Ubuntu is a widespread Linux distribution with many versions available, from stable to development releases. This means that there is an Ubuntu version to suit every user’s needs, whether you are a beginner or a seasoned pro. This is important since you must understand and use the compatible commands with that version.
Checking the Ubuntu version that is currently running on your machine also assists you in quickly finding the root cause of any possible issues.
We will cover every technique that you might employ to locate the latest Ubuntu version in this content.
Ubuntu’s Release Cycle
The cycle for releasing the new versions of Ubuntu is predictable. Ubuntu updates its operating system every six months. The “YY:MM” format is used for all Ubuntu version numbers. For instance, Ubuntu’s most recent release was 23.10 in October 2023.
The team releases an LTS (Long Term Support) version every two years which will continue to receive the upgrades for the following five years. Releases with Long Term Support (LTS), which are sustained for five years, are only permitted in even-numbered years. Interim versions, which receive a nine-month support, are only made available in odd-numbered years.
LTS releases are suggested for use in production systems because they offer more reliability and support over time. Interim releases are recommended for development and testing environments as they provide the latest features and bug fixes.
Prerequisites:
The prerequisites to check the Ubuntu version are:
- A system that runs the Ubuntu OS or an Ubuntu VPS
- A user account that has root or sudo privileges for command execution
- A terminal window to execute the commands
Checking the Ubuntu Version
Both the terminal and the GUI can be used to determine your Ubuntu version.
Method 1: How to Determine the Ubuntu Version Using the Terminal
There are three ways to find out what version of Ubuntu is installed on the machine if you are familiar with the terminal commands and are capable of performing the commands. Let’s examine each of the three methods separately.
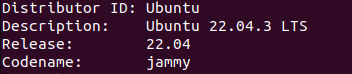
1.1 Using the lsb_release -a Command
The “lsb_release” command lets you view the specifics about your Ubuntu and other Linux distributions. For instance, it displays the details on LSB modules. The version information and the distributor’s ID are also shown.
This command returns all available information if “-a” is included at the end. This approach may be preferred if you need to quickly figure out your Ubuntu version because it is plain and simple.
Launch the Ubuntu terminal first, then use this command:
To view the results, use the “Enter” key. It should appear similar to this.
You can find your Ubuntu version next to the “Description” heading. The codename of your distributor and information on your LSB modules are also displayed.
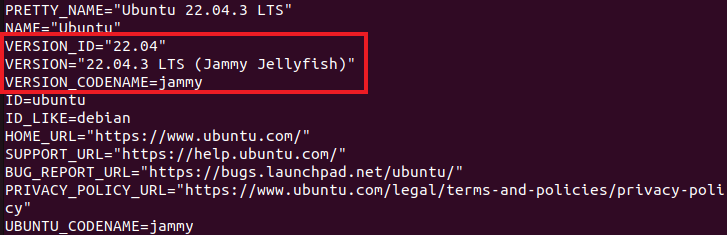
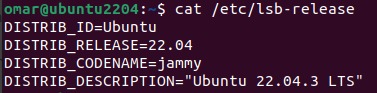
1.2 Using the /etc/lsb-release or /etc/os-release Commands
The “/etc/lsb-release” command displays your Ubuntu version with distinct lines for the version number and description. It is compatible with older systems, so you can use it even if you’re running an old version of Ubuntu.
The same information can also be obtained using the “/etc/os-release” script. Ubuntu 16.04 and later are compatible with this. You must add “cat” before either of them,:
After that, a list of data will appear, including your Ubuntu version number and its release name. There are also a few links to a helpful information on the Ubuntu website.
You can get clearer results, including the release version ID, description, and code using the “/etc/lsb-release” command. The version is displayed without any links or additional information.
1.3 Using the /etc/issue File
This file contains details about your system. It is a simpler method to check your Ubuntu version because it only displays the version number without any additional information about your system.
To check the Ubuntu version in the “/etc/issue” file, launch your Ubuntu terminal and execute the appended command.
Like the previous method, “cat” must be typed before the command.
The numbers preceding LTS indicate your Ubuntu version.
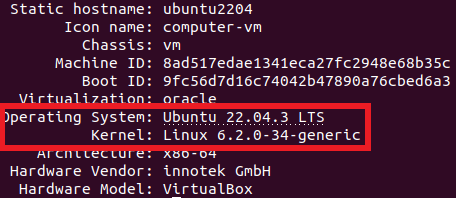
1.4 Using the Hostnamectl Command
Finally, you may check the version of Ubuntu by executing the “hostnamectl” instruction. This is often used to modify or change your system’s hostname. Additionally, it returns the data like your computer’s ID and OS version.
Enter the following command into your terminal:
Once you hit “Enter”, a list of details will appear. This displays the kernel version that is running on your Ubuntu operating system.
Method 2: How to Determine the Ubuntu Version Using the GUI Settings
Your Ubuntu version can also be found in your GUI settings if you’d prefer not to use the command line. This method is a good option if you are new to the OS and its layout, but it may take longer.
First, go to “Show Applications”. It’s the icon at the bottom left of the Ubuntu screen:
After that, select “Settings”. If you still have trouble finding it, try typing “settings” in the search box.
Then, from the left menu, click on the “About” option. To find it, go to the very bottom of the item’s list.
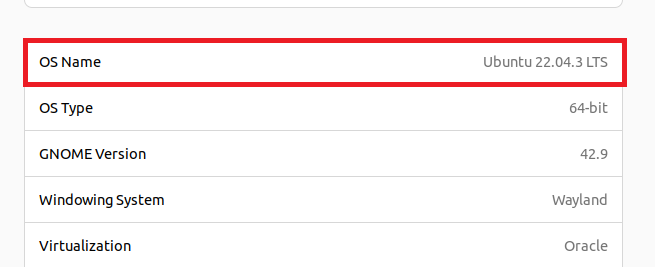
Your Ubuntu version will be displayed here next to the “OS Name” heading.
For instance, our machine is now running the Ubuntu 22.04.
Which Ubuntu Version Should You Use
If you are new to Linux, start with an LTS (Long Term Support) release for stability and long-term support. Use an interim release if you need the latest features or you are using Ubuntu for development or testing.
Here are some additional factors to consider:
- Hardware and software compatibility: Check the Ubuntu hardware and software compatibility lists to ensure that your system and the software that you need are compatible with your chosen version.
- Your needs and requirements: When selecting a version, keep in mind your personal demands and specifications. For example, if you need a stable and reliable release for production use, choose an LTS release. If you need the latest features or you are using Ubuntu for development or testing, choose an interim release.
Conclusion
Ubuntu releases may not be compatible with all of the latest software. Checking your Ubuntu version before installing the new programs is important. We discussed two methods to check your Ubuntu version: command-line and graphical user interface (GUI). Four commands can be used to check the Ubuntu version and some other system information. GUI is also a good option, but it may take longer.