In this tutorial, we will discuss PowerShell Filters in detail. Let’s start!
How to filter results using PowerShell?
In PowerShell, the Where-Object command filters out or narrows down the results with the help of the added comparison operator.
Syntax
To filter any result, use the below syntax of Where-Object piped with PowerShell Object:
PowerShell Comparison Operators
Here, we have enlisted some of the majorly used comparison operators with the Where-Object cmdlet:
| Filter Operator | Description |
|---|---|
| -eq | Equals to |
| -ne | Not equals tp |
| -contain | Contains the particular value |
| -ge | Greater than equals to |
| -le | Less than equals to |
| -gt | Greater than |
| -lt | Less than |
| -match | Match with the particular value |
Have a look at some of the examples of filtering results using Where-Object PowerShell command.
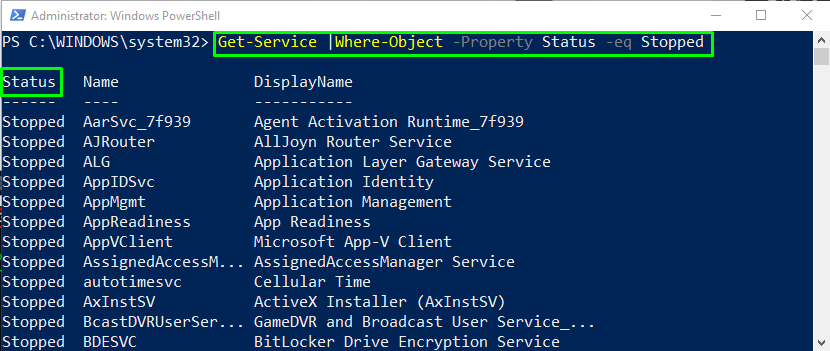
Example 1: PowerShell filter with -eq operator
In this example, we will filter out the services by using the -eq (equals to) operator:
The Get-Service command will fetch the list of the services and piped it as an input to the Where-Object command, which will then filter out the services whose status equals Stopped:
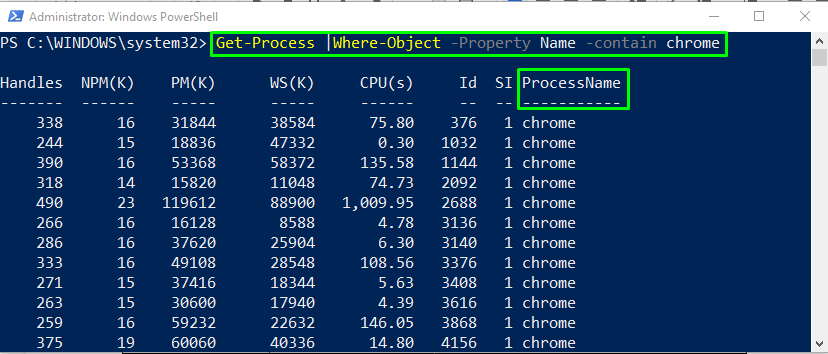
Example 2: PowerShell filter with -contain operator
We will now utilize the -contain operator as a parameter in the Where-Object command to list out the processes containing the ProcessName as chrome:
The Get-Process command will retrieve the list of all processes and piped it to the Where-Object command for further processing that is stated above:
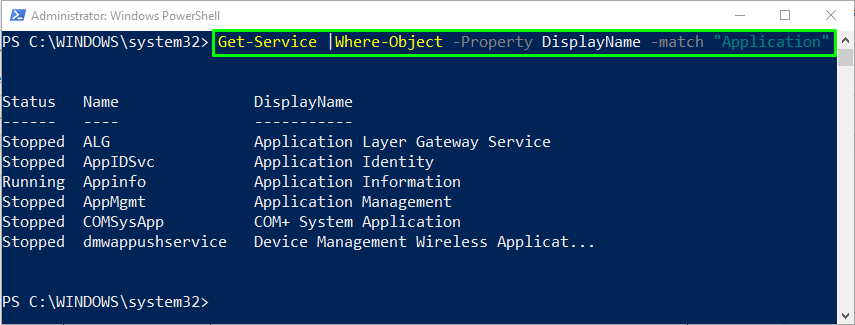
Example 3: PowerShell filter with -match operator
In the below-given command, we will use the -match operator with the Where-Object command:
The output will display the list of all the services with having the word Application in their DisplayName:
That’s all! We have compiled all of the related information about filters in PowerShell with examples.
Conclusion
To filter out the results of your choice, you can use PowerShell filter Where-Object cmdlet. Its syntax is given as: <PS-Object> | Where-Object [-Property] <name> [-Filter] <comparisonoperator> [-FilterValue] <value-name>. The Where-Object command filters out results based on the condition using comparison operators, and its output depends on the specified parameters. This tutorial discussed PowerShell filters with appropriate examples.