How To Get the YAML Library in the C++ Language?
A comparable library for C++ that can produce and read YAML files is called YAML-CPP. Key-value pairs are the foundation of YAML. These include collections, associative arrays (maps, dictionaries), scalars (integers, floats, strings, and bools), and NODES, which are lists containing many keys: value pairs. Additionally, YAML supports the creation of aliases and references. The C++ emitter and YAML parser that adheres to the YAML 1.2 specification is called yaml-cpp. CMake is used by yaml-cpp to facilitate cross-platform building. Install CMake first (Resources -> Download) to continue.
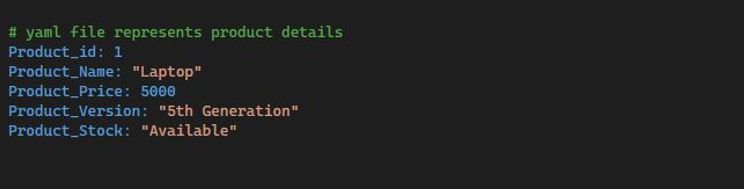
The basic steps in construction are: Be sure to add the bin folder for CMake to your path if you choose not to utilize the available platform-specific installation. Enter the source directory; make a build folder, then launch CMake. The folder YAML-CPP \source\cmake\yaml-cpp must be set to Destination after being built or copied to a preferred path. Let’s start by saving a plain YAML file with the name products.yaml, so it can be read later using C++ scripts. Our product.yaml file contains the following information:
Example of Parsing YAML File in a C++ Program by Using the yaml-cpp Module
For YAML reading and outputting, this script makes use of the libyaml library. An illustration of parsing YAML code is provided here. A series of events are produced by the parser from a stream of input bytes. Based on the “data style”, we divide the interesting events. Let’s set some header files for accessing the functionality of implementing the C++ code and yaml-cpp.
First of all, the statement #include<stdio.h> instructs the compiler to include the data of stdio at that specific location. We use various functions in C/C++ like cout, puts(), and printf(). These procedures are not ones that the programmer has defined. Within the language library, these modules are already defined. The next one is the yaml.h header file, which is from the yaml-cpp package; we can access the yaml-cpp events. Then, the assert.h library file where the considerations by the program can be verified using the assert macro found in the Standard Library’s assert.h header file, which will produce a warning message if the assumption is incorrect. Then, the yaml-cpp header files node.h and parser.h for performing the reading functionalities in C++. Now, we have the main function of this code. Let’s discuss briefly what we have done in our main code.
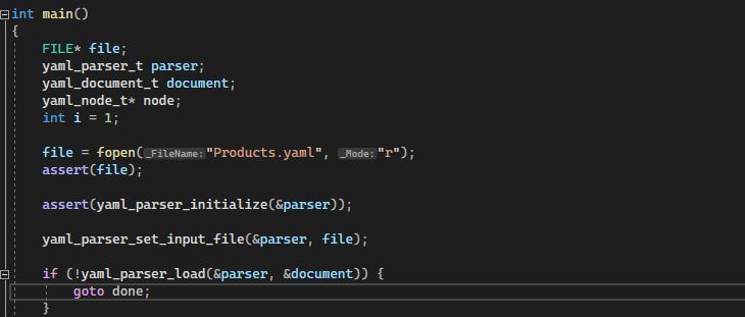
Inside the int main function(), we have declared some function, which includes a file that assigned the file’s pointer to be opened. Then, from the yaml_parser_t, we have defined the parser object. The yaml_parser is the parser architecture in C++. It only has internal members. The family of yaml parser_functions is used to manage the structure. Then comes the yaml_document, which is the structure for the document to be parsed. The yaml_node_t is the node type structure that takes the pointer node variable. After that, we initialized the variable with the value 1, which later iterates throughout the loop. The file is opened by invoking the fopen method inside the variable file, and we have passed the “Products.YAML” file inside the fopen method in the read mode.
The file variable is then passed inside the assert method as an input for the assertion operation. Again, we have utilized the assert method. But this time, we have passed the yaml_parser_initialize function to initialize the empty object parser. The file input is set with the yaml_parser_set_input_file function, which takes the parse object reference and the file object open for reading. To create a series of documents that make up the input stream, we have called the yaml_parser_load function. If no root node exists in the generated document, the document’s completion has been reached.
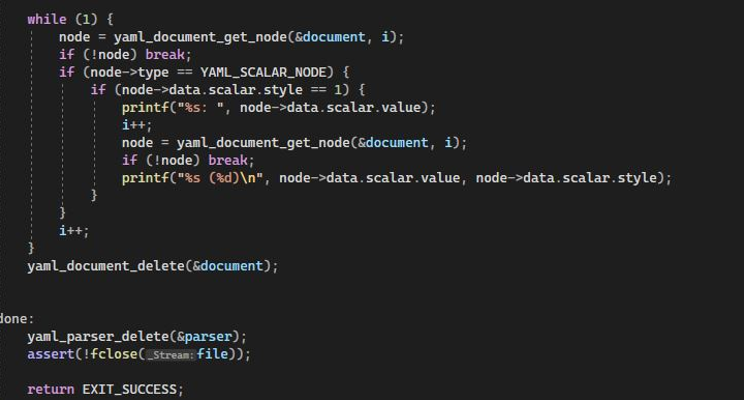
Now, we have a while loop implementation that iterates over each node inside the document. Within the while loop section, we have a variable node initialized with the function yaml_document_get_node. This function takes the document’s reference and the index value of node i. The function returned the node of the document if it is found in the range of the node. The iteration breaks if the node is not found. Then, we have nested if statements where in the first statement, we have node type equal to the YAML_SCALAR_NODE. In the nest, if statement, we have presumed that a string represents the key. In the end, we freed up the memory by the yaml_parser_delete function and closed the file.
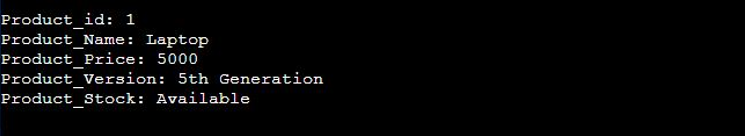
The previous parser code generated the following output, which is in the C++ format style.
Conclusion
Here, we are closing the article. We have generally described the parsing of YAML files in the C++ language. All we have to do is just download the yaml-cpp module in our CMake project and then utilize the yaml.h header file inside our program. We have covered an example in which we have deployed all the possible functions and their members provided by the yaml-cpp module for parsing the YAML file in C++.