Rename a File with ‘mv’ Command
The most commonly used command in Linux to rename a filename is the ‘mv’ command. The syntax of this command is given below.
Syntax
Using any option with the ‘mv’ command is optional. To rename a file, you must type the original filename after the renamed filename with this command. Various uses of the ‘mv’ command are explained in the next section of this article.
Example 1: Rename a File with ‘mv’ Command without Options
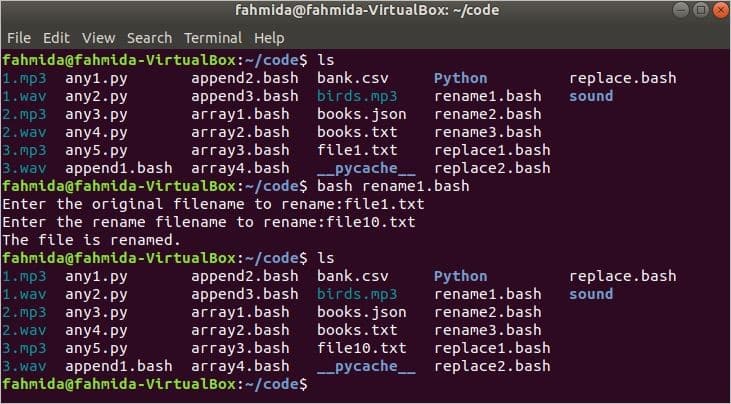
The name of the original file and the name of the renamed file will be taken as the input from the user in the following script. The file will be renamed if the original filename exists. If any file with the renamed filename already exists, then the old file will be overwritten by the content of the newly renamed file.
# Take the original filename
read -p "Enter the original filename to rename:" original
# Take the renamed filename
read -p "Enter the renamed filename to rename:" rename
# Check the original file exists or not
if [ -f $original ]; then
# Rename the file
$(mv $original $rename)
echo "The file is renamed."
fi
Output
Example 2: Rename a File with ‘mv’ Command Using -i option
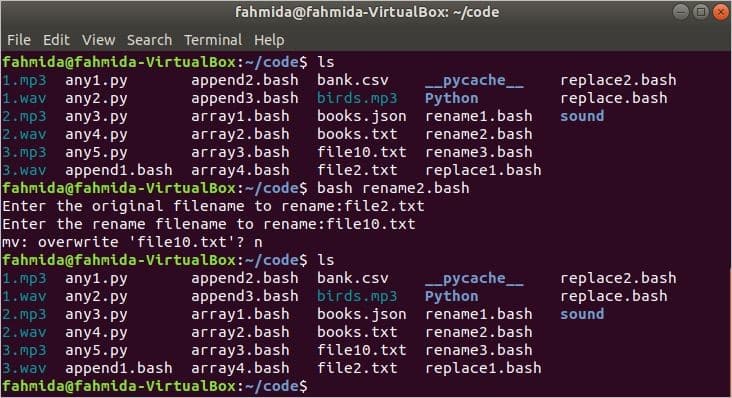
The problem of the above example can be solved by using the ‘-i’ option with the ‘mv’ command. The following script will ask for permission from the user to overwrite before doing the renaming task. If the user press ‘n’ then the rename task will not be done.
# Take the original filename
read -p "Enter the original filename to rename:" original
# Take the renamed filename
read -p "Enter the rename filename to rename:" rename
# Check the original file exists or not
if [ -f $original ]; then
# Check the rename filename exists or not
if [ $(mv -i $original $rename) ]; then
echo "The file is renamed."
fi
fi
Output
Rename a File with ‘rename’ Command
The ‘rename’ method is used for advanced file renaming tasks. Run the following command in the terminal to install the ‘rename’ command.
The syntax of this command is given below.
Syntax
This command can be used with and without options, like the ‘mv‘ command. Multiple files can be renamed at once by using a regular expression. Here, the ‘s’ indicates substitution. If the search text is found, then the files will be renamed by the replacement text.
Example 3: Rename Files that Match with Regular Expression
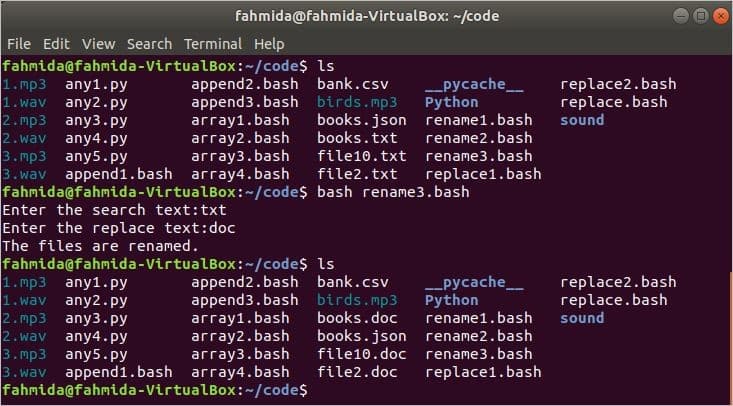
The following script can be used to rename multiple files by using a regular expression pattern that will take the extension of the searched filename and the renamed filename as the inputs. If the current extension matches the search text, then the extension of any file will be renamed by replacing the text.
# Take the search text
read -p "Enter the search text:" search
# Take the replace text
read -p "Enter the replace text:" replace
# Rename all files that match with the pattern
$(rename "s/.$search/.$replace/" *)
echo "The files are renamed."
Output
Conclusion
This article used a number of examples to illustrate the use of the ‘mv’ and ‘rename’ bash commands. Renaming a filename should be easier for bash users after practicing the above examples.