File Access Modes:
It is mentioned before that different types of file access modes can be used in open() method and these are described in this part. Commonly used modes are mentioned below.
| Mode | Purpose |
|---|---|
| t | It indicates a text file and it is the default file type. |
| b | It indicates a binary file. |
| r | It opens the file for reading and it is the default mode for opening any file. |
| w | It opens the file for writing. |
| x | It opens the file for writing if not exists. |
| a | It opens the file for adding content at the end of the file if the file exists, otherwise, create the file and add the content in the beginning. |
| r+ | It opens the file for reading and writing and places the cursor at the beginning of the file. It raises an error if the file does not exist. |
| w+ | It opens the files for reading and writing and overwrites the data if the file already exists. |
| a+ | It opens the file for reading and writing and places the cursor at the end of the file for the existing file. It creates the file if it does not exist. |
Methods:
Many methods exist in Python to read or write the file. The most commonly used methods are mentioned here.
This method contains two arguments. The first argument is mandatory that is used to take the filename for reading or writing. The second argument is optional that is used to set the file access mode. Te default file access mode is ‘rt’. The return type of this method is a file object that is used for reading and writing the file.
Syntax:
close():
This method is used to close the file and make it available for another purpose. After calling this method, the file handler object will be unusable.
This method is used to read a specific amount of bytes from a file using a file object.
This method is used to read a particular line from a file using a file object.
This method is used to read all lines of a file separated by comma(,) using file object.
This method is used to write content into a file using a file object.
Reading Text File:
Create a text file named ‘countryList.txt’ with the following content to use it in the next part of the article.
Bahamas
Belgium
Cuba
Finland
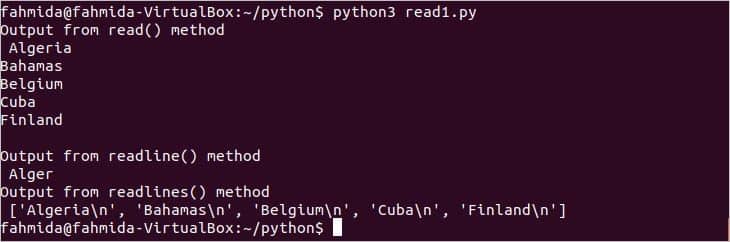
Example 1: Reading file using read(), readline() and readlines()
Create a file named read1.py with the following python script. It will read the file based on the byte size using read(), read the fixed number of characters from a file using readline() and read all lines of a file in an array using readlines().
FileHandler = open("countryList.txt","r")
# Read file content based on size
print('Output from read() method\n',FileHandler.read(2048))
# Close the file
FileHandler.close()
# Open file for reading and writing
FileHandler = open("countryList.txt","r+")
# Read the file content of third line
print('Output from readline() method\n',FileHandler.readline(5))
# Close the file
FileHandler.close()
# Open file for reading and appending
FileHandler = open("countryList.txt","r")
# Read all content of the file
print('Output from readlines() method\n',FileHandler.readlines())
# Close the file
FileHandler.close()
Output:
The following output will appear after running the script.
Example 2: Reading file line by line using a loop
Create a file named read2.py with the following script. It will read and print each line of the file from fileObject using for loop.
fileObject = open("countryList.txt", "r")
# Read a file line by line and print in the terminal
for line in fileObject:
print(line)
Output:
The following output will appear after running the script.
Example 3: Reading file by using with the statement
Create a file named read3.py with the following script. It will read the file without any file object by using the statement.
with open("countryList.txt") as fhandler:
print(fhandler.readlines())
Output:
The following output will appear after running the script.
Writing Text File:
The content can be written in a file by defining the file object or by using with the statement.
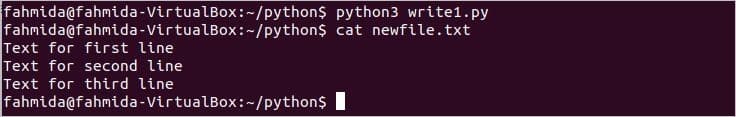
Example 4: Writing to a file using file object
Create a file named write1.py with the following script. It will open a text file for writing and write three lines using write() method.
fileObject = open("newfile.txt", "w")
# Add some text
fileObject.write("Text for first line\n")
fileObject.write("Text for second line\n")
fileObject.write("Text for third line\n")
# Close the file
fileObject.close()
Output:
Run the script and check the file is created with the content or not. The following output will appear after running the script and running the ‘cat’ command.
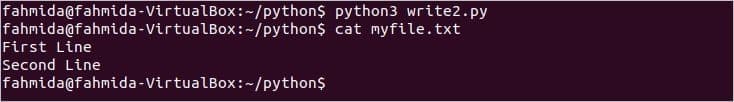
Example 5: Writing to a file using with the statement
The content can be written to a file without defining file object. Create a file named write2.py with the following script. It will write two lines in to file by using with statement.
with open("myfile.txt",'w') as fileObj:
fileObj.write("First Line\n")
fileObj.write("Second Line\n")
Output:
The following output will appear after running the script and ‘cat’ command to read the file.
Conclusion:
Mostly used methods to read content from a file and write content to a file in python are described in this tutorial by using very simple examples. The new python users will be able to know the uses of necessary functions for reading or writing files.ch
Watch Author’s Video: here