In this post, we have explained the working and usage of the Invoke-Command.
How Does the Invoke-Command Work?
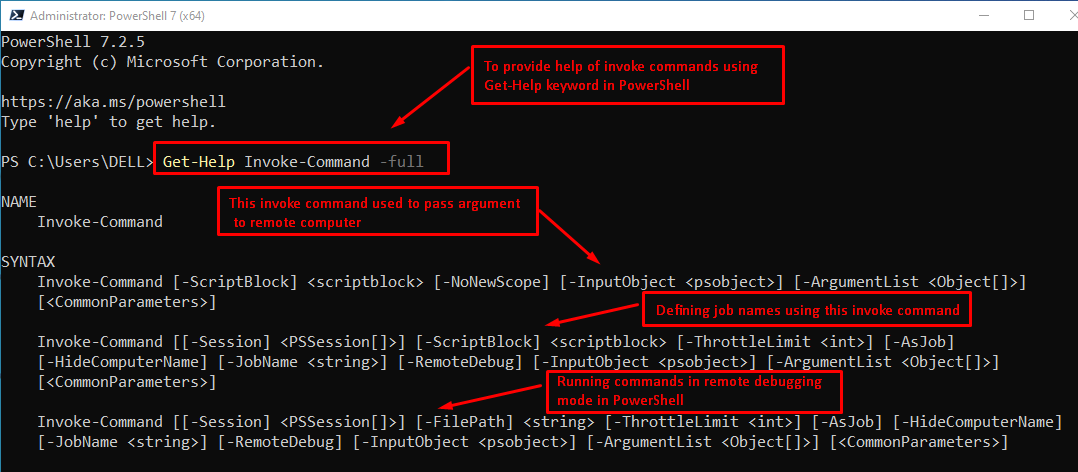
The Invoke-Command enables the user to use a variety of commands according to their needs. For a better overview, the following command will list down all the possible usages of the Invoke-Command cmdlet:
After executing the above code, it will provide a list of parameters and their syntax.
Each syntax has its own purpose according to its situation or requirements. The screenshot of a piece of syntax code is as follows.
In PowerShell, different parameters influence the working of the commands. The most common and popular parameters are described in the following table:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| ArgumentList: | ArgumentList: For passing the variables to the remote command. |
| Application Name: | To specify the application name for Connection URI. Users can use this parameter only if they do not use the Connection URI. |
| Authentication: | To define a procedure to authenticate the remote computers. This service is available only on Windows Server 2008, Windows, and Vista. |
| Computer Name: | To specify the computer’s name where the user runs the script. If the user does not specify the computer name. |
| ConnectionURI | The command represents the connection of URI. |
| HideComputerName | It omits the computer’s name from the display. |
| InputObject | To describe the input object in PowerShell. |
| JobName | It specifies that the user should write the name of the job. |
| ThrottleLimit: | To describe the number of concurrent connections established, the condition is only applied to the current command. |
In PowerShell, there are some examples of how to use the invoke commands for different purposes.
How to Use PowerShell Invoke-Command
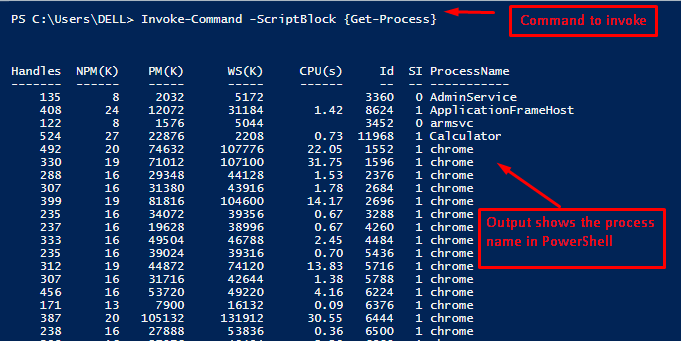
In PowerShell, the Invoke-Command executes the script on local and remote machines. To get the process information of the local machine, the following Invoke-Command is used:
The above display shows the list of processes currently being executed on the local machine.
Using the Invoke-Command to Access the Host Version
Here is an example of how to get the updated host version of a local machine. The command to get this information in PowerShell is provided below:
The output in PowerShell gives information about the host version by using the above command.
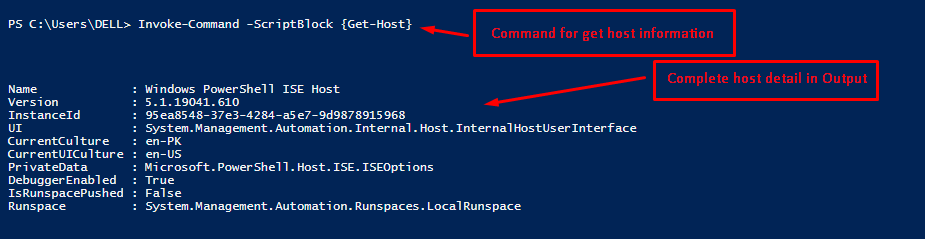
Using the Invoke-Command to Access the Host Information
The Invoke-Command is used to get the complete information about the host in PowerShell. In our case, the command below will print all the host details:
The output represents the host’s complete details, including the name, version, and user interface, and some additional information.
Using Invoke-Command to Access the Cultural Information
One of the examples in PowerShell is getting the specific cultural information of the host. For this purpose, the Invoke-Command cmdlet can be used as shown below:
Code
The above script provides the cultural information of the host in PowerShell.
Output
The display shows that using the Invoke-Command, users can get the cultural information in PowerShell.
Conclusion
The Invoke-Command cmdlet is used to execute various commands on multiple machines. It returns the output obtained from the commands(including the errors if any). This blog post has provided a detailed knowledge about the working and usage of the Invoke-Command cmdlet in PowerShell. For a better understanding, a various use cases of the Invoke-Command cmdlet are also explained.