Pyspark.sql.functions.create_map()
The create_map() is available in the “pyspark.sql.functions” module. It is imported from this module. Basically, the create_map() function creates the Key:Value pair by taking two DataFrame columns as parameters. The first column values are converted as keys and the second column values are converted as values in the map.
Syntax:
We use the select() method to display the map column.
Example 1:
Create a PySpark DataFrame named “employee_df” with 5 rows and 4 columns. Here, the columns are [Employee_name, Employee_branch, state, country].
from pyspark.sql.functions import create_map
from pyspark.sql import SparkSession,Row
linuxhint_spark_app = SparkSession.builder.appName('Linux Hint').getOrCreate()
# create the dataframe with 5 employee details
employee_df = linuxhint_spark_app.createDataFrame([Row(Employee_name='Sravan Kumar',Employee_branch='IT',state='Florida',country='USA'),
Row(Employee_name='Chandrika',Employee_branch='Business',state='Delhi',country='India'),
Row(Employee_name='jaya sree',Employee_branch='Management',state='Dallas',country='USA'),
Row(Employee_name='Seema Rani',Employee_branch='IT',state='Italy',country='UK'),
Row(Employee_name='Deepika singh',Employee_branch='Management',state='Maharashtra',country='India')])
# Actual DataFrame
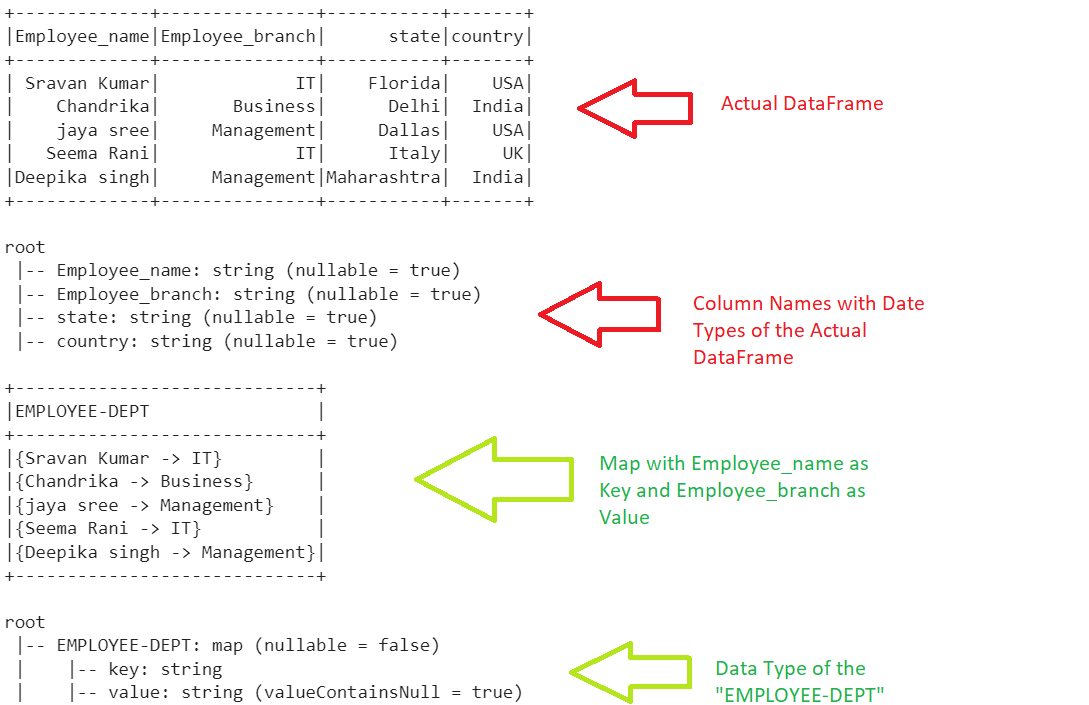
employee_df.show()
# Display the Schema
employee_df.printSchema()
# Map Employee_name and Employee_branch
mapped_data_employee = employee_df.select(create_map(employee_df.Employee_name,employee_df.Employee_branch)
.alias("EMPLOYEE-DEPT"))
# Display the mapped DataFrame
mapped_data_employee.show(truncate=False)
# Display the Schema
mapped_data_employee.printSchema()
Output:
Here, we are mapping the Employee_name and Employee_branch columns. The Employee_name acts as key and the Employee_branch acts as value in the created map. The mapped column name is “EMPLOYEE-DEPT”. the data type of this column is a map.
Example 2:
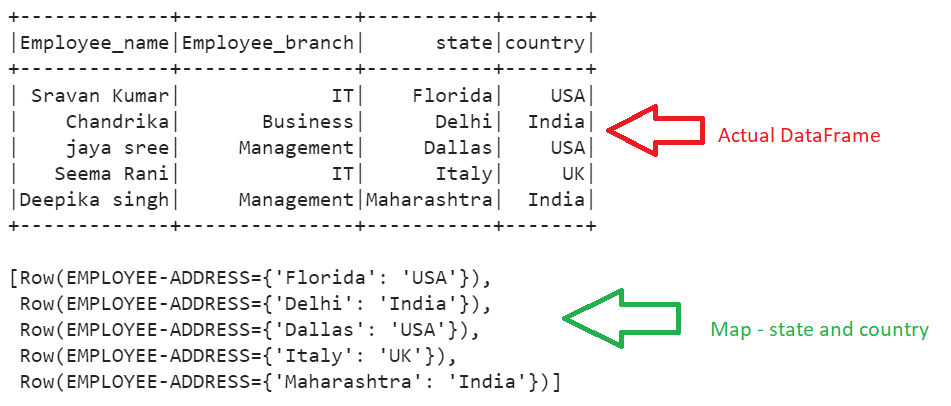
Let’s create a map from the state and country columns and display the map using the collect() function.
from pyspark.sql.functions import create_map
from pyspark.sql import SparkSession,Row
linuxhint_spark_app = SparkSession.builder.appName('Linux Hint').getOrCreate()
# create the dataframe with 5 employee details
employee_df = linuxhint_spark_app.createDataFrame([Row(Employee_name='Sravan Kumar',Employee_branch='IT',state='Florida',country='USA'),
Row(Employee_name='Chandrika',Employee_branch='Business',state='Delhi',country='India'),
Row(Employee_name='jaya sree',Employee_branch='Management',state='Dallas',country='USA'),
Row(Employee_name='Seema Rani',Employee_branch='IT',state='Italy',country='UK'),
Row(Employee_name='Deepika singh',Employee_branch='Management',state='Maharashtra',country='India')])
# Actual DataFrame
employee_df.show()
# Map state and country
mapped_data_employee = employee_df.select(create_map(employee_df.state,employee_df.country).alias("EMPLOYEE-ADDRESS"))
# Display the mapped DataFrame
mapped_data_employee.collect()
Output:
Example 3:
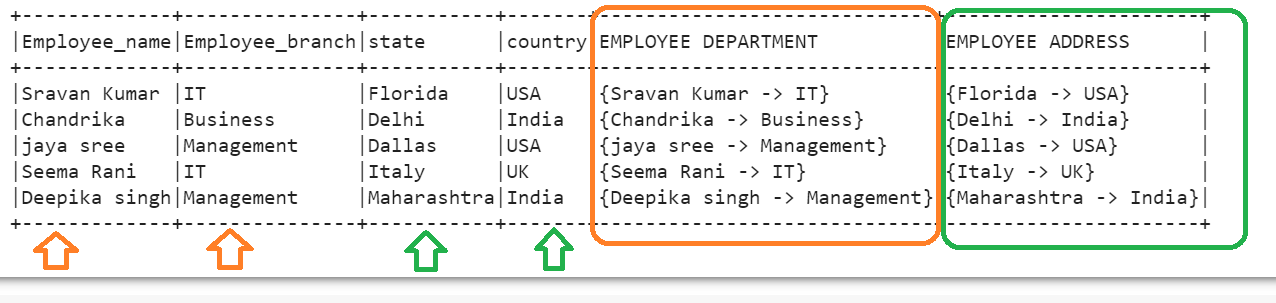
Until now, we just displayed the map column. Now, we add this map column to the existing DataFrame. To achieve this, pass the create_map() function inside the withColumn() function. Basically, this function is used to create new column/s in the existing DataFrame. Let’s add the map columns – “EMPLOYEE DEPARTMENT” (created from the Employee_name and Employee_branch columns) and “EMPLOYEE ADDRESS” (created from the state and country columns).
import pyspark
from pyspark.sql.functions import create_map
from pyspark.sql import SparkSession,Row
linuxhint_spark_app = SparkSession.builder.appName('Linux Hint').getOrCreate()
# create the dataframe with 5 employee details
employee_df = linuxhint_spark_app.createDataFrame([Row(Employee_name='Sravan Kumar',Employee_branch='IT',state='Florida',country='USA'),
Row(Employee_name='Chandrika',Employee_branch='Business',state='Delhi',country='India'),
Row(Employee_name='jaya sree',Employee_branch='Management',state='Dallas',country='USA'),
Row(Employee_name='Seema Rani',Employee_branch='IT',state='Italy',country='UK'),
Row(Employee_name='Deepika singh',Employee_branch='Management',state='Maharashtra',country='India')])
# Map Employee_name,Employee_branch as one column and state,country as another column
employee_df=employee_df.withColumn("EMPLOYEE DEPARTMENT",create_map(employee_df.Employee_name,employee_df.Employee_branch)).withColumn
("EMPLOYEE ADDRESS",create_map(employee_df.state,employee_df.country))
# Display the mapped DataFrame
employee_df.show(truncate=False)
Output:
Example 4:
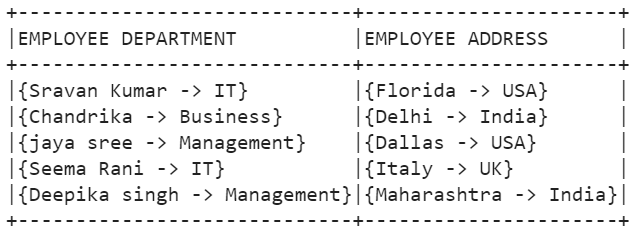
Let’s drop the existing columns and include only the mapped columns. To do this, we can use the drop() funcion which removes the specified columns from the [Employee_name, Employee_branch, state, country] DataFrame.
import pyspark
from pyspark.sql.functions import create_map
from pyspark.sql import SparkSession,Row
linuxhint_spark_app = SparkSession.builder.appName('Linux Hint').getOrCreate()
# create the dataframe with 5 employee details
employee_df = linuxhint_spark_app.createDataFrame([Row(Employee_name='Sravan Kumar',Employee_branch='IT',state='Florida',country='USA'),
Row(Employee_name='Chandrika',Employee_branch='Business',state='Delhi',country='India'),
Row(Employee_name='jaya sree',Employee_branch='Management',state='Dallas',country='USA'),
Row(Employee_name='Seema Rani',Employee_branch='IT',state='Italy',country='UK'),
Row(Employee_name='Deepika singh',Employee_branch='Management',state='Maharashtra',country='India')])
# Map Employee_name,Employee_branch as one column and state,country as another column and drop the actual columns.
employee_df=employee_df.withColumn("EMPLOYEE DEPARTMENT",create_map(employee_df.Employee_name,employee_df.Employee_branch)).withColumn
("EMPLOYEE ADDRESS",create_map(employee_df.state,employee_df.country)).drop('Employee_name',
'Employee_branch','state','country')
# Display the mapped DataFrame
employee_df.show(truncate=False)
Output:
Conclusion
If you want to transform your PySpark DataFrame into a map, you can use this function. The create_map() function in PySpark converts the DataFrame columns into a map. In this guide, we learned the different examples on how to convert two columns into a map. You can utilize the withColumn() function to store the mapped column into the existing DataFrame. The collect() function displays the map in the Key:Value format whereas the show() function displays the Key -> Value format.