Whenever you change the password, make sure that you use a strong and unique password that meets the standard criteria for a Linux password. Having a strong password is a smart move to protect your account from potential thefts and unauthorized access. A strong password should be 16 characters long, containing one uppercase letter, one lowercase letter, one number, and one special character. It is a good habit to update your password frequently to save it from hackers and other unwanted access.
Changing the User Password
To change the password of your user account, run the “passwd” command without any additional argument, as shown below.
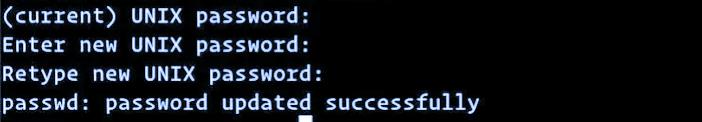
After running the above command, the user is prompted to provide the current password to change the password. If the entered password is correct, enter the new password and confirm it by entering again. You can see that the passwords are not shown on the screen. You will be required to enter the new password whenever you log in again.
Changing the Password for Another User
If you want to change the password for another user, use the root user or the user with sudo access. Here in the later examples, we consider that you are using the user with the sudo access.
If you wish to change the password for another user, you will have to use the “passwd’ command along with the desired username for which you are looking to change the password. Here, we are using the user “dum” to change the password.
After running this command, you will be asked to enter the new password and then confirm it. You will get the output as below without displaying your password on the screen.
Retype new UNIX password:
Once the process is complete, you will get the below output for the successful password change for that user.
Forcefully Changing the User’s Password at the Next Login
By default, the password for any user will not expire. You need to explicitly mention the time and date when the password will be valid for the user. If you want the user to change their password forcefully whenever they log in next time, you can use the “passwd” command along with the “expire” option, as shown below.
It will immediately expire the password of the user “dum”.
So whenever the user logs in with the below command next time, he will get the below message.
After the user sets the new password for its account, the connection will get closed immediately.
Conclusion
Linux is considered the safest OS and provides a safe working environment by setting a password for their accounts. If you are a normal person, then you can only set the password for your working account. For changing the password for another user on the Linux system, you need to have the root privileges or sudo access to do that. Setting and changing passwords for various users will be done by the Linux administrators, managing the accounts for users.
We hope now you understand the role of the “passwd” command and how to successfully change the password for your and other users’ accounts.

