In this post, we will explore the “Python os.mkdir()” method using numerous examples. Let’s start with the below-listed content:
- What is Python os.mkdir() Method?
- Using os.mkdir() to Create a Single Directory.
- Using os.mkdir() to Create Multiple Directories.
- Using os.mkdir() to Create Nested Directories.
- Using os.mkdir() to Handle Errors.
What is the “Python os.mkdir()” Method?
The “os.mkdir()” method is utilized to create a new directory at the specified path. The method returns an error if the directory/folder already exists.
Syntax
In the above syntax:
- The “path” parameter specifies the path of the directory where it needs to be created.
- The optional parameter “mode” indicates the mode of the directory to be created/generated. (Default value is “0o777”).
- “dir_fd” serves as a file descriptor specifically for the directory. (Default value is “None”).
Example 1: Utilizing the “os.mkdir()” Method to Create a Single Directory
This example is used to create a single directory at a specified location using the “os.mkdir()” method:
os.mkdir(r'C:\Users\p\Documents\program\new_directory')
print('New Directory Successfully Created!')
In the above code, apply the “os.mkdir()” to create a new directory by specifying the complete path along with the name of the directory, respectively, and print the stated success message.
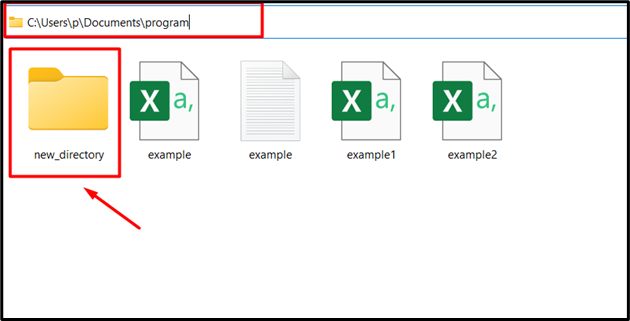
Output
In the above output, it can be analyzed that the directory named “new_directory” has been created successfully.
Example 2: Utilizing the “os.mkdir()” Method to Create Multiple Directories
In this example, the discussed method can be applied to create multiple directories instead:
location = r'C:\Users\p\Documents\program'
directories = ['directory1', 'directory2', 'directory3']
for directory in directories:
os.mkdir(os.path.join(location, directory))
In the above code:
- The path of the directory is assigned to the variable “location”.
- The name of the multiple directories is initialized in a list named “directories”.
- Lastly, the “for” loop iterates over the list of directories and creates all the multiple directories in the list using the combined “os.mkdir()” and “os.path.join()” methods.
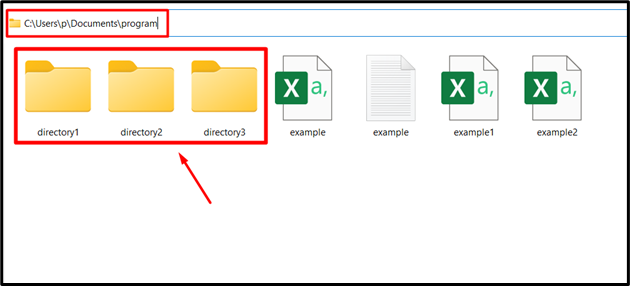
Output
The above output shows that multiple directories have been created successfully.
Example 3: Utilizing the “os.mkdir()” Method to Create Nested Directories
This example applies the discussed method to create nested directories:
os.mkdir(r'C:\Users\p\Documents\program\directory1\new_directory')
In the above code block, the “os.mkdir()” method creates a nested directory by specifying the absolute path along with the “main” and the “nested” directory names, respectively.
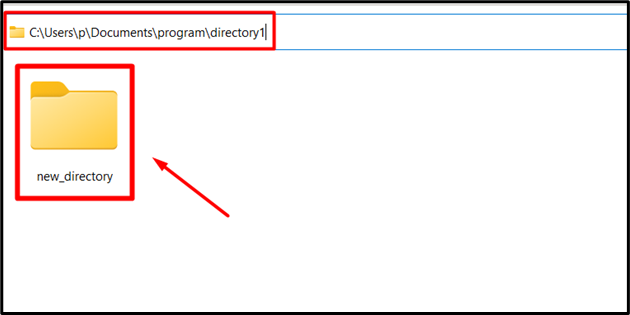
Output
In the above output, the nested directory “new_directory” has been created inside the directory named “directory1” accordingly.
Example 4: Utilizing the “os.mkdir()” Method to Handle Errors
In this particular example, the discussed method can return an error if the directory already exists at the specified path. To handle this error, the “try-except” block is used in the program by using this example code:
try:
os.mkdir(r'C:\Users\p\Documents\program\directory1')
except FileExistsError:
print("Directory Already Exists")
In the above code snippet:
- Likewise, the directory is created using the “os.mkdir()” method in the “try” block.
- The “except” block code is used to handle the probable error and display an exception message that indicates that the directory already exists at the specified path.
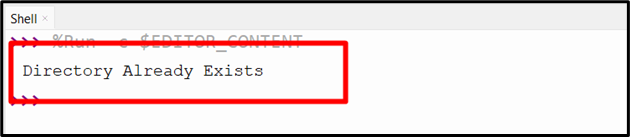
Output
The above snippet indicates that the directory i.e., “directory1” already exists at the specified path.
Conclusion
The “os.mkdir()” method of the “os” module is used to create single, multiple, and nested directories in Python. This method takes the absolute path along with the directory name as an argument and creates a new directory. The “for” loop can be combined with the “os.mkdir()” method to create multiple directories and the “try-except” block to handle the limitations while creating a directory. This post presented an in-depth guide on the Python “os.mkdir()” method with appropriate examples.