This article covers how to use the sort command to perform sorting operations on specific columns in a file.
Basic Usage
The sort command is simple to use and very useful in daily Linux operations. The general syntax of the command is as:
The options you pass to the command modifies how the file is sorted and the specific conditions to sort the target file. You can omit the options to use the default sorting parameters.
By default, the sort command:
- Sorts the alphabets in ascending order.
- Letters come after numerical values
- Assigns higher precedence to lowercase letters than to uppercase letters.
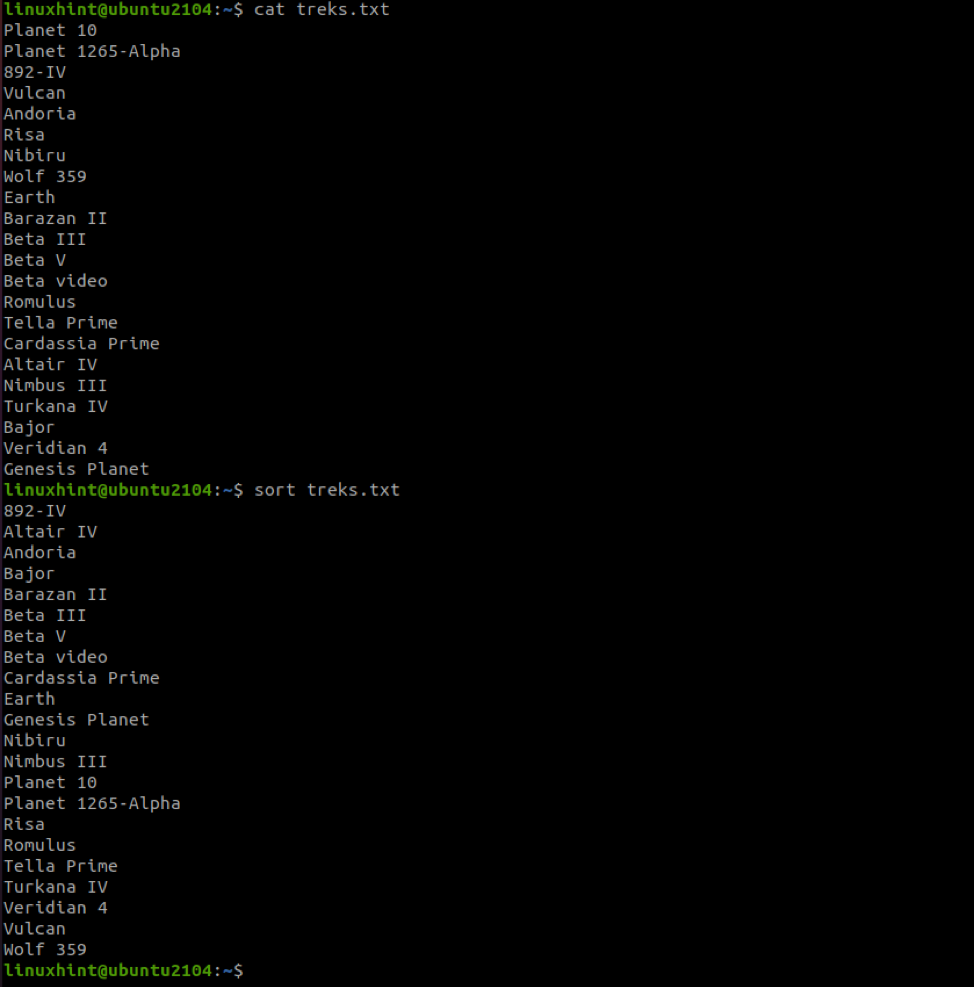
For example, to sort a file without options:
Once we run the sort command against the file, we get the information sorted in alphabetical order (ascending).
NOTE: Numerical values take precedence as from the example above.
Sort Command Options
You can use the following options in conjunction with the raw command to modify how the values are sorted.
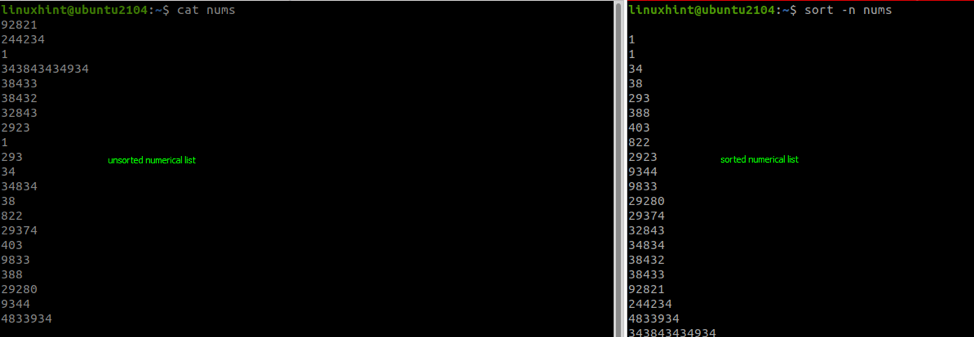
- -n – sorts in numerical values.
- -h – compares human-readable numbers such as 1k, 1G
- -R – sort in random order but group the identical keys.
- -r – sort the values in reverse (descending order).
- -o – save ouput to a file
- -c – check if the input file is sorted; do not sort if true.
- -u – show unique values only.
- -k – sort the data via a specific key (useful when sorting columnar data).
Those are some popular options you can tweak to get the best-sorted result. For more options, check the manual.
How to Sort In Linux Bash By Numerical Values
How to Sort In Linux Bash By Reverse Order
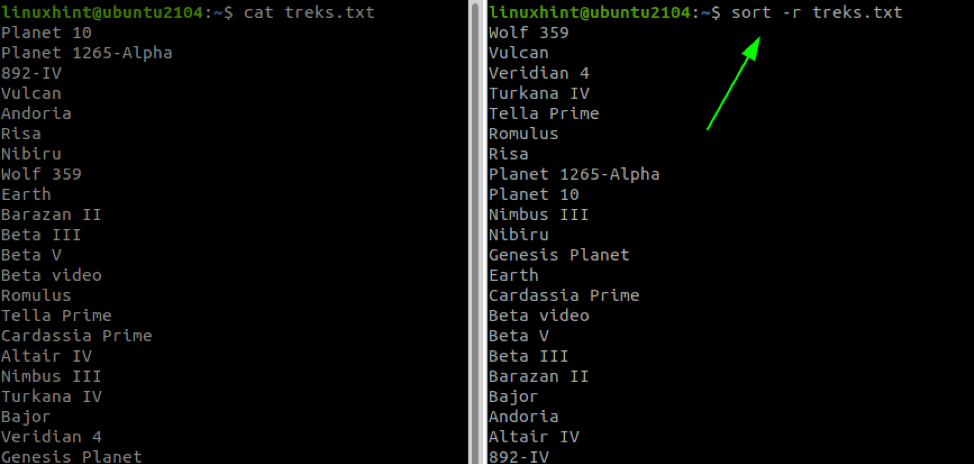
To sort input in reverse order, we use the -r flag. For example:
The command above will sort in ascending alphabetical order (numerical values first) and reverse order.
How to Sort In Linux Bash by Column
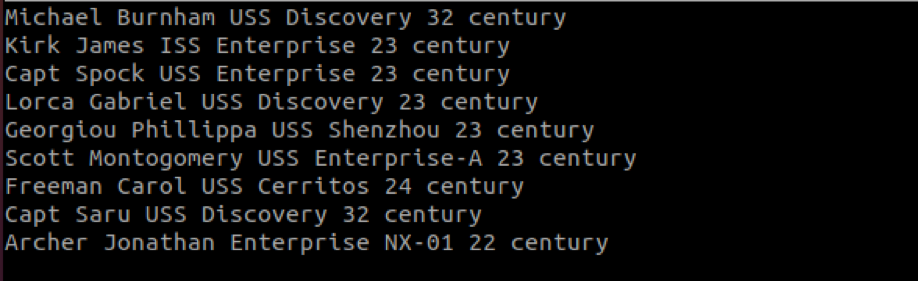
Sort allows us to sort a file by columns by using the -k option. Let us start by creating a file with more than one column. In sort, we separate a column by a single space.
In the example file below, we have six columns.
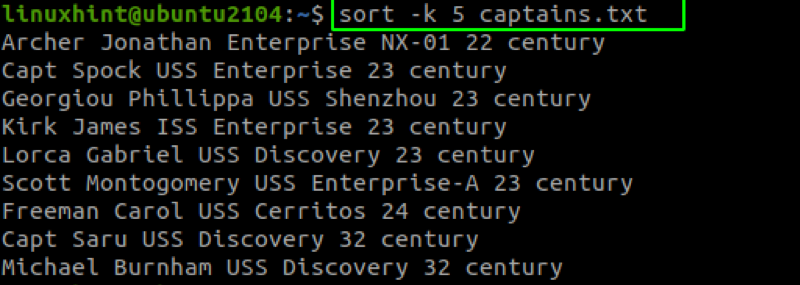
To sort the captains’ file above by their century, we can specify the -k followed by the column number as:
Once we specify the column to sort the data, the sort command will try to sort the values in ascending order. In the example above, the command sorts the values from the earliest century to the latest.
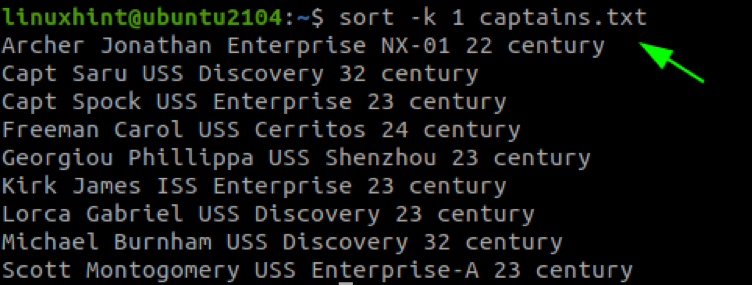
To sort by the first name, set the sort column as 1:
How to Save Sort Output to a File
To save the sorted output to a file, we can use the -o option as:
The command above will sort the captains.txt file by the 5th column and save the result to the captains_century.txt file.
Conclusion
That is the end of this tutorial on the sort command in Linux. We covered the basics of using the sort command to get the most out of your sorted data. Feel free to explore how you can use the sort command.