Syntax:
The syntax of the DATE_FORMAT() function has given below.
Here, the first argument contains a date or DateTime value from the date field of the database table. The second argument contains the format specifier defined by ‘%’ to get the formatted output of the date value. Different types of format specifiers have been described in the next part of the tutorial.
Date Format Specifiers:
One or more format specifiers can be used as the format value of the DATE_FORMAT() function. The format specifiers used to format the date in MySQL are given below.
| Specifier Name | Description |
| %a | It is used to print short weekday names. (Sun..Sat) |
| %b | It is used to print short month names. (Jan..Dec) |
| %c | It is used to print numeric month names. (0..12) |
| %d | It is used to print the day of the month with the leading 0. (00..31) |
| %D | It is used to print the day of the month with the suffix, such as 1st, 2nd, 3rd, 4th, etc. |
| %e | It is used to print the day of the month without leading 0. (0..31) |
| %f | It is used to print date values in microseconds. (000000..999999) |
| %j | It is used to print the day of the year with the leading 0. (000..366) |
| %m | It is used to print the numeric month value with leading 0. (00..12) |
| %M | It is used to print the full month name. (January..December) |
| %U | It is used to print the week number of the year starting with 00, where Sunday is the first day of the week. WEEK() mode 0. (00..53) |
| %u | It is used to print the week number of the year starting with 00, where Monday is the first day of the week. WEEK() mode 1. (00..53) |
| %V | It is used to print the week number of the year starting with 01, where Sunday is the first day of the week. WEEK() mode 2. (01..53) |
| %v | It is used to print the week number of the year starting with 01, where Monday is the first day of the week. WEEK() mode 3. (01..53) |
| %w | It is used to print the numeric day of the week where 0 represents Sunday. (0..6) |
| %W | It is used to print the full weekday name. (Sunday..Saturday) |
| %X | It is used to print the year for the week where Sunday is the first day of the week, numeric, four digits; used with %V |
| %x | It is used to print the year for the week, where Monday is the first day of the week, numeric, four digits; used with %v |
| %y | It is used to print two digits year. |
| %Y | It is used to print four digits year. |
Use of DATE_FORMAT():
Different uses of the DATE_FORMAT() function in MySQL have been shown in this part of the tutorial.
Example-1: Using a single format specifier
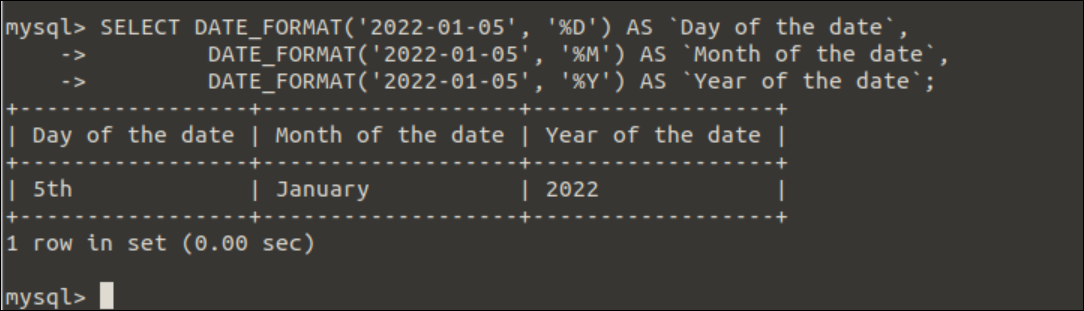
Three different specifiers have been used in the DATE_FORMAT() function of the following SELECT query. The %D will print the day of the month with the suffix of the date. The %M will print the full month name of the date. The %Y will print the 4-digits year value of the date.
DATE_FORMAT('2022-01-05', '%M') AS `Month of the date`,
DATE_FORMAT('2022-01-05', '%Y') AS `Year of the date`;
Output:
Example-2: Using multiple format specifier
In the previous example, a single format specifier has used in each DATE_FORMAT() function. The multiple format specifiers have been used in the DATE_FORMAT() function of the following SELECT query. The formatted date value will be printed after executing the following query.
DATE_FORMAT('2022-05-03', '%d-%m-%Y') AS `Formatted Date`;
Output:
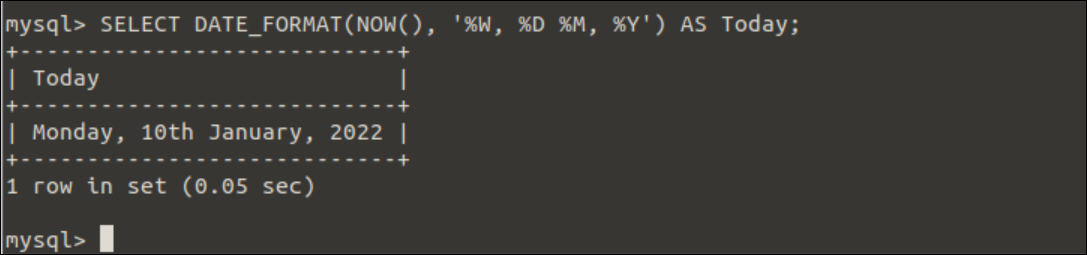
Example-3: Using multiple format specifiers for the current date
The multiple format specifiers have been used in the DATE_FORMAT() function of the following SELECT query to format the current system date. The weekday name of the current date, the day of the current date with suffix, and the 4-digits years of the current date will be printed in the output.
Output:
Example-4: Format date field of the database table
You have to create a database table with the data in a MySQL database to check the use of the DATE_FORMAT() function in the table’s data.
Open the terminal and connect with the MySQL server by executing the following command.
Run the following command to create a database named test_db.
Run the following command to select the database.
Run the following query to create a table named employees with four fields.
`id` int(11) AUTO_INCREMENT,
`name` varchar(50) NOT NULL,
`post` varchar(25) NOT NULL,
`joining_date` date NOT NULL, PRIMARY KEY(id));
Run the following query to insert two records into the employees table.
VALUES (NULL, 'Nur Jahan', 'Assistant Manager', '2021-01-05'),
(NULL, 'Asif Iqbal', 'Manager', '2019-03-20');
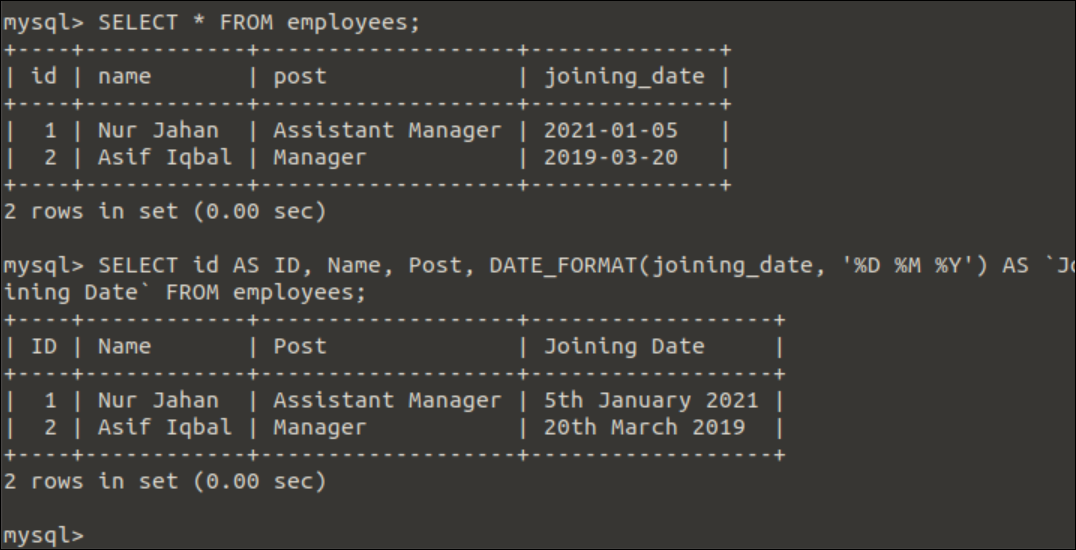
Run the following two SELECT queries to check the original content of the employees table and the formatted date value of the employees table.
SELECT id AS ID, Name, Post, DATE_FORMAT(joining_date, '%D %M %Y') AS `Joining Date` FROM employees;
Output:
Conclusion:
Using the DATE_FORMAT() function with different date format specifiers in the SELECT query has been described in this tutorial with the table data and without the table data. I hope the MySQL users will be able to use this function properly in the query after reading this tutorial.