In this guide, we will mainly focus on reading/loading the parquet file into the PySpark DataFrame/SQL using the read.parquet() function which is available in the pyspark.sql.DataFrameReader class.
Topic of Contents:
Read the Parquet File to the PySpark DataFrame
Read the Parquet File to the PySpark SQL
This function is used to read the parquet file and load it into the PySpark DataFrame. It takes the path/file name of the parquet file. We can simply use the read.parquet() function since this is the generic function.
Syntax:
Let’s see the syntax of read.parquet():
First, install the PySpark module using the pip command:
Get the Parquet File
To read a parquet file, you need the data in which the parquet file is generated from that data. In this part, we will see how to generate a parquet file from the PySpark DataFrame.
Let’s create a PySpark DataFrame with 5 records and write this to the “industry_parquet” parquet file.
from pyspark.sql import SparkSession,Row
linuxhint_spark_app = SparkSession.builder.appName('Linux Hint').getOrCreate()
# create the dataframe that store Industry details
industry_df = linuxhint_spark_app.createDataFrame([Row(Type='Agriculture',Area='USA',
Rating='Hot',Total_employees=100),
Row(Type='Agriculture',Area='India',Rating='Hot',Total_employees=200),
Row(Type='Development',Area='USA',Rating='Warm',Total_employees=100),
Row(Type='Education',Area='USA',Rating='Cool',Total_employees=400),
Row(Type='Education',Area='USA',Rating='Warm',Total_employees=20)
])
# Actual DataFrame
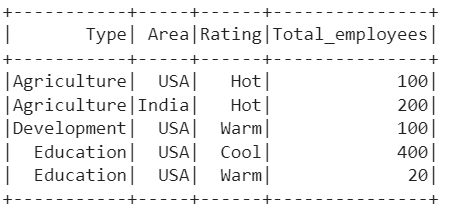
industry_df.show()
# Write the industry_df to the parquet file
industry_df.coalesce(1).write.parquet("industry_parquet")
Output:
This is the DataFrame that holds 5 records.
A parquet file is created for the previous DataFrame. Here, our file name with an extension is “part-00000-ff70f69d-f1fb-4450-b4b4-dfd5a8d6c7ad-c000.snappy.parquet”. We use this file in the entire tutorial.
Read the Parquet File to the PySpark DataFrame
We have the parquet file. Let’s read this file using the read.parquet() function and load it into the PySpark DataFrame.
from pyspark.sql import SparkSession,Row
linuxhint_spark_app = SparkSession.builder.appName('Linux Hint').getOrCreate()
# Read the parquet file into dataframe_from_parquet object.
dataframe_from_parquet=linuxhint_spark_app.read.parquet("part-00000-ff70f69d-f1fb-4450-b4b4-dfd5a8d6c7ad-c000.snappy.parquet")
# Display the dataframe_from_parquet-DataFrame
dataframe_from_parquet.show()
Output:
We display the DataFrame using the show() method which was created from the parquet file.
SQL Queries with Parquet File
After loading into the DataFrame, it can be possible to create the SQL tables and display the data that is present in the DataFrame. We need to create a TEMPORARY VIEW and use the SQL commands to return the records from the DataFrame which is created from the parquet file.
Example 1:
Create a temporary view named “Sectors” and use the SELECT command to display the records in the DataFrame. You can refer to this tutorial that explains how to create a VIEW in Spark – SQL.
from pyspark.sql import SparkSession,Row
linuxhint_spark_app = SparkSession.builder.appName('Linux Hint').getOrCreate()
# Read the parquet file into dataframe_from_parquet object.
dataframe_from_parquet=linuxhint_spark_app.read.parquet("part-00000-ff70f69d-f1fb-4450-b4b4-dfd5a8d6c7ad-c000.snappy.parquet")
# Create View from the above parquet file named - "Sectors"
dataframe_from_parquet.createOrReplaceTempView("Sectors")
# Query to display all records from the Sectors
linuxhint_spark_app.sql("select * from Sectors").show()
Output:
Example 2:
Using the previous VIEW, write the SQL query:
- To display all records from the Sectors that belong to “India”.
- To display all records from the Sectors with an employee that is greater than 100.
linuxhint_spark_app.sql("select * from Sectors where Area='India'").show()
# Query to display all records from the Sectors with employee greater than 100
linuxhint_spark_app.sql("select * from Sectors where Total_employees>100").show()
Output:
There is only one record with area which is “India” and two records with employees that is greater than 100.
Read the Parquet File to the PySpark SQL
First, we need to create a VIEW using the CREATE command. Using the “path” keyword within the SQL query, we can read the parquet file to the Spark SQL. After the path, we need to specify the filename/location of the file.
Syntax:
Example 1:
Create a temporary view named “Sector2” and read the parquet file into it. Using the sql() function, write the select query to display all records that are present in the view.
from pyspark.sql import SparkSession,Row
linuxhint_spark_app = SparkSession.builder.appName('Linux Hint').getOrCreate()
# Read the parquet file into Spark- SQL
linuxhint_spark_app.sql("CREATE TEMPORARY VIEW Sector2 USING parquet OPTIONS (path "part-00000-ff70f69d-f1fb-4450-b4b4-dfd5a8d6c7ad-c000.snappy.parquet")")
# Query to display all records from the Sector2
linuxhint_spark_app.sql("select * from Sector2").show()
Output:
Example 2:
Use the previous VIEW and write the query to display all records with the rating of “Hot” or “Cool”.
linuxhint_spark_app.sql("select * from Sector2 where Rating='Hot' OR Rating='Cool'").show()
Output:
There are three records with the rating of “Hot” or “Cool”.
Conclusion
In PySpark, the write.parquet() function writes the DataFrame to the parquet file. The read.parquet() function reads the parquet file to the PySpark DataFrame or any other DataSource. We learned how to read the parquet file into the PySpark DataFrame and into the PySpark table. As part of this tutorial, we also discussed how to create the tables from the PySpark DataFrame and filter the data using the WHERE clause.