This post demonstrates the functionality of the Get-Date cmdlet in PowerShell.
How to use PowerShell Get-Date Cmdlet?
The Get-Date cmdlet is used in PowerShell to show the date/time in the output. To get the latest date and time on your machine using the PowerShell, you need to use the Get-Date cmdlet. This cmdlet will give you the date and time in alphanumeric format.
Syntax
Syntax elements are explained as:
- Get-Date: used to get the date/time
- [[-date] DateTime]: allows you to specify a specific date and time.
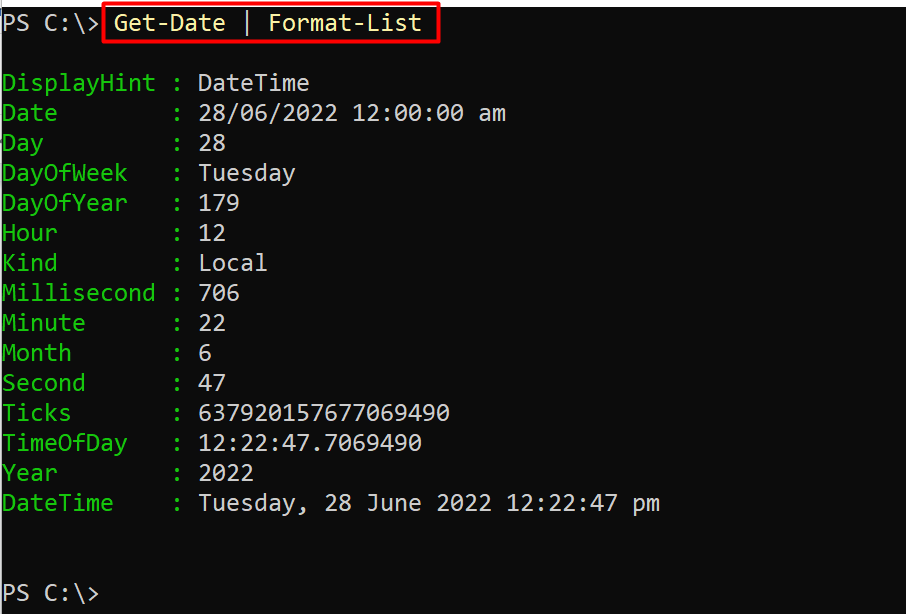
Example 1: Get the Formatted date and time
The Format-List cmdlet displays the detailed output of any command in PowerShell. In the below-given command, the Get-Date cmdlet is piped with the Format-List to get the formatted output of the date/time:
The output showed us the list of formats returned by the Format-List cmdlet.
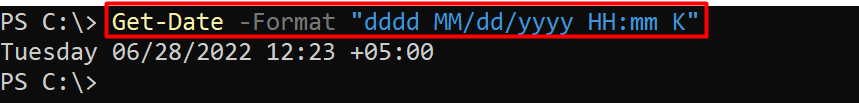
Example 2: Get the current Timezone along with the date/time
You can obtain the Date/Time in a specific format using the -Format parameter. In the example command below, the dd denotes the day, the mm denotes the month, and yyyy denotes the year. Whereas the HH:MM and K denote the hours:minutes, and time zone, respectively. You can get the Date Time in the specified format by using the -Format parameter.
The output shows the current date and time with the time zone, returned by the above line of code.
Example 3: Get the current time or current date only
WIth the help of the -Format parameter, you can get the current date or current time separately. If we use the t along with the -Format parameter, it will show you the time in 12-hour format. The example command is provided here:
The output time is displayed in the 12-hour format.
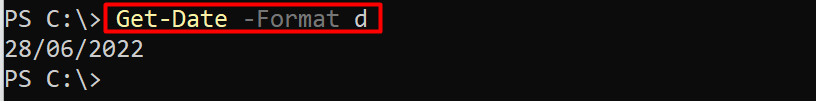
Similarly, you can provide the value “d” to the -Format parameter to get the current date:
The current date is printed on the terminal.
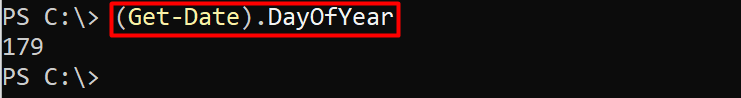
Example 4: Retrieve the specific day of the current year
You can also find which day number is today by simply running the following code. It will give you the day number. To do so, the DayOfYear property is used as follows:
Hence, the output returned the day number of the year, returned by the command
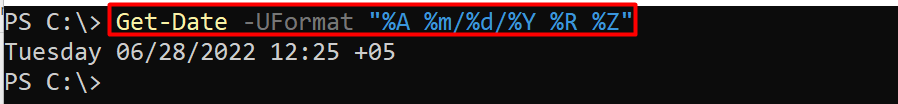
Example 5: Get the current date and time using format specifiers
The format specifiers are single characters used to display the specific date and time. Some of the most used format specifiers are listed below:
%A: denotes the day name of the week
%m: represents the month of the year
%d: shows the date of the month
%Y: indicates the year
%R: represents the time in 24-hour format
%Z: refers to the time zone
The following cmdlet will exercise the -UFormat parameter to get the date in a UTC format:
The date, time, time, and time-zone is printed in UTC format.
Congrats! You have learned to use the Get-Date cmdlet of PowerShell.
Conclusion
The Get-Date command is mainly used for getting the current date and time running on the system. However, various parameters of the Get-Date cmdlet can be used to get the time/date in the formatted output. This post describes the functionality of the Get-Date cmdlet in PowerShell. The -Format and the -UFormat are the primary two parameters that are used to get the date/time in a detailed format.