Topic of Contents:
- Common Disk Partitioning Programs for Debian 12
- Using the GNOME Disk Utility for Disk Partitioning
- Using GParted for Disk Partitioning
- Using Parted for Disk Partitioning
- Using Fdisk for Disk Partitioning
- Using Cfdisk for Disk Partitioning
- Conclusion
- References
Common Disk Partitioning Programs for Debian 12
Some of the common GUI (graphical user interface) disk partitioning programs available on Debian 12 are:
- GNOME Disk Utility or GNOME Disks
- GParted
Some of the common command-line disk partitioning programs available on Debian 12 are:
- Parted
- fdisk
- cfdisk
Out of the disk partitioning programs that we listed, we consider the following beginner-friendly or easy-to-use disk partitioning:
- GNOME Disk Utility or GNOME Disks (GUI)
- cfdisk (Command-line)
Using the GNOME Disk Utility for Disk Partitioning
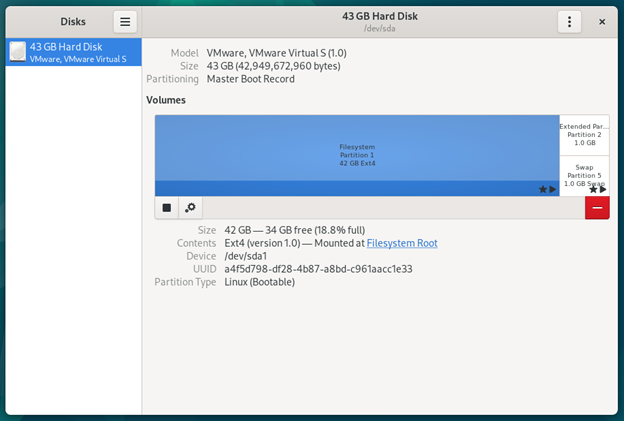
GNOME Disk Utility or simply GNOME Disks is the default graphical partitioning program of the GNOME desktop environment. It has a simple and easy-to-use user interface (UI). If you’re using the GNOME desktop environment (or other desktop environments that default the GNOME disks as the partitioning program) on Debian 12, you can use it to do the disk partitioning very easily. To learn how to use the GNOME Disks to partition your storage devices, read this article.
If you’re using a different desktop environment (than GNOME) where the GNOME Disks are not installed by default, you can run the following commands to install the GNOME Disks on your Debian 12 operating system:
$ sudo apt install gnome-disk-utility
A screenshot of the GNOME Disks app is shown in the following:
Using GParted for Disk Partitioning
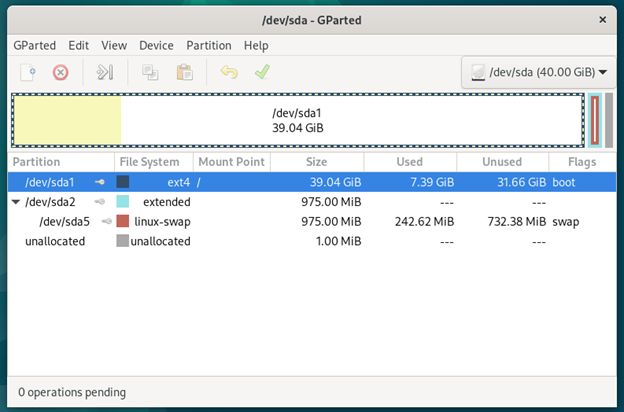
GParted is an advanced graphical partitioning program based on the command-line program parted. It is full of advanced features and the user interface is not as friendly as GNOME Disks. If you’re a beginner, it’s very easy to get overwhelmed by all the features/terms of GParted.
If you need to do some advanced partitioning that GNOME Disks can’t perform, you might want to use GParted. To learn how to use GParted to partition the disks on your Debian 12 operating system, read this article.
GParted is not installed on Debian 12 by default. To install GParted on Debian 12, run the following commands:
$ sudo apt install gparted
A screenshot of GParted is shown in the following:
Using Parted for Disk Partitioning
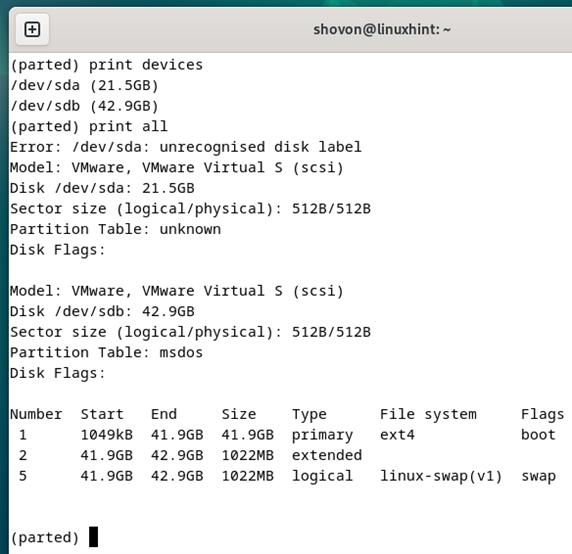
Parted is an advanced terminal-based partitioning program. It is full of advanced features and is aimed at advanced users (who love the Linux command line).
If you need to do some advanced partitioning from the command line, look no further than Parted. To learn how to use Parted to partition the disks from the command line on your Debian 12 operating system, read this article.
Parted is not installed on Debian 12 by default. To install Parted on Debian 12, run the following commands:
$ sudo apt install parted
A screenshot of running Parted from the command line is shown in the following:
Using Fdisk for Disk Partitioning
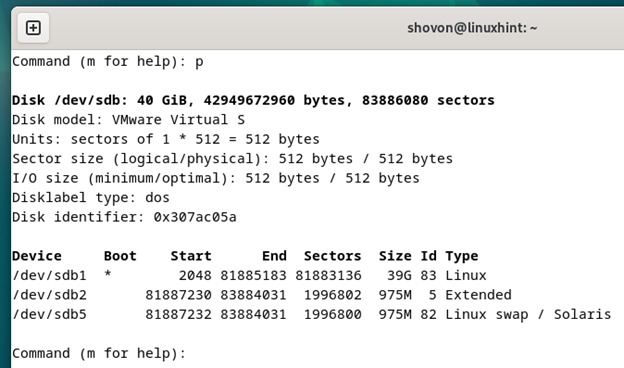
The fdisk is also an advanced terminal-based partitioning program. Its text-based user interface is a bit easier to understand and use for beginners than Parted. Although it has fewer features than Parted/GParted, it’s still capable of doing many disk partitioning tasks.
To learn how to use fdisk to partition the disks from the command line on your Debian 12 operating system, read this article.
The fdisk is installed on the Debian 12 server and desktop operating systems by default. So, you won’t have to install it manually.
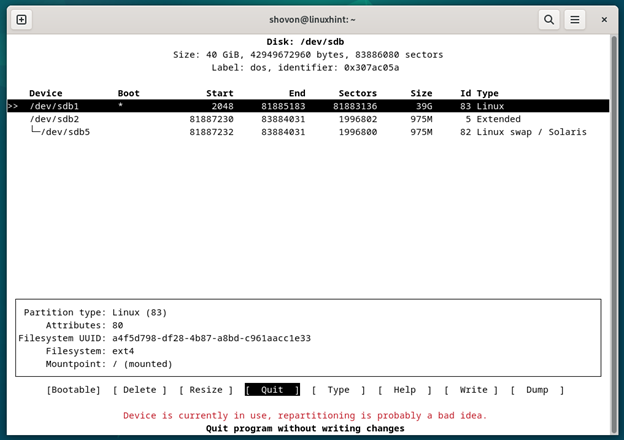
A screenshot of running fdisk from the command line is shown in the following:
Using Cfdisk for Disk Partitioning
The cfdisk is a terminal-based partitioning program. It’s a slimmed-down version of fdisk. It does not have a lot of features but it’s enough to do the basic disk partitioning. The cfdisk has an easy-to-use text-based user interface. It’s a great disk partitioning program for beginners as well as advanced users.
To learn how to use cfdisk to partition the disks from the command line on your Debian 12 operating system, read this article.
The cfdisk is part of fdisk. So, it’s installed on the Debian 12 server and desktop operating systems by default. There is no need to install it manually.
A screenshot of running cfdisk from the command line is shown in the following:
Conclusion
In this article, we talked about some of the GUI and command-line disk partitioning programs available on Debian 12 that you can use to partition the disks of your computer. Out of these disk partitioning programs, the GNOME Disk Utility or GNOME Disks and cfdisk have very self-explanatory user interface (UI). GParted, parted, and fdisk have a lot of advanced features and are mainly aimed at advanced users. Compared to GParted and parted, fdisk is a bit easier to use.