In this article, we will elaborate on you on how to change the time zone of the Debian 10 buster system using different methods.
Debian 10 buster offers you to set the time zone of your system using the two different ways:
- Change the time zone using the Gnome desktop environment
- Change the time zone using the Gnome terminal
Method 1: Using the Gnome desktop environment
To set the time zone of the Debian 10 system, you will click on ‘Activities’ that is located on the top left corner of your desktop and type date and time in the application search bar as follows:
Now, click on the displaying result. The following window will be displayed on the desktop.
Alternatively, you can also open the above displaying window by clicking on settings icon from the start of the desktop as follows:
Now, click on the ‘Time Zone’ option from all displaying options.
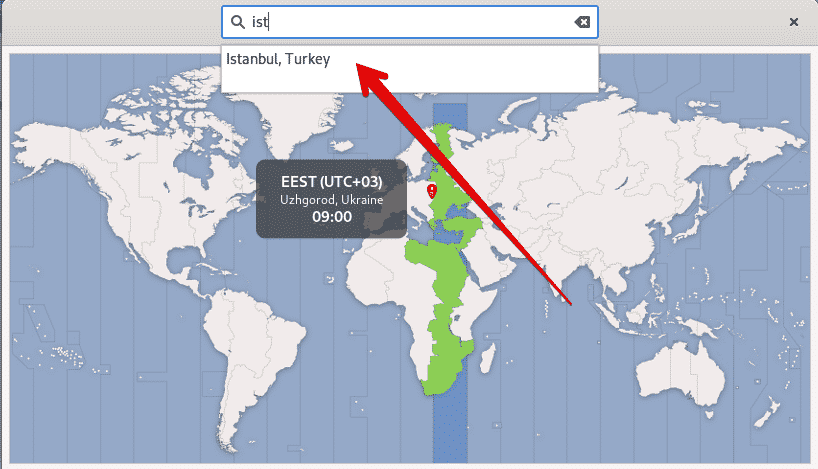
The following window will appear on the screen where you can search for a particular location using the search bar and change the time zone of your Debian 10 system.
Method 2: Change the time zone using the Gnome terminal
You can also change the time zone of the Debian 10 system using the command line or gnome-terminal application. To do this, click on the ‘Activities’ and open the terminal using the application search bar as follows:
Display current using timedatectl utility
Using the timedatectl command-line utility, you can display the information about the current time zone of your system, and you can change the system’s date and time. This common line utility is available on all modern Linux systems. Use the following command to display the current time zone information:
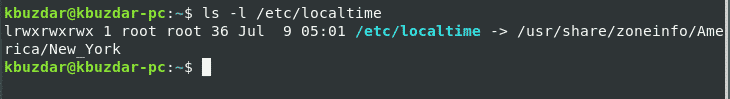
In the below output, you can see that the time zone is set as America/New_york.
The time zone of your system will be configured by symlinking /etc/localtime into a time zone binary identifier in the /usr/share/zoneinfo folder path.
You can find the time zone by using the symlink path through the ls command as follows:
The following output will display on the terminal. Here, the symlink path is /etc/localtime, which points to the particular directory.
Changing the time zone on Debian 10 buster
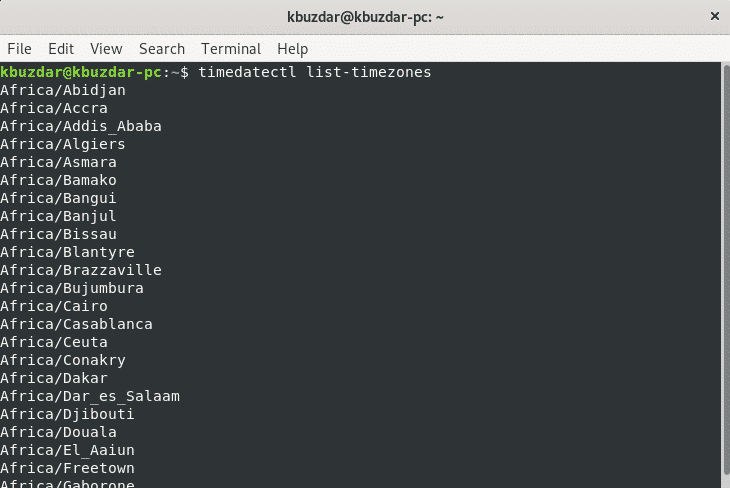
To change the time zone in Debian 10, it is easy for you that first, you list all available time zones of the world. For this purpose, using the following command display the list of all available time zones of the world.
You will see the long list of time zones on the terminal as follows:
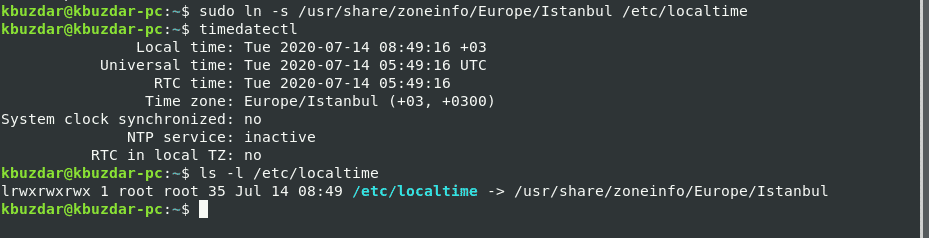
Now, we will change the time zone using the available time zones list. For example, we want to set the time zone of our system Europe/Istanbul. To do that, unlink the local time with the system time using the following command:
Using the following command, you can easily change the time zone of your system.
In the above command, replace the ‘your-time-zone’ with Europe/Istanbul as follows:
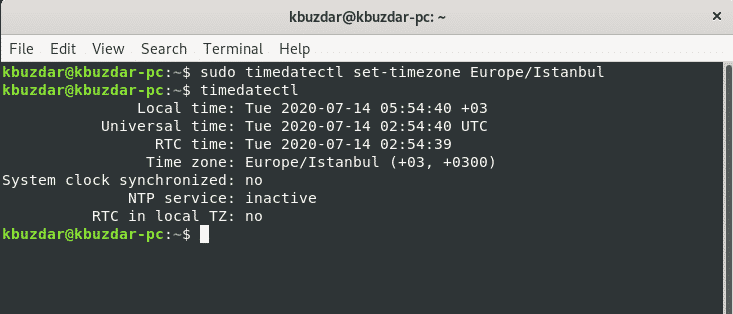
Now, create the symlink and display the time zone information of your system using the ‘timedatectl’ command.
$ timedatectl
In the following displayed output, you can see that the time zone is set to Europe/Istanbul.
Conclusion
In this article, you have learned how to change the time zone of your system Debian 10 buster using both ways command line and GUI. Furthermore, you also learned various sets of commands related to timedatectl command-line utility. How this utility provides help in changing the time zone of the Linux system. I hope this article will be useful for you in the future.