This article will look at the methods to monitor the system performance using PowerShell.
How to Monitor System Performance with PowerShell?
The performance of the system performance can be checked using the number of methods, some of which are listed below:
- Display system information.
- Check CPU usage.
- Monitor memory usage.
- Check disk usage.
- Get the performance of a specified counter.
- Get the performance of a single counter.
Example 1: Display System Information
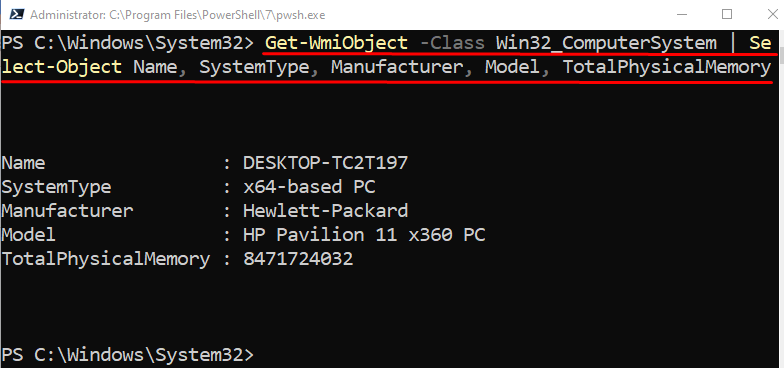
To display the system information using PowerShell, first, use the “Get-WmiObject” cmdlet and then assign a “Win32_ComputerSystem” class to the “-Class” parameter. Next, pipe it to the “Select-Object” cmdlet and then specify the types separated by comma whose information you want to display:
Example 2: Check CPU Usage
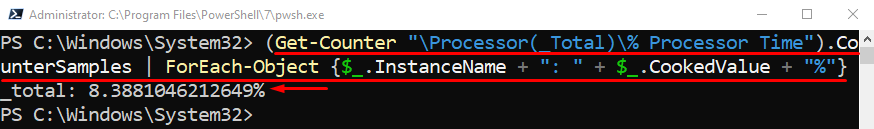
To get the details of the CPU usage, first, specify the “Get-Counter” cmdlet and specify the query “\Processor(_Total)\% Processor Time” and concatenate it with the “CounterSamples” cmdlet. After that, pipe the whole query to the “ForEach-Object” cmdlet. Next, specify the “$_.InstanceName” variable to retrieve the CPU variables display name and then create the “$_.CookedValue” variable to get the usage in numbers:
Example 3: Monitor Memory Usage
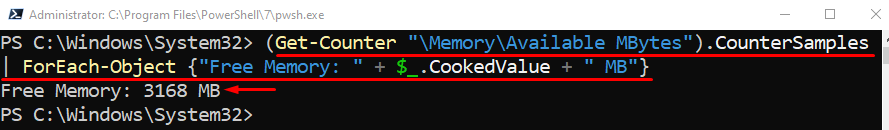
Execute the below query in PowerShell to retrieve the total memory usage:
Example 4: Check Disk Usage
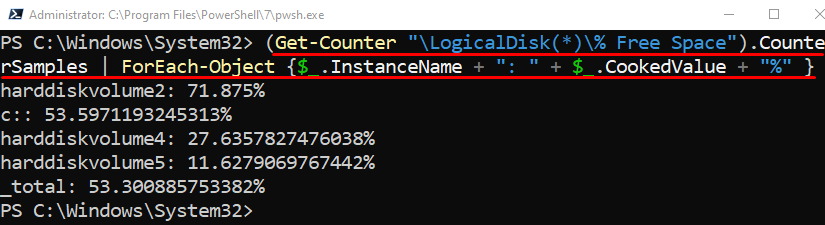
To retrieve the total CPU usage in PowerShell, execute the given query:
Example 5: Get the Performance of a Specified Counter
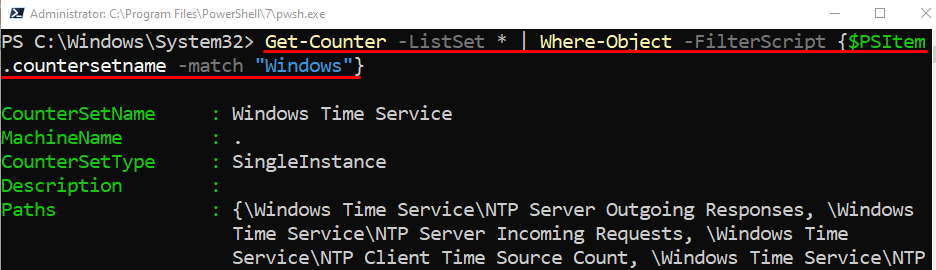
In order to retrieve the detailed performance of a specific counter, first, specify the “Get-Counter” cmdlet, add the “-ListSet” parameter along with the wild character, and pipe it to the “Where-Object” cmdlet. After that create a matching filter and assign it to the “-FilterScript” parameter:
Example 6: Get the Performance of a Single Counter
Lastly, to retrieve the performance of a single counter, first, use the “Get-Counter” cmdlet along with the “-ListSet” parameter and specify the counter name which is “Memory”:
It can be observed that the performance details of the specified counter are displayed in the above output.
Conclusion
To monitor the system performance with PowerShell, use the “Get-Counter” cmdlet. This cmdlet can monitor the CPU usage, memory usage, and disk space usage with PowerShell. This write-up has explained the process to check the system performance with PowerShell.