Some Useful Methods of DateTime Class
| Method Name | Purpose |
|---|---|
| __construct() | It is used to return the object of the DateTime class. |
| add() | It is used to add the day, month, year, hour, minutes, and seconds with the DateTime object. |
| sub() | It is used to subtract a day, month, year, hour, minute, and second with the DateTime object. |
| modify() | It is used to modify the timestamp value. |
| createFromFormat() | It is used to read the date and time strings based on a specified format. |
| setDate() | It is used to set the date value. |
| setTime() | It is used to set the time value. |
| setTimestamp() | It is used to set the date and time based on the UNIX timestamp value. |
| setTimezone() | It is used to set the time zone for the DateTime object. |
| getLastErrors() | It is used to return the warnings and errors. |
Different Examples of DateTime Class
The different uses of the DateTime class are shown in this part of the tutorial using multiple examples.
Example 1: Read the Current Date and Time
Create a PHP file with the following script that prints the formatted date and time values. The object of the DateTime class is created here without using the constructor parameter to read the current date and time values. Next, the format() function is used to print the current date and time in the particular format.
//Read the current date and time
$date = new DateTime();
//Print the formatted current date and time
echo "<center><h3>The current date and time is : ".$date->format("d-M-Y, H:i:s")."</h3></center>";
?>
Output:
The following output appears after executing the previous script:
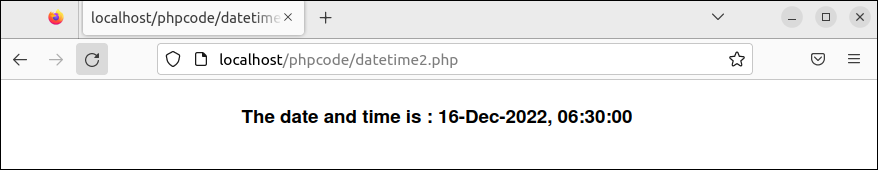
Example 2: Read the Particular Date and Time
Create a PHP file with the following script that prints the particular date and time values with the formatting. The object of the DateTime class is created here with a constructor parameter to print the particular date and time values. Next, the format() method is used to print the date and time in the particular format.
//Read the particular date and time
$date = new DateTime("2022/12/16 06:30:00");
//Print the formatted date and time
echo "<center><h3>The date and time is : ".$date->format("d-M-Y, H:i:s")."</h3></center>";
?>
Output:
The following output appears after executing the previous script:
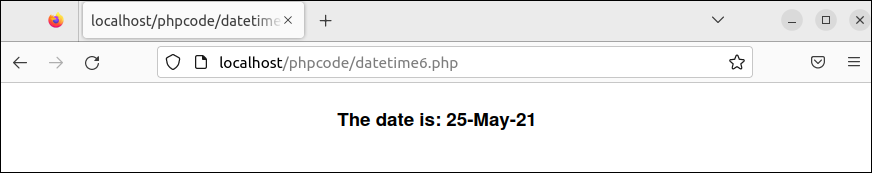
Example 3: Read the Date and Time in a Readable Format
Create a PHP file with the following script that reads the date value based on the English-like string value and print the particular date value with the formatting. Next, the format() method is used to print the date in the particular format.
//Read the particular date
$date = new DateTime("last day of december");
//Print the formatted date
echo "<center><h3>The date is: ".$date->format("d-M-Y")."</h3></center>";
?>
Output:
The following output appears after executing the previous script:
Example 4: Create Date Using CreateFromFormat()
Create a PHP file with the following script that generates a date using the createFromFormat() method of the DateTime class. Next, the format() method is used to print the date in the particular format.
//Read the particular date
$date = DateTime::createFromFormat("d/m/y", "01/12/22");
//Print the formatted date
echo "<center><h3>The date is: ".$date->format("d-M-y")."</h3></center>";
?>
Output:
The following output appears after executing the previous script:
Example 5: Modify the Current Date by Adding Days, Months, and Years
Create a PHP file with the following script that generates a date after adding 10 days, 1 month, and 2 years using the modify() method of the DateTime class. Next, the format() method is used to print the date in the particular format.
//Read the current date
$date = new DateTime();
//Add 10 days 1 month and 2 years with the current date
$date->modify("+10 day 1 month 2 year");
//Print the new formatted date after modification
echo "<center><h3>The date is: ".$date->format("d-M-y")."</h3></center>";
?>
Output:
The following output appears after executing the previous script:
Example 6: Modify the Current Date by Subtracting Days, Months, and Years
Create a PHP file with the following script that generates a date after subtracting 5 days, 6 months, and 1 year using the modify() method of the DateTime class. Next, the format() method is used to print the date in the particular format.
//Read the current date
$date = new DateTime();
//Subtract 5 days 6 months and 1 year with the current date
$date->modify("-5 day -6 month -1 year");
//Print the new formatted date after modification
echo "<center><h3>The date is: ".$date->format("d-M-y")."</h3></center>";
?>
Output:
The following output appears after executing the previous script:
Example 7: Add Days, Months, and Years with the Current Date
Create a PHP file with the following script that generates a date after adding 5 days, 1 month, and 3 years by creating the object of DateInterval class and the add() method of this class. Next, the format() method is used to print the date in the particular format.
//Read the current date
$date = new DateTime();
//Set the interval of 3 years 1 month and 15 days
$interval = new DateInterval('P3Y1M15D');
$date->add($interval);
//Print the new formatted date after modification
echo "<center><h3>The date is: ".$date->format("d-M-y")."</h3></center>";
?>
Output:
The following output appears after executing the previous script:
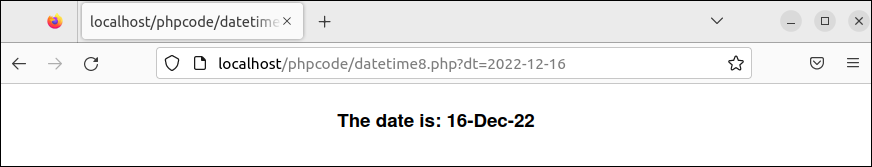
Example 8: Read the Date with the Exception Handling
Create a PHP file with the following script that prints the particular date value that is taken from the URL parameter with the formatting. The try-catch block is used in the script to display the error message for the wrong date value.
if(isset($_GET['dt']))
{
///Read URL value
$dt = $_GET['dt'];
try
{
//Set the date based on the URL value
$date = new DateTime($dt);
//Print the formatted date
echo "<center><h3>The date is: ".$date->format("d-M-y")."</h3></center>";
}
catch (Exception $e)
{
//Print the error message
echo $e->getMessage();
}
}
?>
Output:
The following output appears after executing the previous script:
Conclusion
The DateTime class of the PHP is used to generate the date and time in multiple ways. Some commonly used methods of this class are explained in this tutorial using simple examples.