A regular expression (regex) is used to find a given sequence of characters within a file. Symbols such as letters, digits, and special characters can be used to define the pattern. Various tasks can be easily completed by using regex patterns. In this tutorial, we will show you how to use regex patterns with the `awk` command.
The basic characters used in patterns
Many characters can be used to define a regex pattern. The characters most commonly used to define regex patterns are defined below.
| Character | Description |
|---|---|
| . | Match any character without a newline (\n) |
| \ | Quote a new meta-character |
| ^ | Match the beginning of a line |
| $ | Match the end of a line |
| | | Define an alternate |
| () | Define a group |
| [] | Define a character class |
| \w | Match any word |
| \s | Match any white space character |
| \d | Match any digit |
| \b | Match any word boundary |
Create a file
To follow along with this tutorial, create a text file named products.txt. The file should contain four fields: ID, Name, Type, and Price.
ID Name Type Price
p1001 15″Monitor Monitor $100
p1002 A4tech Mouse Mouse $10
p1003 Samsung Printer Printer $50
p1004 HP Scanner Scanner $60
p1005 Logitech Mouse Mouse $15
Example 1: Define a regex pattern using the character class
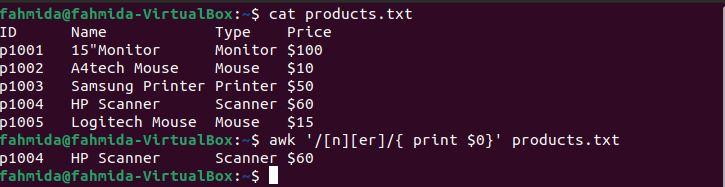
The following `awk` command will search for and print lines containing the character ‘n’ followed by the characters ‘er’.
$ awk '/[n][er]/ {print $0}' products.txt
The following output will be produced after running the above commands. The output shows the line that matches the pattern. Here, only one line matches the pattern.
Example 2: Define a regex pattern using the ‘^’ symbol
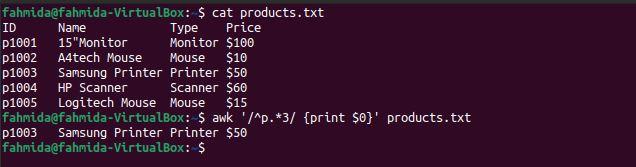
The following `awk` command will search for and print lines that start with the character ‘p’ and include the number 3.
$ awk '/^p.*3/ {print $0}' products.txt
The following output will be produced after running the above commands. Here, there is one line that matches the pattern.
Example 3: Define a regex pattern using the gsub function
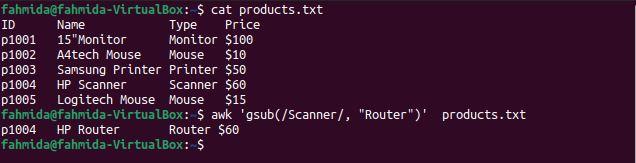
The gsub() function is used to globally search for and replace text. The following `awk` command will search for the word ‘Scanner’ and replace it with the word ‘Router’ before printing the result.
$ awk 'gsub(/Scanner/, "Router")' products.txt
The following output will be produced after running the above commands. There is one line that contains the word ‘Scanner‘, and ‘Scanner‘ is replaced by the word ‘Router‘ before the line is printed.
Example 4: Define a regex pattern with ‘*’
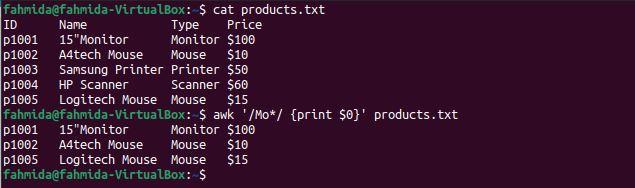
The following `awk` command will search for and print any string that starts with ‘Mo’ and includes any subsequent character.
$ awk '/Mo*/ {print $0}' products.txt
The following output will be produced after running the above commands. Three lines match the pattern: two lines contain the word ‘Mouse‘ and one line contains the word ‘Monitor‘.
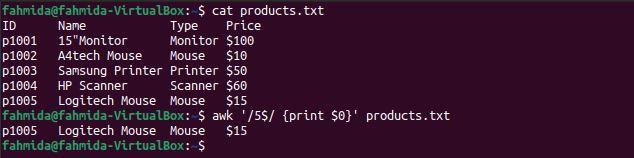
Example 5: Define a regex pattern using the ‘$’ symbol
The following `awk` command will search for and print lines in the file that end with the number 5.
$ awk '/5$/ {print $0}' products.txt
The following output will be produced after running the above commands. There is only one line in the file that ends with the number 5.
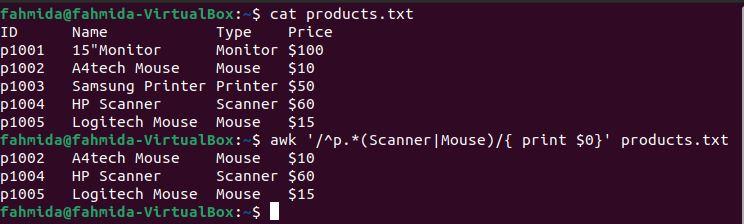
Example 6: Define a regex pattern using the ‘^’ and ‘|’ symbols
The ‘^‘ symbol indicates the start of a line, and the ‘|‘ symbol indicates a logical OR statement. The following `awk` command will search for and print lines that start with the character ‘p‘ and contain either ‘Scanner‘ or ‘Mouse‘.
$ awk '/^p.* (Scanner|Mouse)/' products.txt
The following output will be produced after running the above commands. The output shows that two lines contain the word ‘Mouse‘ and one line contains the word ‘Scanner‘. The three lines start with the character ‘p‘.
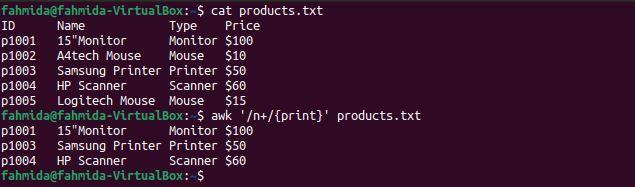
Example 7: Define a regex pattern using the ‘+’ symbol
The ‘+‘ operator is used to find at least one match. The following `awk` command will search for and print lines that contain the character ‘n‘ at least once.
$ awk '/n+/{print}' products.txt
The following output will be produced after running the above commands. Here, the character ‘n‘ contains occurs at least once in the lines that contain the words Monitor, Printer, and Scanner.
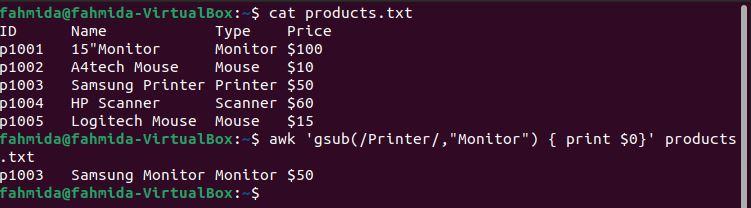
Example 8: Define a regex pattern using the gsub() function
The following `awk` command will globally search for the word ‘Printer‘ and replace it with the word ‘Monitor‘ using the gsub() function.
$ awk 'gsub(/Printer/, “Monitor”) { print$0}' products.txt
The following output will be produced after running the above commands. The fourth line of the file contains the word ‘Printer‘ twice, and in the output, ‘Printer‘ has been replaced by the word ‘Monitor‘.
Conclusion
Many symbols and functions can be used to define regex patterns for different search and replace tasks. Some symbols commonly used in regex patterns are applied in this tutorial with the `awk` command.