How To Get the YAML Package in the Rust Language in Ubuntu 20.04
Rust provides us with a package called yaml_rust, which we have to implement inside our program while parsing any YAML file. A memory safety feature and other advantages of the Rust language are present in the yaml_rust, a pure Rust implementation of YAML 1.2. Let’s use the cargo command to build a new project inside. We have given a command “$ cargo new example1_cargo”. This command creates a new directory named example1_cargo. To name the project, we have used the command “$ cd example1_cargo”.
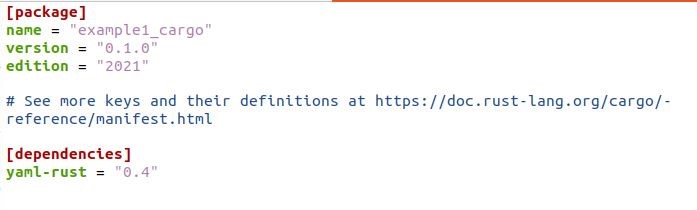
The files that Cargo creates are stored in a directory with the same name as our project, example1_cargo, by the second command. List the files by entering the example1_cargo directory. You will notice that Cargo has produced a Cargo.toml file and src directory with the main.rs file. To add the yaml-rust inside the Rust, open the cargo.toml file and insert the “yaml-rust = 0.4” in the dependencies section. As the yam-rust dependency is added in our cargo.toml file, save it, and let’s move to write a code in the src main.rs file to parse YAML.
Example # 1
With this solution, we want to offer YAML parsers that are 100% compliant with YAML 1.2. There are only a few known issues that prevent the parser from correctly parsing nearly all examples in the specification. In some circumstances, an empty plain scalar is an exception. It may not be a major issue for most users, though, as the popular library libyaml also has trouble parsing these samples.
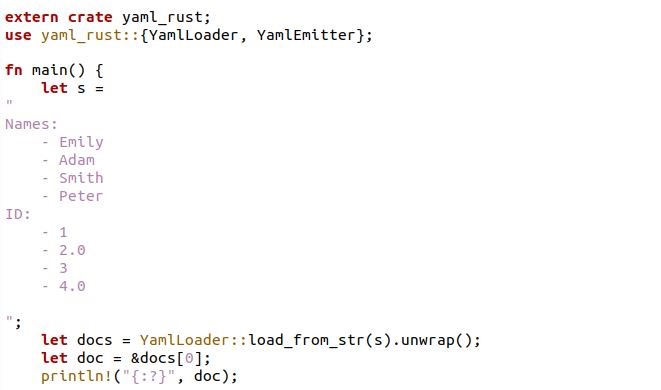
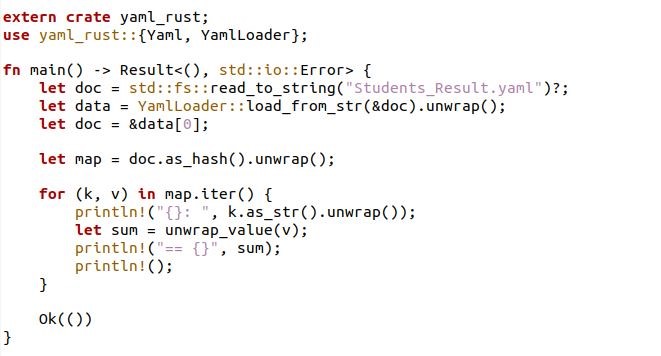
Here, we have to import the yaml-rust dependency with the extern crate. A dependency yaml-rust written with the external crate is specified by an extern crate declaration. The extern crate declaration’s given identifier is then used to bind the external crate into the declaring scope. After that, the YAML documents are loaded using yaml::YamlLoader and accessed as a Vec/HashMap. Then, within the fn main() of the Rust program, we have a let statement used to create the YAML structure data. There is another let statement which is called with the variable docs. Inside that docs variable, we have unwrapped the YAML data, which is loaded inside the variable “s”.
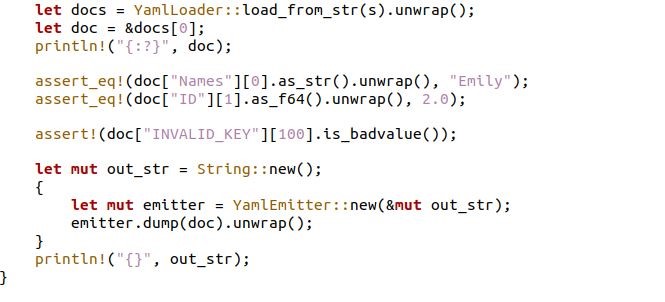
The unwrap function is used to give the results of the computation and return panic if something unexpected occurs. The doc variable selects the first document, which is defined by the let expression. With the println command, the debugging of the document is handled. With the “assert_eq!” expression, we have access to the index for the map and array. The invalid array or key is also verified by the assert method, which throws the BadValue message if they do not exist. Then, the YAML object is dumped into the string.
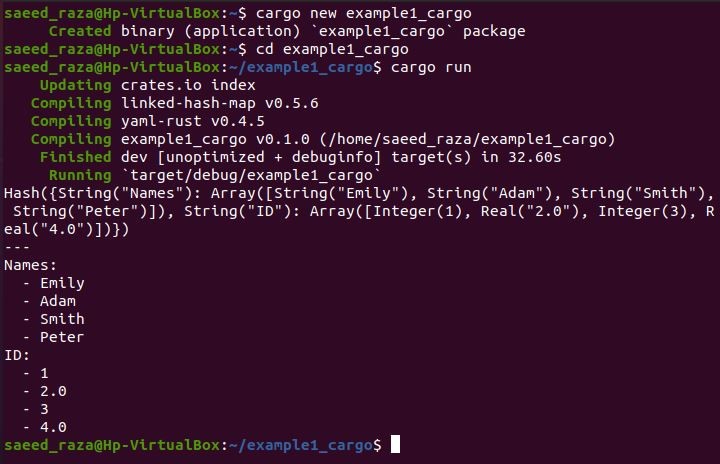
The previous code compiles with the cargo run command, which generates the maps and array of the YAML document in the Rust format. Also, the YAML document is printed inside the following figure:
Example # 2
The previous example demonstrates the parsing of a YAML document inside the Rust program. Here, we have created a separate YAML file that Rust will process. Note that keep the YAML file inside the directory where the src folder and cargo.toml file is located or else the compiler could not parse the file. We have a Students_Result.YAML file for the parsing in Rust. The document inside this YAML file is as follows:
Here, we have the Rust program for parsing the YAML file. Before that, we have to add the yaml_rust dependency in the cargo.toml file.
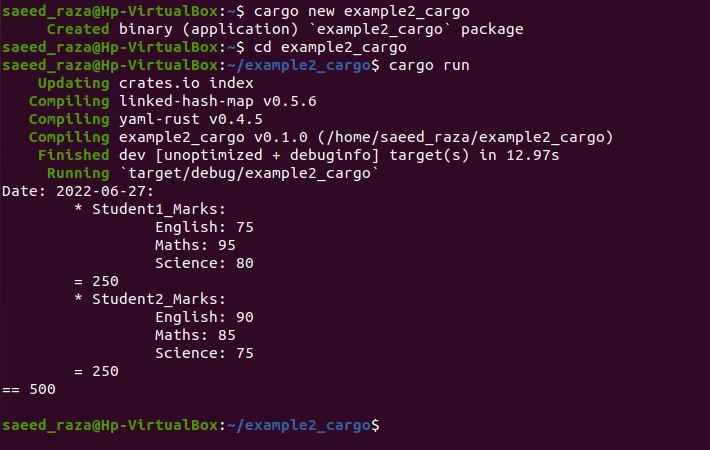
Here, we have included the yaml_rust package with the extern create declaration and also declared the yaml_rust, which has the YAML loader and YAML emitter objects. The YAMLloader loads the YAML document and the YAML emitter act as the output stream. Then, we entered our main function implementation, where the io error is assigned for the file system operations failure. Inside the fn main(), we have let statements declare the variables. The docs variable has the std::fs command for copying the file “Student_Results.yaml”.
There is another variable data that load the YAML file. With the unwrap method, we have displayed the results of the computation. Through the variable doc, we have accessed the YAML document. Then, we iterated the map key values and got the sum of the values. The marks inside the YAML document will be the sum of the map iteration operation. Then, the Rust match pattern for the case: yaml::hash operation. Also, for the yaml::Array, Yaml::string, and the yaml::integer.
Conclusion
The article is all about the parse of the YAML file in Rust. The Rust language supports YAML files and documents. With the yaml-rust dependency, we can easily manipulate the YAML files or documents in Rust. We have to configure the yaml-rust dependency inside the cargo.toml file, which can permit us to access the YAML module of Rust. We have given two examples with the YAML syntax and parsed them with the Rust language.