Session Handling in PHP
The session_start() function is used to create a new session for the user. The default session name is PHPSESSID and it is used to check the session exists or not. If no cookie or session information is found then a new session will be generated for the user, otherwise, the current session will be used for the user.
Setting Session Timeout
The timeout limit of the session can be set by setting the value of two directives in the php.ini file or using the ini_set() function in the PHP script. The directives are given below.
- session.gc_maxlifetime
- session.cookie_lifetime
It is used to set the time limit in seconds to store the session information in the server for a long time.
It is used to set the expiration time limit for the PHPSESSID cookie.
Set Session Timeout in PHP
The ways to set the session timeout value in PHP for handling a user’s session have been shown in this part of the tutorial by using multiple examples.
Example-1: Set session timeout value using PHP directives
Create a PHP file with the following script to know the way of setting session timeout by using PHP directives and handling sessions based on the directive values. The ini_set() function has been used in the script to set the value of the session.gc_maxlifetime and session.cookie_lifetime directives. The duration of the session has been set to 2 seconds for testing purposes. The superglobal variable $_COOKIE array has been used here to handle the session. The new session will be generated for the user when the script will execute in the browser and after two seconds the session will be expired.
//Set the session timeout for 2 seconds
$timeout = 2;
//Set the maxlifetime of the session
ini_set( "session.gc_maxlifetime", $timeout );
//Set the cookie lifetime of the session
ini_set( "session.cookie_lifetime", $timeout );
//Start a new session
session_start();
//Set the default session name
$s_name = session_name();
//Check the session exists or not
if(isset( $_COOKIE[ $s_name ] )) {
setcookie( $s_name, $_COOKIE[ $s_name ], time() + $timeout, '/' );
echo "Session is created for $s_name.<br/>";
}
else
echo "Session is expired.<br/>";
?>
Output:
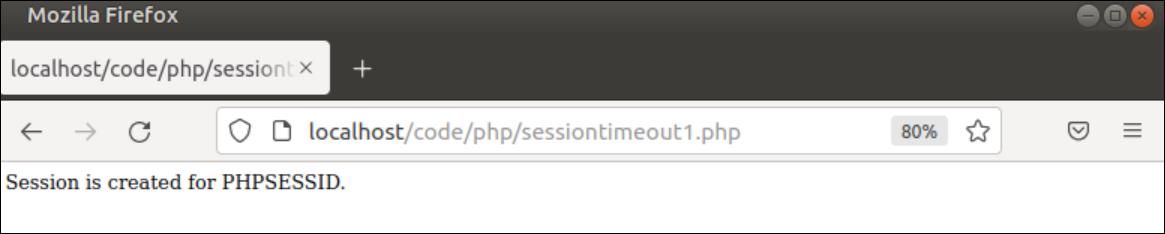
The following output will appear after executing the above script for the first time. The output shows the default session user name, PHPSESSID.
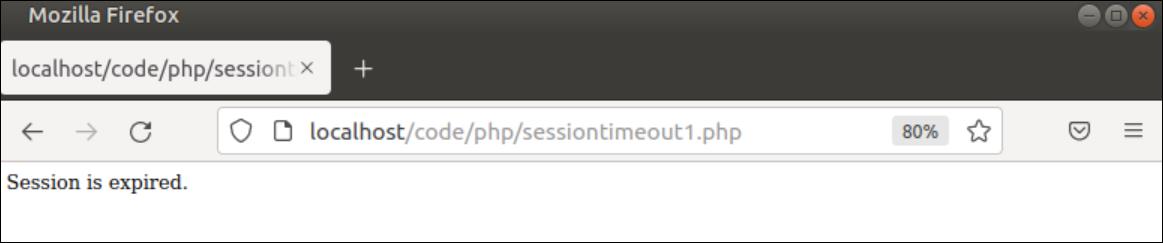
The following output will appear if the page is refreshed after 2 seconds.
Example-2: Set session timeout value using $_SESSION array
Create a PHP file with the following script to set the session timeout value using the PHP superglobal variable, $_SESSION. The time duration of the session has been set to 5 seconds for testing purposes. Next, the request time of the user for the page has stored in a variable named $time. When the time duration between the $time variable and the user’s last activity will be more than 5 seconds, then the current session of the user will be destroyed and a new session will be generated. The session_unset() and session_destroy() functions have used in the script to destroy the session.
//Start a new session
session_start();
//Set the session duration for 5 seconds
$duration = 5;
//Read the request time of the user
$time = $_SERVER['REQUEST_TIME'];
//Check the user's session exist or not
if (isset($_SESSION['LAST_ACTIVITY']) &&
($time - $_SESSION['LAST_ACTIVITY']) > $duration) {
//Unset the session variables
session_unset();
//Destroy the session
session_destroy();
//Start another new session
session_start();
echo "New session is created.<br/>";
}
else
echo "Current session exists.<br/>";
//Set the time of the user's last activity
$_SESSION['LAST_ACTIVITY'] = $time;
?>
Output:
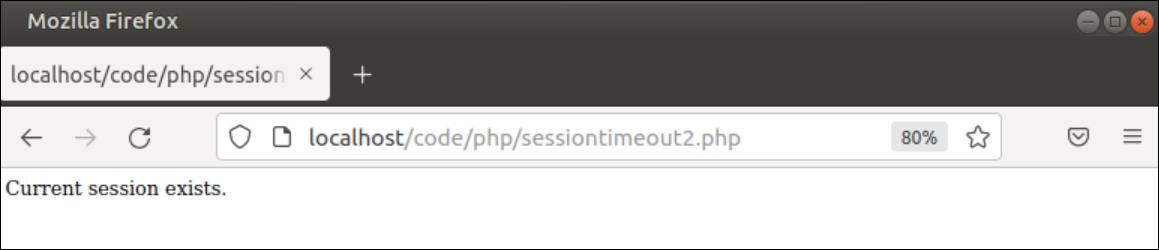
The following output will appear after executing the above script for the first time.
The following output will appear if the page is refreshed after 5 seconds.
Example-3: Set session timeout value using $_SESSION array and time() function
Create a PHP file with the following script to set the session timeout value using PHP superglobal variable, $_SESSION, and the built-in PHP function, time(). The time() function returns the current timestamp value of the system. The time duration of the session has been set to 600 seconds (10 minutes) in the script.
The $_SESSION[‘start’] has been used to store the starting time of the session. When the time duration between the current time and the session starting time will be more than 10 minutes, then the current session of the user will be destroyed. The session_unset() and session_destroy() functions have been used in the script as the previous example to destroy the session.
//Start a new session
session_start();
//Check the session start time is set or not
if(!isset($_SESSION['start']))
{
//Set the session start time
$_SESSION['start'] = time();
}
//Check the session is expired or not
if (isset($_SESSION['start']) && (time() - $_SESSION['start'] >600)) {
//Unset the session variables
session_unset();
//Destroy the session
session_destroy();
echo "Session is expired.<br/>";
}
else
echo "Current session exists.<br/>";
?>
Output:
The following output will appear after executing the above script for the first time. The expired message will be displayed if the page is refreshed after 10 minutes.
Conclusion
Three different ways to set the session timeout value for handling a user’s session in PHP have been shown in this tutorial. The PHP users will get the basic concept of implementing the user’s session by using $_COOKIE and $_SESSION variables and be able to apply it in their script after reading this tutorial.