Pipe (|) operator
pipe(|) operator is used to run two or more related commands at a time. The input of the next command will be the output of the previous command. So, the success of each command depends on the success of earlier command without first command. In the following command, the first command, ls will find out the list of files and folders of the current location and send the output as input for the second command, wc. It will print the total number of lines, words, and characters based on the input data.
Semicolon (;) Operator
Semicolon(;) operator is used to running two or more unrelated commands at a time. This means that the output of each command is not dependent on other commands. In the following example, three types of commands are combined together and the failure of each command will not create an effect on the output of other commands. The first command will print the content of a file, the second command will make a directory and the third command will change the current directory.
Logical AND (&&) operator
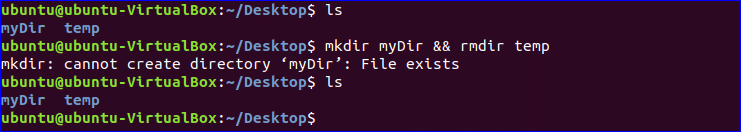
The commands which run by Logical AND (&&) are related with each other like pipe (|) command. So, if the previous command will not execute successfully then the next commands will not work. In the following example, two commands, mkdir, and rmdir combined by && operators. So, it mkdir command is failed to execute successfully then rmdir command will not execute. According to the output of ls command, myDir directory already exists in the current location. So the first command will not execute and for this second command will not execute also.
$ mkdir myDir && rmdir temp
$ ls
Logical OR (||) operator
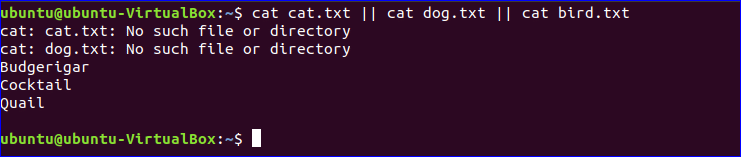
Logical OR (||) operator is the opposite of the Logical AND (&&) operator. The next command will execute if the previous command fails to execute. Three cat commands are combined with OR (||) operator in the following example. When you will run the command, first of all, it will try to display the content of cat.txt file. If no such file exists in the current location then it will try to execute the next command. According to the output, bird.txt file exists in the current location and the content of this file is displayed.
Multiple commands with multiple operators
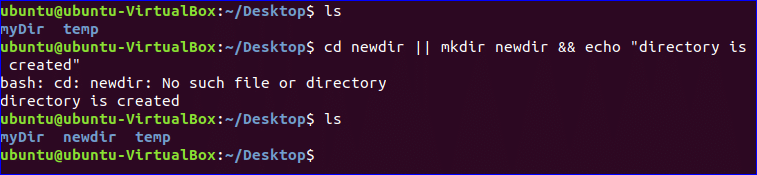
You can use multiple operators to run multiple commands at a time. In the following example, three commands are combined with OR (||) and AND (&&) operators. After running the command, first of all, it will change the current directory to newdir if the directory exists. If this command fails then it will create the directory by executing the second command and print the message, “directory is created.” According to the output, newdir directory not exist in the current location. So, the error message is displayed and the directory is created later.
Combination operator {}
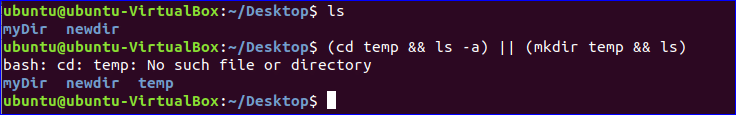
Two or more commands can be combined using this operator and if the execution of the first command fails then the second command will not execute. In the following example, OR, AND and combination operators are used together. First commands will check the temp directory is exist in the current location or not. If the first command fails then it will create a temp directory and print a message. The last command will show the current directory list.
Precedence operator ()
You can use this operator for grouping the commands at the time of execution. Here, each group will work as a single task. In the following example, two command groups are defined and if the first group fails to execute then the second group will execute.
Conclusion
This tutorial explained the mostly used operators for running multiple commands in Linux. But there are many others operators exist in bash which are used to run two or more commands together. These are ampersand (&), redirection (<,>,>>), Logical NOT (!), Combination ({}) etc.