This article presents a detailed guide to remove unused old kernel images from the Debian system.
Remove Unused Old Kernel Images on Debian
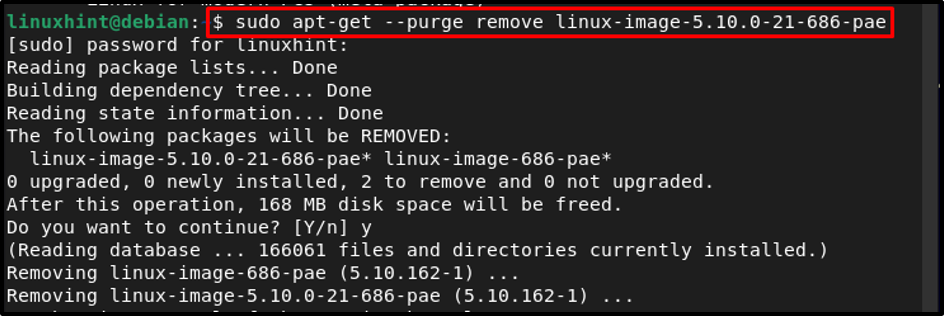
To remove the unused old kernel images on Debian, follow the below-mentioned steps:
Step 1: Checking the Currently Used Kernel
To remove the old kernel, you must be logged into the new kernel, and to verify that, display the kernel you are using by running any the following command:
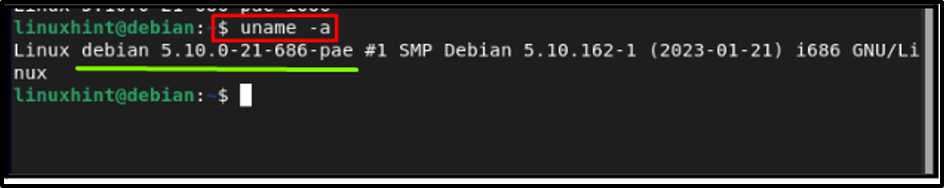
Step 2: Listing all Installed Kernels
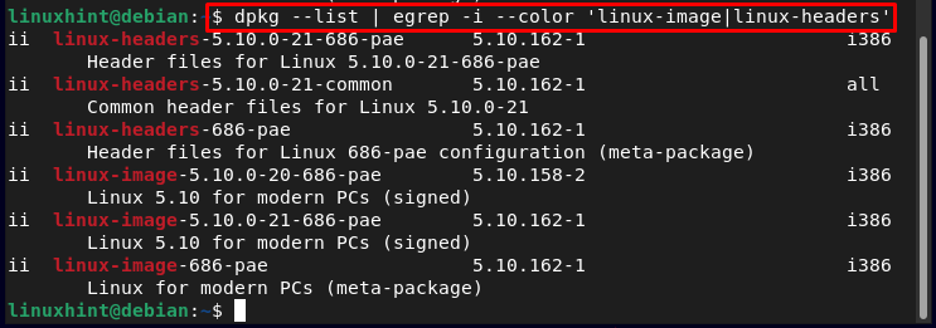
Now to list all the installed kernels, run the below-mentioned command:
In the output, you will get the list of all the kernels, as shown in the image below:
Note: You might find some very old kernel-images in the list, as my system is updated so I only have new 5.10 version kernel images.
Step 3: Removing Unused Kernel Images
Once you have gotten the list of all installed kernel images, now you can remove all the kernel images that you think you don’t need any longer, and for that use the below-written command:
For example:
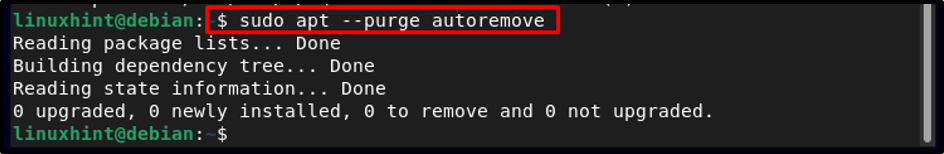
Step 4: Auto Removing
In latest Linux systems, usually the unused packages are marked for un-installation, so to automatically clean the Debian system it’s better to remove the unused kernel images by running the below-written command:
After following all of the above-mentioned steps, your Debian system will have more space on the disk and all the unused packages and kernel images will get removed from the system. You can reboot the system for a fresh start if you want but that is not mandatory.
Conclusion
To remove the old unused kernel images on Debian, firstly list all the installed kernels after which you can remove the old kernel images that are no longer required by running the “apt-get purge remove” command along with the name of the kernel image. Finally, run the auto-remove command to clean the system from unused packages and to free up the space on the system’s disk.