Redis uses simple commands to perform operations using the Redis CLI utility. In this tutorial, you will learn how to fetch the keys in Redis databases.
Setting a Key/Value
Before we get to retrieving keys and the values associated with them, let us learn how to create them.
To create a key and its associated value, use the SET command in the Redis CLI followed by the value.
For example:
The “username” acts as a key to the specified value in the example above.
In the example above, we created a key and set an associated value. What if we want to store another username without creating a new key?
To do this, we can use the namespace notation. For example:
SET username:3 "user103"
Getting the Key
To get the value stored in a key, you can use the GET command followed by the name of the key.
For example:
"user101"
The above command tells Redis to fetch the value stored in the specified key.
We can use the GET command followed by the unique value as:
"user103"
Fetching all Keys
Suppose we want to view all the keys stored in the database? To do this, we can use the KEY command followed by a pattern to match.
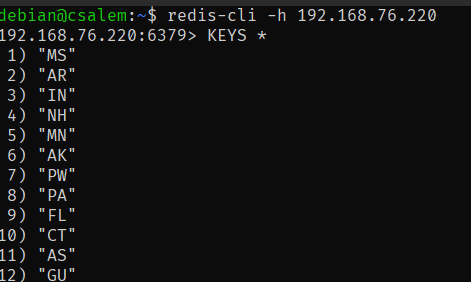
We can pass the pattern as an asterisk to fetch all the keys. For example, consider the following database containing all the states and their code.
To fetch all the keys, we can do:
The resulting value is as shown:
Although fetching all the keys in the data store can be helpful, it is not recommended to run the command in production or on a large dataset.
Conclusion
In this guide, we discussed how to use the GET command in Redis. You can fetch the values stored in a specified key using this command.