This guide will discuss the procedure for pushing a new Git local branch to a Git remote repository and tracking it.
Push a New Local Branch to a Remote Git Repository and Track it too?
For pushing a new Git local branch to a Git remote repository and tracking it, first, move to the desired Git repository and clone the remote repository. Create a new local branch and immediately switch to it. Lastly, run the “$ git push origin <branch-name>” command to push the newly created branch to the remote Git repository and track it on the hosting server.
Now, move ahead and perform the above-stated scenario!
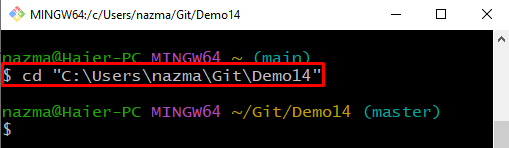
Step 1: Move to Git Directory
First, move to the desired Git local repository by executing the “cd” command:
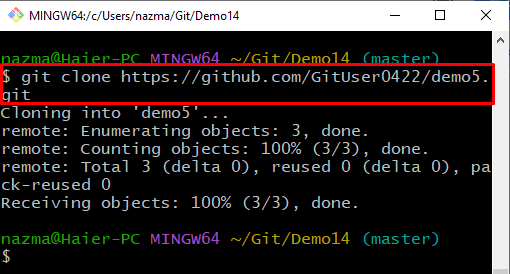
Step 2: Clone Repository
Next, clone the Git remote repository by executing the following command and specifying its URL:
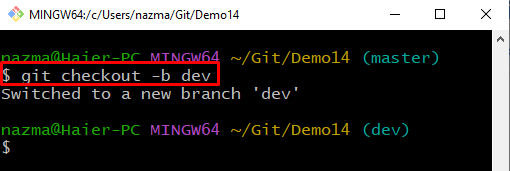
Step 3: Create and Switch Branch
Next, create and immediately switch to the local branch by executing the “git checkout” command with the “-b” option:
The above command will create a branch named “dev” and immediately switch to it:
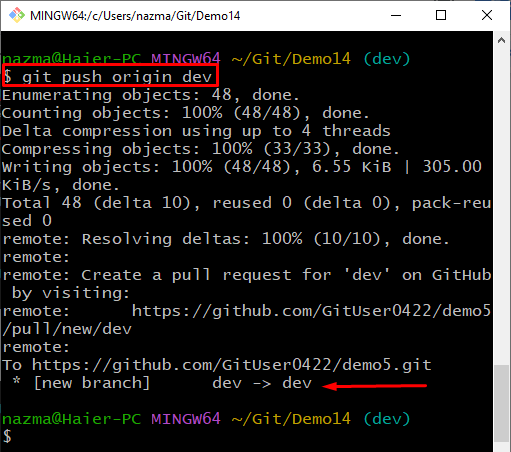
Step 4: Push Local Branch
Lastly, run the “git push origin” command with the branch name to push the newly created local branch to the remote repository:
According to the below-provided output, the newly created “dev” local branch is pushed successfully:
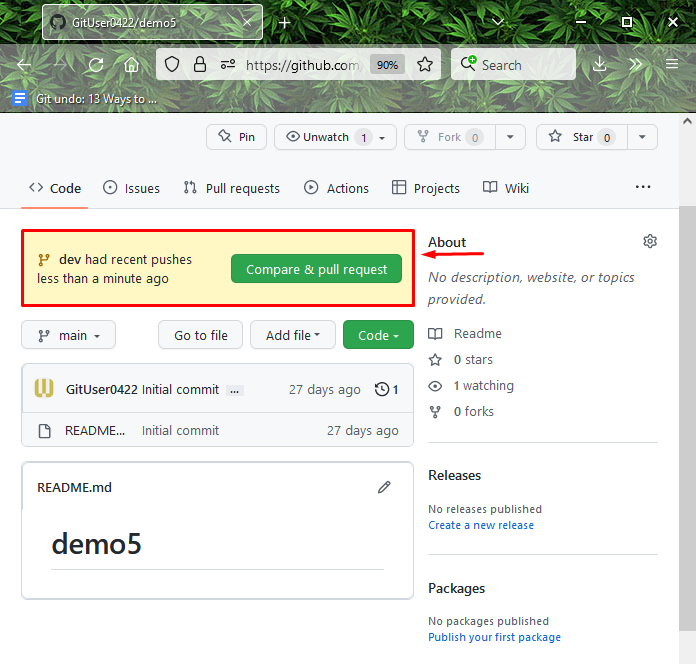
You can also verify if the newly Git local pushed branch is tracked on GitHub:
We have demonstrated the method to push a new local branch to a remote Git repository and track it.
Conclusion
For pushing a new Git local branch to a Git remote repository and tracking it, first, navigate to the desired Git repository and clone the remote repository. Next, create a local branch and immediately switch to the new branch by executing the “$ git checkout -b <branch-name>” command. Lastly, run the “$ git push origin <branch-name>” command to push the newly created branch to the remote Git repository and track it on the hosting server. This guide explained the procedure for pushing a Git branch to Git remote repository and tracking it.