One of the popular version control systems is git, which serves developers from their local systems to the cloud. Now, there are various ways through which you can utilize the power of git, for example, paying for remote repositories on services such as GitHub, GitLab, and many more. You can also build your own git system hosted on a server on the cloud and use it for your own projects and teams.
This tutorial will learn how to set up your version control system on Linux using Debian 10 and GOGs. Stay tuned to the end to learn more.
Introduction to GOGs
GOGs is a simple, painless self-hosted Git service written in Go language. It is simple, and it does not require heavy computing resources. Due to the nature of its programming language, GOGs is also incredibly fast.
GOGs is a popular choice for anyone looking to set up their own private git service without paying for a server on GitHub providers.
This tutorial will use a local Debian system, Go programming language, and MySQL as the database.
Installing Go Lang
Go is a fast, open-source programming language that is efficient at building applications. Since GOGs is written in Go, we need to install it before compiling GOGs on the system.
Installing Go language is simple.
First, open the terminal and download the go archive using wget as:
Next, extract the archive in /usr/local directory:
Once we have extracted the archive, we need to export the go binary location to the path in the .bashrc file.
Edit the file and add the following entries
export GOROOT=/usr/local/go
export PATH=${PATH}:$GOROOT/bin
Now save the file and apply the changes by sourcing the bashrc file:
Now verify that go is installed by calling the command go:
Installing the Database
Let us now build the backend database for the GOGs system. It is good to note that a database is completely optional, and GOGs will run with or without it.
The first step is to ensure you have your system is up to date:
Next, install the MySQL server:
Next, launch the SQL shell and enter the commands:
mysql> CREATE DATABASE gogs;
mysql> GRANT ALL ON gogs.* TO 'gogs';
Installing GOGs
Now that we have all the requirements to run GOGs on our system, we can proceed to compile the application.
First, download it using the git clone command:
Navigate to gogs directory
Compile the main program
Once completed, launch the gogs binary:
This will launch the webserver and listen for incoming http connections.
Configuring GOGs
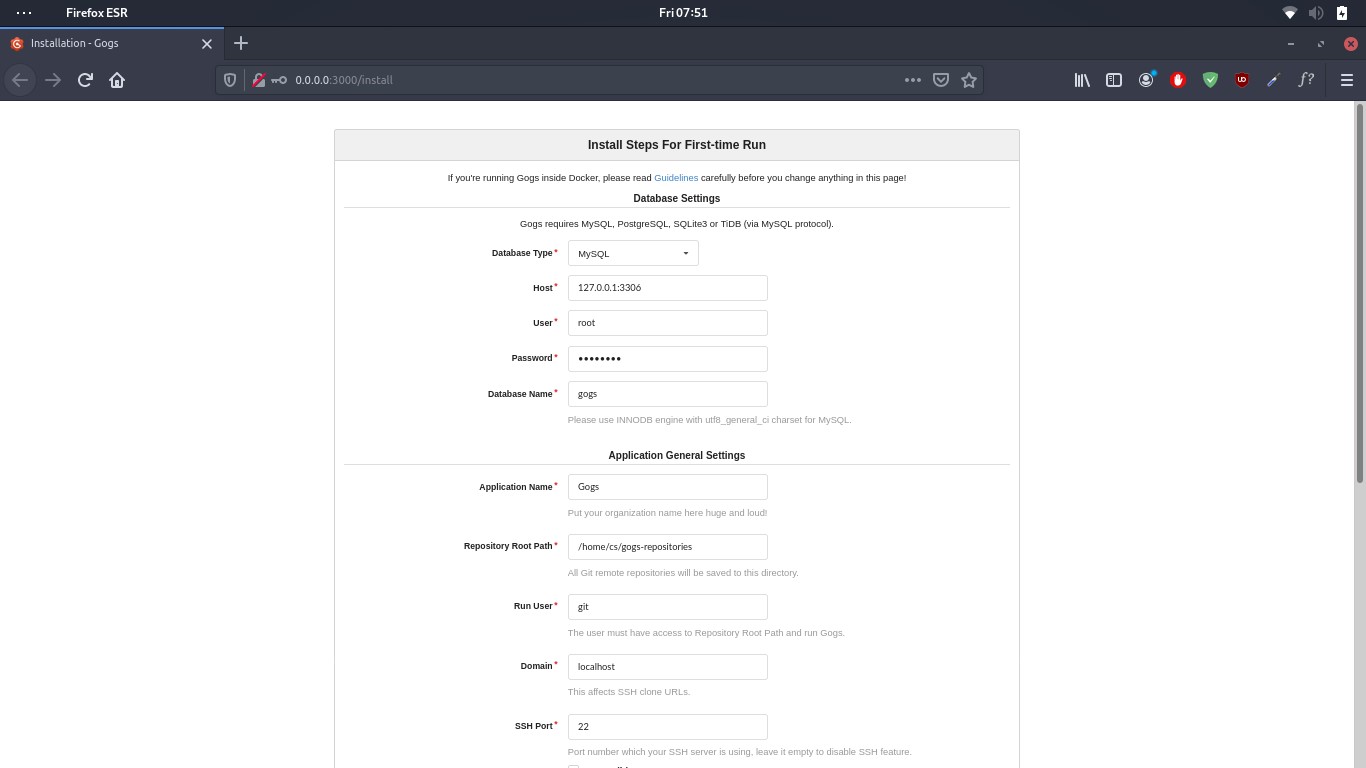
Once the webserver is running, launch the gogs web interface using the address http://localhost:3000
This will launch the GOGs installer allowing you to configure GOGs backend.
Modify the information as we created in the MySQL database earlier.
Host = 127.0.0.1:3306
User = gogs
Password =
Database Name = gogs
Once you have configured the server correctly, create an admin account and start using GOGs.
If you are looking for a git tutorial, consider the article on how-to-install-and-use-git-on-Linux.
Conclusion
In this quick guide, we discussed installing and using GOGs, a self-hosted git service on a Debian system. This tutorial can be expanded greatly to host GOGs on a live server with a web address. However, it is a good starter guide for beginners.