('2023-01-15', 150.00),
('2023-01-16', 100.00),
('2023-01-17', 50.00),
('2023-01-18', 75.00);
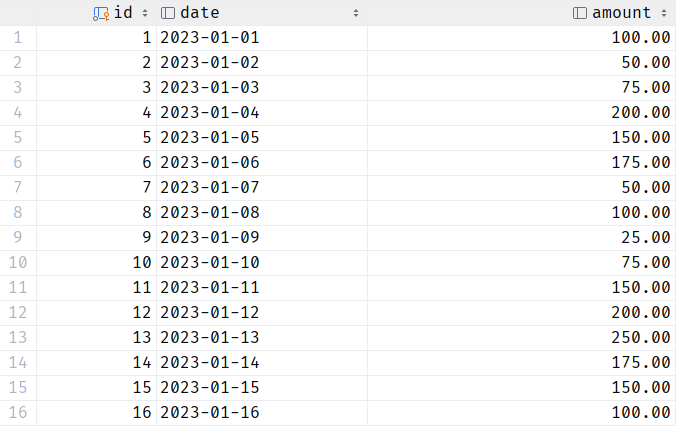
This should add the random data to the transactions table. We can use the select statement to show the resulting table as follows:
Output Table:
Once we have the data prepared, we can proceed to the next step.
SQL Group by Date
As you can guess, we use the GROUP BY clause to partition the data in a given table based on specific values. The clause syntax is as follows:
FROM table_name
GROUP BY column1, column2, ...;
In the previous syntax, we use the GROUP BY clause to specify the columns that you want to group the data by.
From the previous table, we can use the date column to group the data as shown in the following query:
FROM transactions
GROUP BY date;
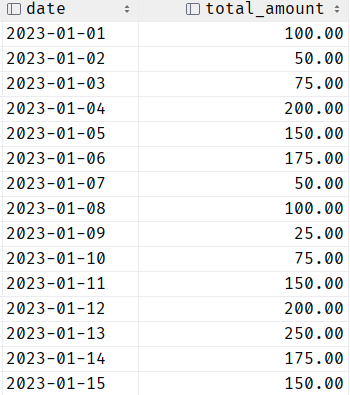
The previous query performs the basic calculations and adds the total amount for each day using the sum() function. We then group the data based on the date values. The resulting table is as follows:
Format Date
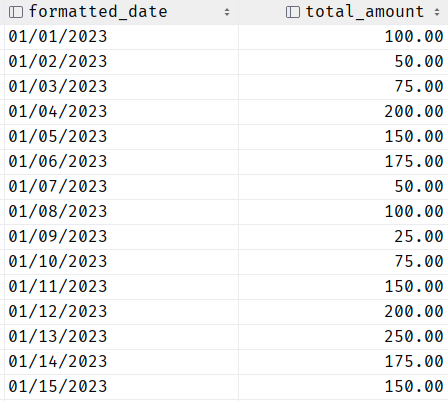
Sometimes, we may need to format the date and make it more readable. An example is as follows:
FROM transactions
GROUP BY date;
This should return the date values in the specified format as follows:
SQL Filter Date Range
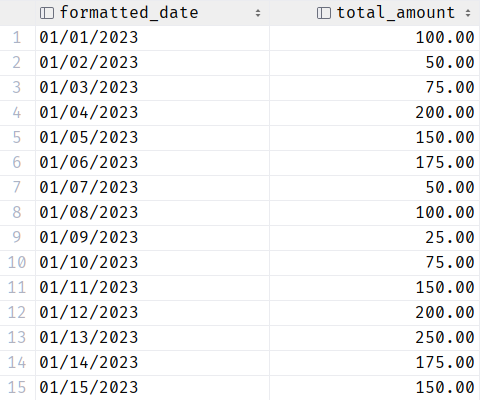
We can also filter the result set by a date range using the WHERE clause. An example is as follows:
FROM transactions
WHERE date BETWEEN '2023-01-01' AND '2023-01-15'
GROUP BY date;
The resulting table is shown in the following:
There you have it! A way to group the data from a given table based on date values.
Conclusion
This tutorial explored the fundamentals of working with the GROUP BY clause in SQL to sort the data based on specific values. This allowed us to cover how to use the GROUP BY clause to divide the data based on date values.