SFTP is the acronym of “Secure File Transfer Protocol” which is used to transfer files from one place to another place using the internet and it works similarly to FTP (File Text Protocol), but the difference in both of them is that SFTP also ensures the privacy of the file using SSH service, which secures the data of the file by encrypting it, so no one can access the data.
Though it has the advantage that it encrypts the data and transfers it to the destination location more securely, it has a disadvantage as well; on reaching the destination location, any user can access it. So to make it more secure, we should restrict the other users to access it, other than the allowed users.
In this article, we will discuss how to install SFTP in Ubuntu, if it is not already installed, and how to set it up by using the simple commands of Ubuntu.
How to install SFTP server in Ubuntu
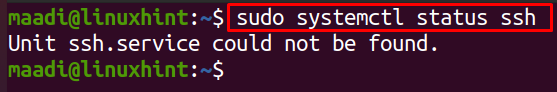
SFTP server is usually installed in Ubuntu by default, but if it is not already installed, one can install SSH by using the simple commands of Ubuntu. Because SFTP uses the SSH server, so to check the SFTP server is already installed or not we will run the below-mentioned command:
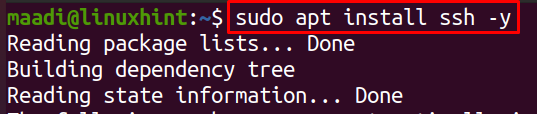
The output is shows, SSH is not installed in our Ubuntu, to install it, run the following command of Ubuntu:
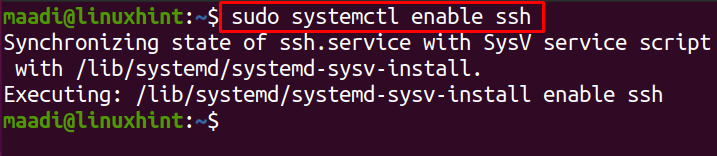
Once it is installed, we will enable it using the systemctl command:
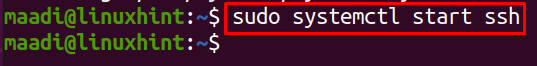
Now, again using the systemctl command, start it:
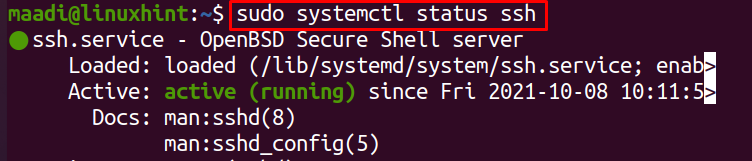
To verify the installation of ssh checks its status using the systemctl command:
The running status of SSH shows it has been installed successfully.
How to create an SFTP user account
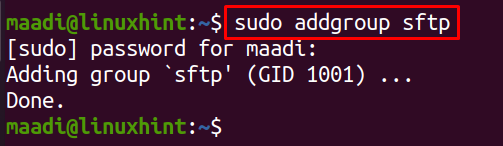
We can either create users directly or by creating a group of SFTP and then create users to give them access to the SFTP. To create a group, for example, we name it “sftp”, you can name it according to your choice, execute the following in a terminal:
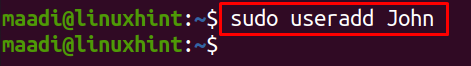
To create a user, “John”, you can rename “John” with your own username, run the following command:
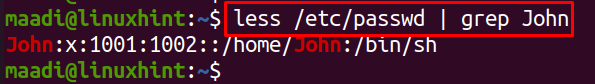
For the verification of newly user-created, execute:
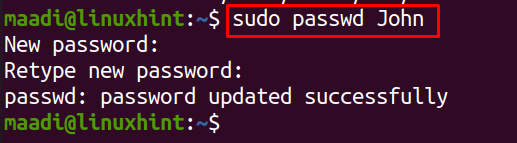
To add a password for this new user, run:
To move user, “John” to the group “sftp” run the command:
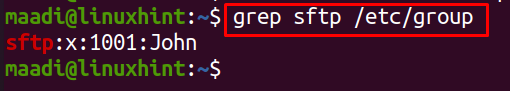
To verify that the user, John, has been added to the group,sftp, run the statement:
How to create a directory for file transfers
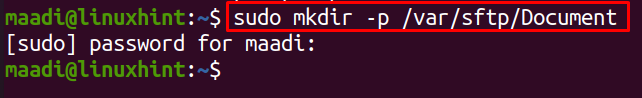
To understand how to restrict access to a directory for other users, we will create a directory “Document” in path /var/sftp which will be owned by root. Then only the “John” user which we have created can access this directory and upload files in it.
To do so, first, we will create a directory of “Document” using the mkdir command:
Allow the root, to recognize the owner of /var/sftp:
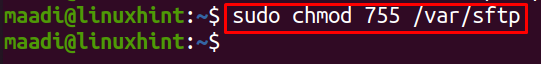
Grant write permissions of this directory to the same directory, and allow other users to read-only:
Now grant the permissions of the Document to the user John:
How to configure SSH daemon
Once the installation is completed, we will open the configuration file of the SSH server with any editor and configure it. In this configuration, we are restricting the user, John, to the directory /var/sftp, and also none of the other users can access this directory. We are using a nano text editor to configure it so we will run the following command:
Once the file opened, type the following text in it:
ChrootDirectory /var/sftp
X11Forwarding no
AllowTcpForwarding no
ForceCommand internal-sftp
When the file is opened, at the bottom you will see the text “Subsystem sftp /usr/lib/openssh/sftp-server”, write those lines after this line. The explanation of these five lines are:
- Match User tells the SSH to implement these changes on the mentioned user, in our case, it is “John”
- ChrootDirectory ensures the user will not have access to any other directory except that whose part is being provided, in our case it is “/var/sftp”
- AllowTcpForwarding and X11Forwarding will enable or disable the port tunneling and X11forwarding, in our case, both are being disabled by typing “no”
- ForceCommand ensure the SSH run the SFTP server only after the login
Once the changes are made, save the changes by pressing CTRL+S, and then terminate the editor by pressing CTRL+X.
To apply these new changes, restart the SSH server using:
How to verify the restriction configurations
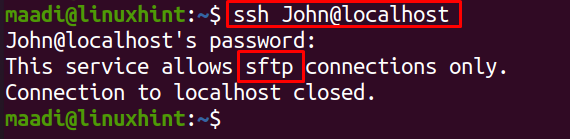
To verify the restriction configurations, we will try to access the files using the normal SSH command:
The output is showing that John cannot be accessed by any other SSH.
How to login SFTP server using command line
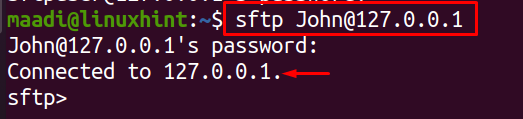
We can log in to the user protected by the SFTP server in the command line by the use of loop address which is by default 127.0.0.1, once the command has been executed it will ask for the password set for the user:
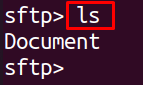
It has been connected to the SFTP server. List down the directories of this user using the ls command:
The output showing the directory, Document which was restricted for this user. Now, this user cannot access any other directory other than this one.
How to login SFTP server using GUI
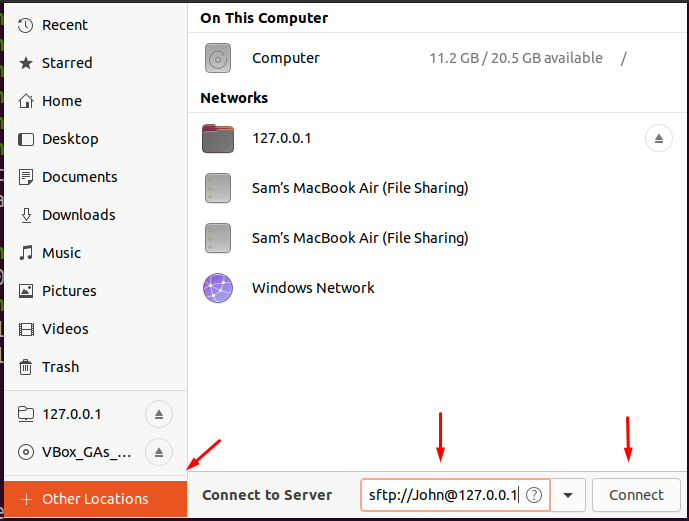
We can also access SFTP using the GUI mode, simply go to the home folder, choose other locations, type sftp://[email protected] and click on the connect.
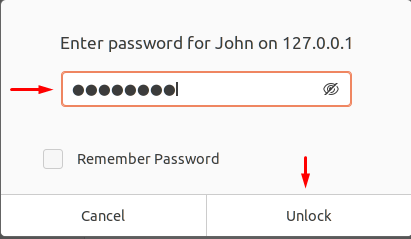
It will ask the password of the user, type the password, and click on Unlock:
Finally, It will open the directory:
How to Remove SFTP server
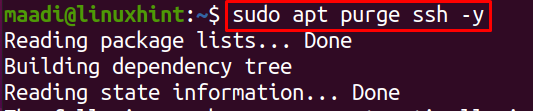
To remove or uninstall the SFTP server, just remove the ssh by using the command:
Conclusion
SFTP server encrypts the file and transfers it to the destinations, and decodes the file there to communicate the data safely. Safety is necessary for transferring files as sometimes files contain sensitive pieces of information which should only be delivered to the authorized person, this can be done with the help of SFTP. In this article, we have learned how to install SFTP if it is not installed by default in Ubuntu, then we learned how to create a user of SFTP directly or with the help of the group. We also learned the feature of restricting the files to only selected users as well as restricting the user to that particular file so that the user cannot move to any other directory. Finally, we learned how to remove the ssh server from Ubuntu 20.04.