How to get the YAML library in the Bash language in Ubuntu 20.04?
Here, we have given an example of parsing the YAML file by using the bash scripting language with the Ubuntu 20.04 terminal. Check out the example of parsing a YAML file in the bash programming language below.
Example # 1: Program of parsing the YAML file in bash script in Ubuntu 20.04
Using sed and awk, the following bash-only parser can analyze straightforward YAML files. This program will read each key and value pair as a bash variable, assigns the value to that variable, and then reads the next key and value pair. The person.yaml file shown below is going to be parsed in the bash script.
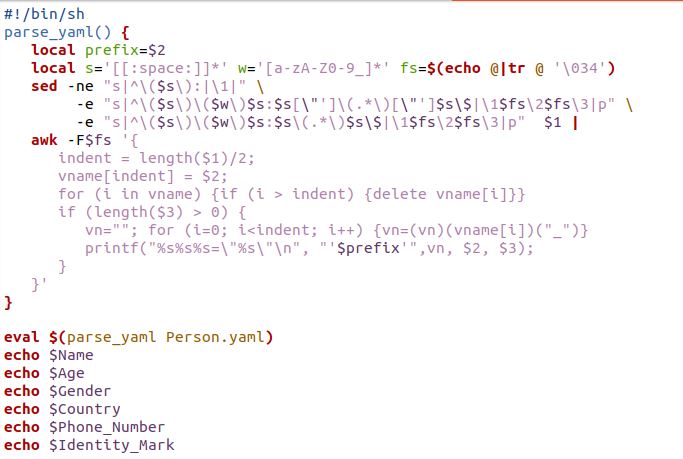
As we are in the file of the bash script, begin with the bash header section. We have given a path ‘#!/bin/sh’. Some of these approaches require a shebang in the script’s header, which in this case signifies that the script is a shell script or bash script. So, be careful in placing this command at the beginning of the file. The script will be run using the command and the bash interpreter. Even if it functions without them, writing the shebang header is required. After that, we created the function and named it parse_yaml(). Inside that function, we have a keyword local which indicates the variable here. The only code block that can view a local variable is the one where it was declared.
Local “scope” is present. A local variable in a function is only meaningful within the boundaries of the function block. We have defined the first variable as a prefix and assigned it the $2 which is sometimes referred to as a positional argument. Here, $2 is indicated as the second command-line parameter. Then, we have two other local variables ‘s’ and ‘fs’. The ‘s’ is used for reading the standard input from the bash and ‘fs’ is utilized as the separator between input fields while using regular expression.
After that, we have to deploy the sed and awk operation in the parse_yaml function. The line editor sed is not interactive. It accepts text input from either stdin or a file, processes specific lines of the text one at a time, and sends the results to stdout or a file. The sed uses ne and e options. The -ne option displays the first line from the input file. The -e option instructs the sed program to run the following command-line argument as sed. Then, come the awk operation that is “data-driven”; you describe the processes to be carried out when the data you’re looking for is found. In addition to automatically opening and shutting records, reading records, segmenting records into fields, and counting records are just a few of the things that awk can do for you. The parse_yaml function is then closed. In the end, we have the command “eval” that comes with Linux or Unix. To run the inputs as a shell command on a Linux or Unix system, the “eval” command must be used. The “eval” command takes the parse_yaml function with the Person.yaml file.
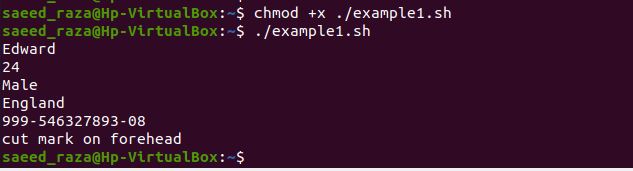
The YAML file’s specific data is printed using the echo command. We have executed the above bash script for parsing the YAML file by using the bash command in ubuntu 20.04. The output generated in the shell is having the data of the YAML file in the bash format.
Example # 2: Program of parsing the complex YAML file in bash script in Ubuntu 20.04
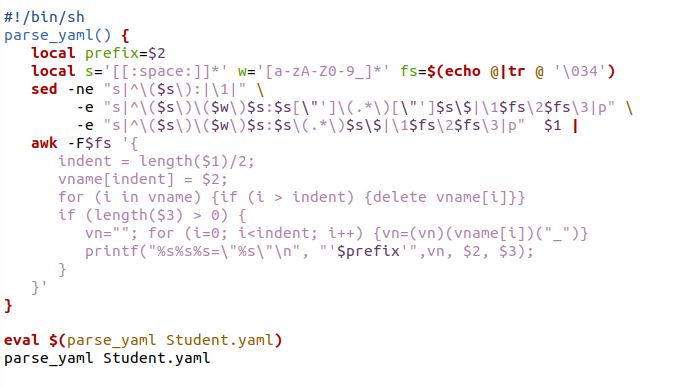
As aforementioned example briefly demonstrated the parsing of the yaml file. Now, we have taken a complex YAML file structure to show how bash parses this YAML file. Also, we are trying to parse the yaml file data that is not present in the YAML file. The following is the student.yaml file content:
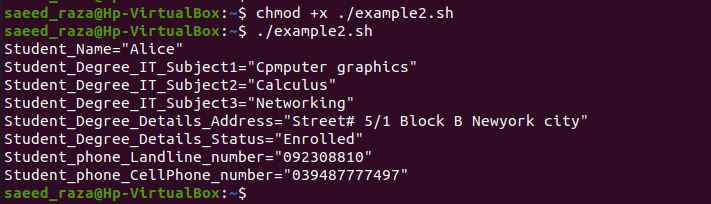
This particular bash script is the same as the above bash program. We have just used the different files here. The student.yaml file is going to parse by the bash. In the previous example, we have printed the field one by one by invoking the echo command. But here, we have just printed the function name parse_yaml with the student.YAML file. On the subsequent snap of Ubuntu 20.04, you can view the results.
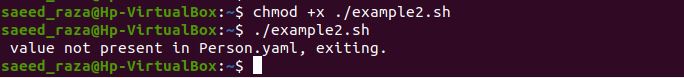
Here, we have included another function as verify_param() in our bash script to check the existing inputs. The function will check each input in the file Student.yaml.
As we have provided the input $student_Result which does not exist in the Student.yaml file. Upon interpretation of the bash script, the exception message is shown that we have provided to the echo command in the verify_param() function. You can now use the straightforward function to manage all of your parameters. You don’t need to initialize each one separately and verify for null values.
Conclusion
The article aims to parse the YAML file in a bash scripting language which we have shown you by giving two examples. The first example of a bash script is to show the selected data from the YAML file by calling the echo command on the specific input. The next example parses the whole YAML file by just giving one command. Furthermore, the second example adds one more function of verifying the parameter values. That is especially helpful if you want to run an operation that requires a certain result from a YAML file.