Git is a tracking tool that enables developers to work parallelly, which means several contributors can make changes to the same project. The GitHub hosting service manages the Git repositories and a variety of project sizes that vary from small to large projects.
However, sometimes, large projects take up more space and mesh of directories. The Git sparse checkout is the solution to the option previously discussed by enabling this option and updating the configure file.
This blog provides the procedure to sparse checkout only the specific file from a Git repository.
How to Sparsely Checkout Only One Single File From a Git Repository?
To sparsely checkout only one single file from a Git repository, follow the below-stated instructions:
- Go to the Git particular repository and initialize it.
- Add the remote URL and fetch the latest version of the remote repository simultaneously.
- Configure the sparseCheckout by enabling it to be “true”.
- Initialize the sparse process and apply the sparse checkout to the fetched file.
- Pull the local branch to the origin.
- Verify the added changes by listing their content.
- Run the “$ git sparse-checkout disable” command to disable the sparse-checkout process.
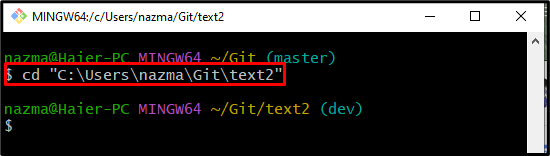
Step 1: Move to Git Required Repository
First, run the below command to navigate to the Git repository:
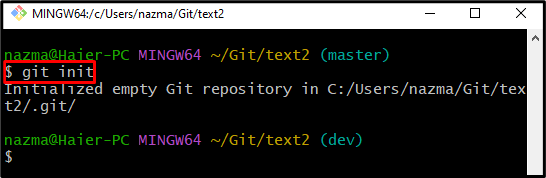
Step 2: Initialize Git Repository
Then, initialize the Git repository by running the “git init” command:
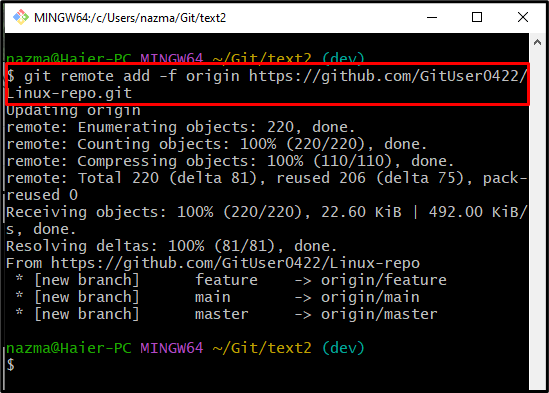
Step 3: Add Git Remote and Fetch
Execute the “git remote add” command along with the “-f” flags, remote name, and required remote repository URL:
Here, you can see the remote URL is added and fetched repository content, simultaneously:
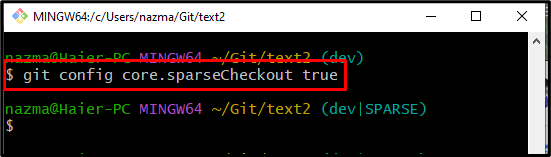
Step 4: Update Configure File and Enable Sparse Setting
After that, set the “sparseCheckout” settings to “true” by running the following command:
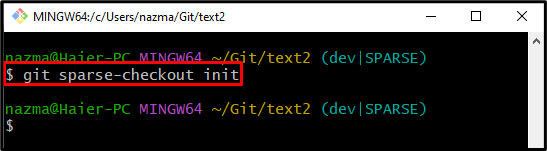
Step 5: Initialize sparse-checkout
Next, execute the “git sparse-checkout init” command to initialize the sparse:
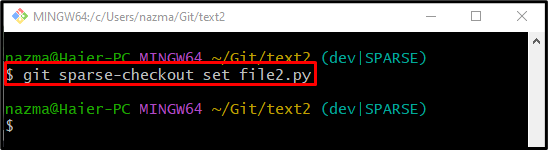
Step 6: Apply sparse-checkout to Fetched Remote Repository
To get the particular remote repository file, use the “git sparse-checkout” command:
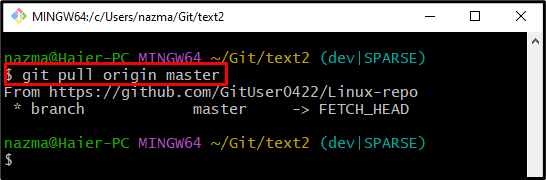
Step 7: Pull Remote Repository
After that, execute the “git pull“ command to pull the “master” branch while using the sparse-checkout first time in the remote repository:
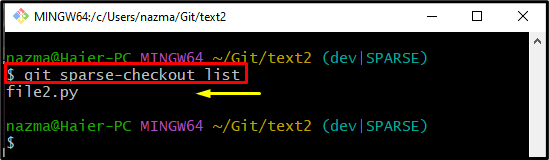
Step 8: Verify Changes Through Listing Content
To ensure that the changes are added successfully or not, utilize the given command:
Step 9: Disable sparse-checkout
If you want to disable the sparse-checkout, then execute the “git sparse-checkout” command along with the “disable” value:
That’s all! We have explained the method of sparse checkout only for specific files from a Git repository.
Conclusion
To sparsely checkout only one single file from a Git repository, first, go to the Git particular repository and initialize it. After that, add the remote URL and fetch the latest version of the remote repository simultaneously. Then, configure the sparsecheckout by enabling it to be “true”. Next, initialize the sparse process, apply the sparse checkout to the fetched particular file and pull the local branch to the origin. Lastly, verify the added changes. If you want to disable sparse-checkout, run the “$ git sparse-checkout disable” command. This blog illustrated the procedure of sparse checkout only the specific files from a Git repository.