[adthrive-in-post-video-player video-id=”MororcvS” upload-date=”2020-03-26T14:40:11.000Z” name=”How to do port scan in linux” description=”How to do port scan in linux” player-type=”collapse” override-embed=”true”]
TCP Scanning
TCP is stateful protocol because it maintains the state of connections. TCP connection involves a three-way handshaking of Server socket and client-side socket. While a server-socket is listening, the client sends a SYN and then Server responds back with SYN-ACK. Client then, sends ACK to complete the handshake for the connection
To scan for a TCP open port, a scanner sends a SYN packet to the server. If SYN-ACK is sent back, then the port is open. And if server doesn’t complete the handshake and responds with an RST then the port is closed.
UDP Scanning
UDP on the other hand, is a stateless protocol and doesn’t maintain the state of connection. It also doesn’t involve three-way handshake.
To scan for a UDP port, a UDP scanner sends a UDP packet to the port. If that port is closed, an ICMP packet is generated and sent back to the origin. If this doesn’t happen, that means port is open.
UDP port scanning is often unreliable because ICMP packets are dropped by firewalls, generating false positives for port scanners.
Port Scanners
Now that we’ve looked at how port scanning works, we can move forward to different port scanners and their functionality.
Nmap
Nmap is the most versatile and comprehensive port scanner available till now. It can do everything from port scanning to fingerprinting Operating systems and vulnerability scanning. Nmap has both CLI and GUI interfaces, the GUI is called Zenmap. It has a lot of varying options to do quick and effective scans. Here’s how to install Nmap in Linux.
sudo apt-get upgrade -y
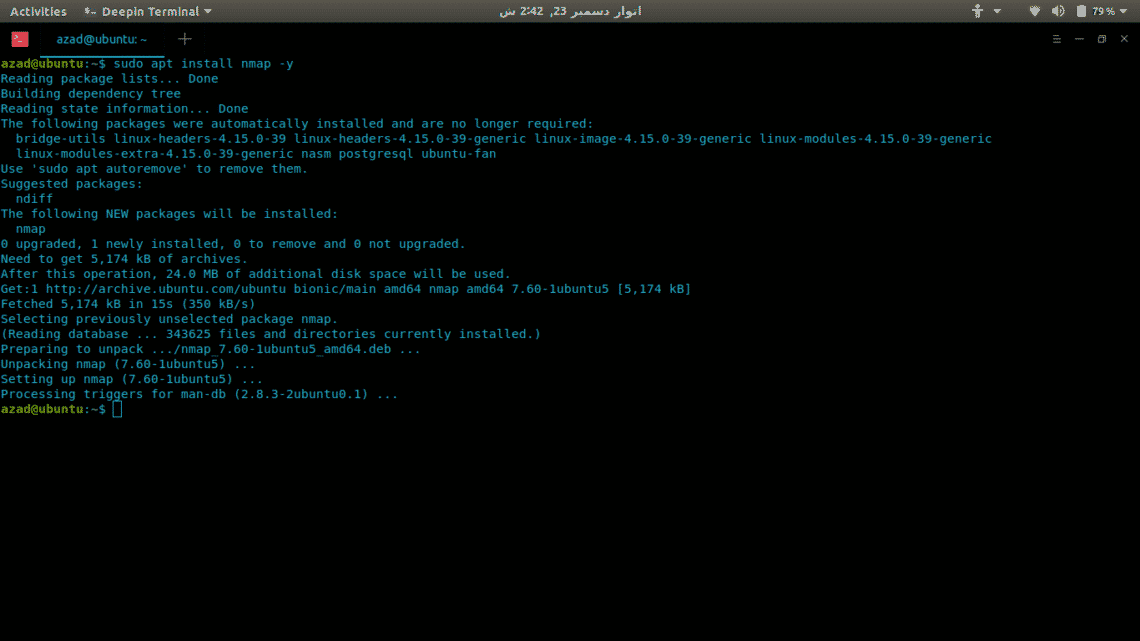
sudo apt-get install nmap -y
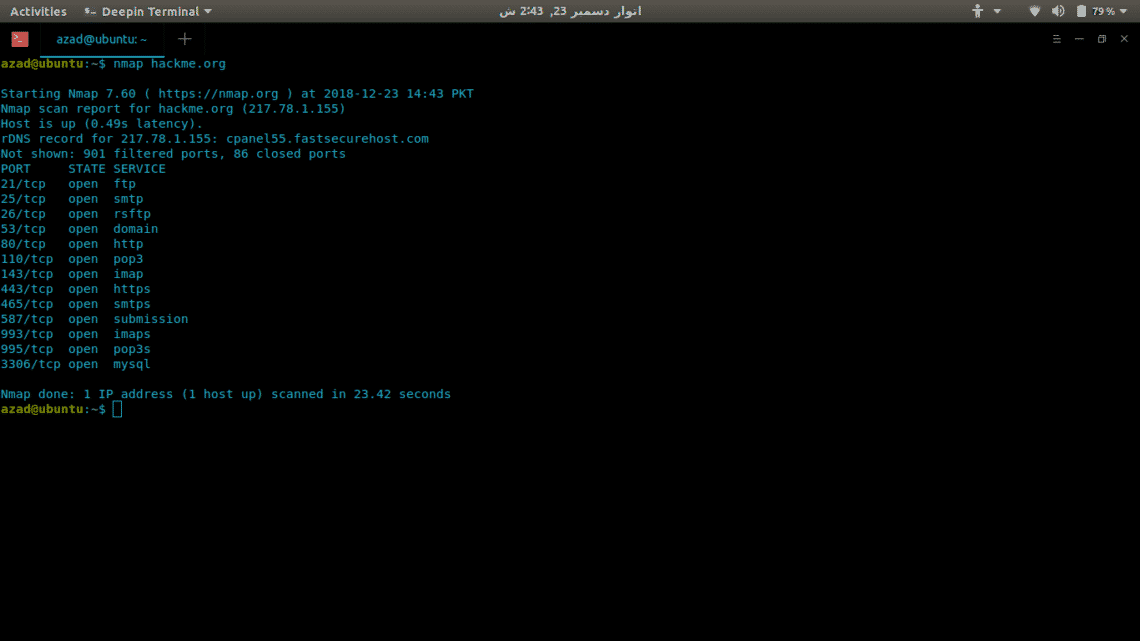
Now we’ll use Nmap to scan a server (hackme.org) for open ports and to list services available on those ports, its really easy. Just type nmap and the server address.
To scan for UDP ports, include -sU option with sudo because it requires root privileges.
There are a lot of other options available in Nmap such as:
-sT : TCP connect scan
-O : Scans for operating system running
-v : Verbose scan
-A : Aggressive scan, scans for everything
-T[1-5] : To set the scanning speed
-Pn : In case the server blocks ping
Zenmap
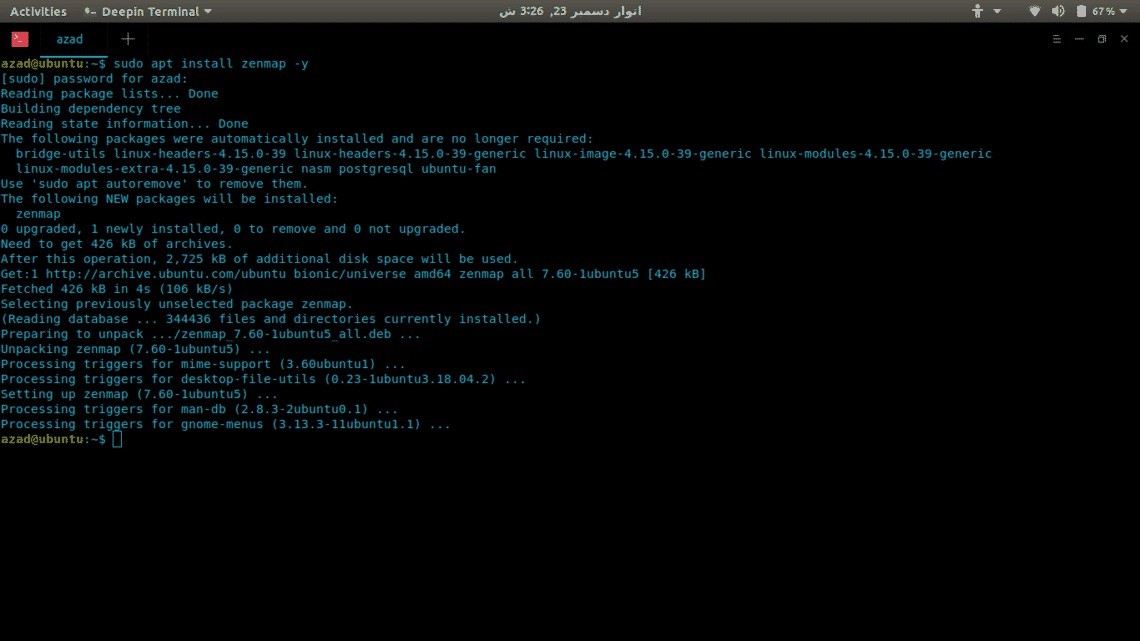
Zenmap is a GUI interface of Nmap for click-kiddies so that you won’t have to remember its commands. To install it, type
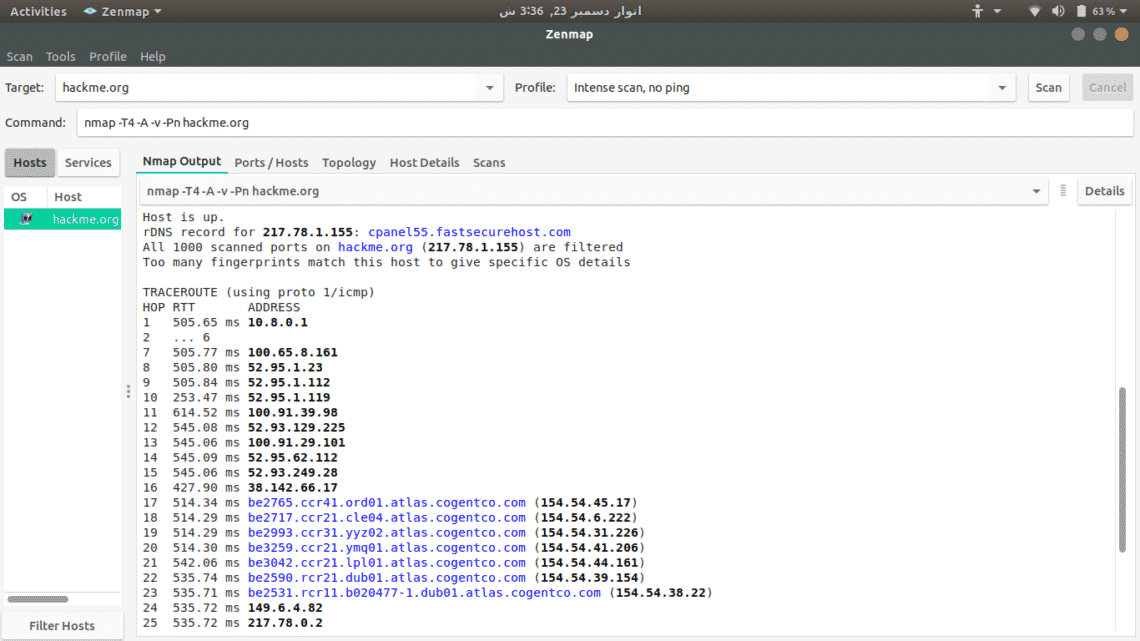
To scan a server, just type its address and select from available scan options.
Netcat
Netcat is a raw TCP and UDP port writer which can also be used as a port scanner. It uses connect scan that’s why it is not so fast like Network Mapper. To install it, type
To check for an open port, write
...snip...
hackme.org [217.78.1.155] 80 (http) open
To scan for a range of ports, type
(UNKNOWN) [127.0.0.1] 80 (http) open
(UNKNOWN) [127.0.0.1] 22 (ssh) open
Unicornscan
Unicornscan is a comprehensive and fast port scanner, built for vulnerability researchers. Unlike Network Mapper, it uses its own User-land Distributed TCP/IP stack. It has a lot of features that Nmap doesn’t, some of them are given,
- Asynchronous stateless TCP scanning with all variations of TCP Flags.
- Asynchronous stateless TCP banner grabbing
- Asynchronous protocol specific UDP Scanning (sending enough of a signature to elicit a response).
- Active and Passive remote OS, application, and component identification by analyzing responses.
- PCAP file logging and filtering
- Relational database output
- Custom module support
- Customized data-set views
To install Unicornscan, type
To run a scan, write
TCP open ftp[ 21] from 127.0.0.1 ttl 128
TCP open smtp[ 25] from 127.0.0.1 ttl 128
TCP open http[ 80] from 127.0.0.1 ttl 128
...snip...
Conclusion
Ports scanners come in handy whether you are a DevOp, Gamer or a Hacker. There is no real comparison between these scanners, none of them is perfect, each of them has its benefits and drawbacks. It completely depends upon your requirements and how you use them.