Syntax:
or
- The first argument of the strptime() function is mandatory and takes any DateTime value or the time value.
- The second argument of the strptime() function is optional that takes the format string to read the first argument.
- It returns the struct_time by gmtime() or localtime().
Different types of directives can be used in the strptime() function to define the format string. Some of them are mentioned below.
| Directive | Purpose |
| %d | It is used to get the day of the month (01 to 31). |
| %m | It is used to get the month in number (01 to 12). |
| %y | It is used to get the year of two digits (00 to 99). |
| %Y | It is used to get the year of four digits. (0000 to 9999) |
| %H | It is used to get the hour of the 24-hour clock (00 to 23) |
| %M | It is used to get the minute. |
| %S | It is used to get the second. |
| %w | It is used to get the day of the week in number where Sunday=0. |
| %D | It is used to get the date as %m/%d/%y. |
| %T | It is used to get the time as %H:%M:%S. |
| %B | It is used to get the full month name. |
| %A | It is used to get the full weekday name. |
Example-1: Use of the strptime() Function with the DateTime Module
Create a Python file with the following script where the DateTime module has been used to print the formatted date, time, and both the date and time values.
from datetime import datetime
#Set the datetime value
dt = "22/04/22 06:40:30"
#Set the formatting for the datetime value
format = "%d/%m/%y %H:%M:%S"
'''
Format the datetime value using
strptime() function
'''
date = datetime.strptime(dt, format)
#Print the date and time
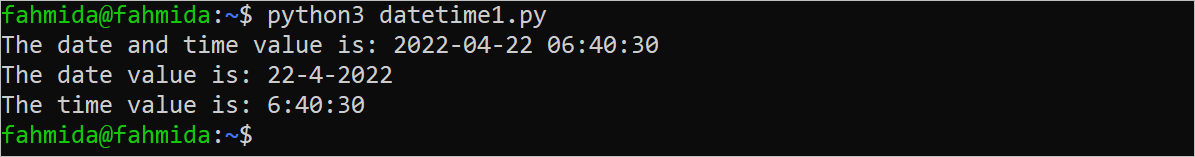
print("The date and time value is:", date)
#Print the date
print("The date value is: %s-%s-%s" %(date.day,date.month,date.year))
#Print the time
print("The time value is: %s:%s:%s" %(date.hour,date.minute,date.second))
Output:
The following output will appear after executing the above script.
Example-2: Use of the strptime() Function with Time Module
Create a Python file with the following script where the time module has been used to print the formatted date and time value, and each part of the date and time separately.
import time
#Assign a date and time value
dt = '12-16-2022 13:25:45'
#Print the assigned value
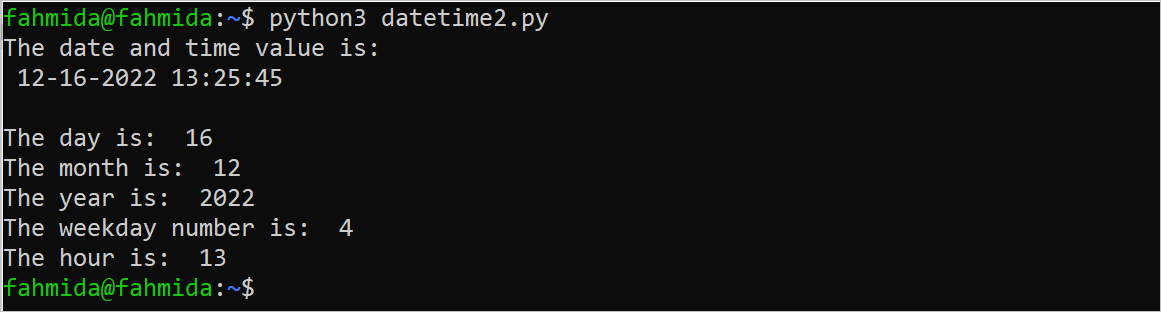
print("The date and time value is:\n", dt)
#Convert the string value using strptime() function
value = time.strptime(dt, '%m-%d-%Y %H:%M:%S')
#Print day of the date
print("\nThe day is: ", value.tm_mday)
#Print month value of the date
print("The month is: ", value.tm_mon)
#Print Year value of the date
print("The year is: ", value.tm_year)
#Print weekday value of the date
print("The weekday number is: ", value.tm_wday)
#Print hour value from the datetime value
print("The hour is: ", value.tm_hour)
Output:
The following output will appear after executing the above script.
Example-3: Convert a List of Date Values Using DateTime
Create a Python file with the following script where the time module has been used to print the formatted date and time value, and each part of the date and time separately. Here, the ‘if’ condition has been used to add the leading zero for the one-digit day or month value.
from datetime import datetime
#Declare a string of dates
date_list = ['04-05-2022', '17-05-2022', '21-05-2022']
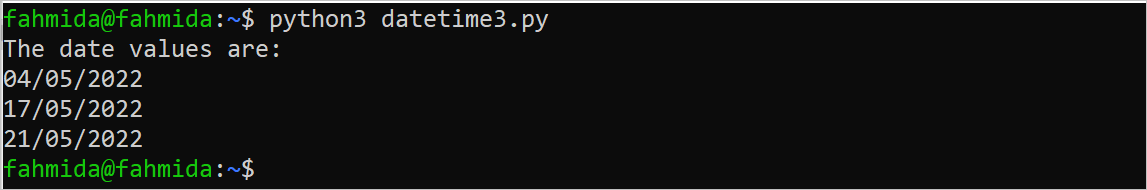
print("The date values are:");
for value in date_list:
#Convert the string data into datetime format
dateValue = datetime.strptime(value, '%d-%m-%Y').date()
#Add leading zero with the day if the day value is one digit
if dateValue.day < 10:
d_day = '0' + str(dateValue.day)
else:
d_day = dateValue.day
#Add leading zero with the month if the month value is one digit
if dateValue.month < 10:
d_month = '0' + str(dateValue.month)
else:
d_month = dateValue.month
#Print the formatted date value of the list
print("%s/%s/%s" %(d_day, d_month, dateValue.year))
Output:
The following output will appear after executing the above script. Each element of the list has been printed after formatting.
Example-4: Convert the String Value into the Date and Time Object
Create a Python file with the following script where the DateTime module has been used to convert the date value in string into the date object and the time value in string into the time object. Next, the type of the converted object and the formatted date and time values will be printed. The date() function has been used to convert the date string value into the date object. The time() function has been used to convert the time string value into the time object.
from datetime import datetime
#Set a string value of date
dateVal = '25-04-22'
#Convert the string into date object
d_obj = datetime.strptime(dateVal, '%d-%m-%y').date()
#Print the object type
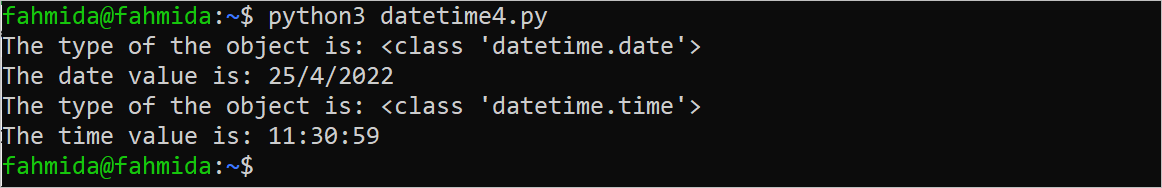
print("The type of the object is:", type(d_obj))
#Print the formatted date value
print("The date value is: %s/%s/%s" %(d_obj.day, d_obj.month, d_obj.year))
#Set a string value of time
timeVal = '11:30:59'
#Convert the string into time object
t_obj = datetime.strptime(timeVal, '%H:%M:%S').time()
#Print the object type
print("The type of the object is:", type(t_obj))
#Print the formatted time value
print("The time value is: %s:%s:%s" %(t_obj.hour, t_obj.minute, t_obj.second))
Output:
The following output will appear after executing the above script.
Conclusion
Different ways of using strptime() function by importing DateTime module and time module has been shown in this tutorial by using multiple examples. The Python users can use any of the modules to work with the date and time-related tasks.