What Is Ethereum?
That being said it is actually used to fuel this ecosystem known as Ethereum. Ethereum is a decentralized platform with its block chain for its apps to function, and these apps are powdered by these tokens known as ether. So basically ether may or may not be used as a currency, but rather as a fuel to power the Ethereum ecosystem, however it’s widely used as fungible currency as an alternative to bitcoins.
Furthermore, like Bitcoins, Ethereum can be mined, and this process is known as mining ether. Even though the term Ethereum is used interchangeably, it’s more appropriate to use the term ether as it’s actually mined through this process. Ether can be mined with either CPU or GPU, and there are many miners around the world developed by various professionals specifically for this purpose only. The mined tokens then can be stored in wallets, which then can be exchanged or consumed to fuel the app running on Ethereum ecosystem.
What Is Ethminer?
This articles demonstrates how to make use of Ethminer which is used to mine ether with the help of a GPU. Ethminer is an open source cross platform application developed specifically for mining ether, and makes use of OpenCL, and Nvidia CUDA technologies for mining purposes. It also supports stratum protocol which is used for pool mining across a network; hence it can be used even without having a physical computer nearby, as long as the user has access to the Internet that’s all that is needed.
Ethminer is at the moment developed for Windows, MacOS and Linux, and uses the command line to execute its codes. App developers use AppVeyor, and Travis CI which respectively generate Windows executables and MacOS, Linux executables with each commit made in the Github repository, and thus there is no need to compile the source codes like with many Bitcoins miners available out there. Ethminer is easy to use, and extremely fast as long as the recommended hardware is utilized for mining purpose.
How to Install Ethminer
Ethminer, at a glance does seem hard to install, at least on Linux systems, but it’s actually rather easy to install given the right commands. This tutorial assumes the user has either Ubuntu 16 or 17, but it may still work for both newer and older versions as well though it isn’t recommended. Since Ubuntu is free of charge, it’s recommended to upgrade to at least Ubuntu 16.04 prior to following these steps.
The installation assumes the user has either AMD or Nvidia hardware installed on the system, and some steps of the installation should be slightly altered depending on the graphics card.
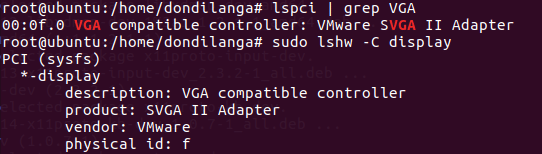
1. First install the graphics drivers. If it’s unable to locate the information related to the graphics adapter, use the following commands in the terminal. Either one is fine, however the second command requires access to the root as it returns more information of the graphics adapter.
$ sudo lshw -C display
2. Once the currently installed graphics adapter is located, note it down somewhere as it’s useful in later steps.
3. Now install the appropriate graphics driver. Only Nvidia and AMD GPUs are supported at the moment, however CPU mining is also possible through Go-Ethereum which has native support for CPUs, but it’s not recommended to use CPUs to mine as it’s not feasible to generate a profit out of it.
- Visit this URL for Installation instructions for Nvidia: https://linuxhint.com/install-nvidia-drivers-linux/
- Visit this URL to download Nvidia drivers for Ubuntu http://www.nvidia.com/Download/Find.aspx?lang=en-us
- Visit this URL to download AMD drivers for Ubuntu http://support.amd.com/en-us/download/linux
4. Now depending on the hardware adapter, install the appropriate graphics driver.
5. For Nvidia adapters, install the CUDA toolkit. CUDA is a property API (application programming interface) developed for general purpose processing on CUDA enabled hardware such as most of Nvidia graphics adapters. This is useful for a range of applications such as mathematical calculations, video and audio converting, simulation applications. Make sure to use sudo su and get root access.
6. For AMD adapters, install OpenCL ICD (installable client driver) which allows multiple implementations of OpenCL to exist on the same system. OpenCL is same as CUDA, an API for general purpose processing, but works on a range of hardware devices, including Nvidia graphics adapters as well.
7. Once either step is completed, install GIT package for retrieving the latest sources of Ethminer, MESA developer package which is a 3D graphics library works on graphics adapter to assist in mining, then cmake to build the sources.
8. Now make a directory to store retrieved Ethminer sources, and then focus on that directory. Creating the directory in Terminal makes the folder in the HOME directory of the currently logged in user. CD changes the focus to the stated folder.
cd ethminer
9. Retrieve the source codes from Github straightly to aforesaid folder with the following command.
10. Then Build the sources with cmake.
cd build
cmake ..
cmake --build .
11. To gain full potential on graphics adapters, use the DETHASHCUDA=ON flag DETHASHCL=OFF flags. What these flags do are respectively enable CUDA, and disable OpenCL. So, the cmake step should be slightly altered like this
12. Additionally if pool mining is intended to be used, then append the following flag as well to enable Stratum protocol. -DETHSTRATUM=ON, then cmake is altered like this.
13. Once the package is built, now it’s time to install it. So install it with the following command. This assumes the user is already in root access as suggested earlier.
14. Now use the following command to make sure it’s installed for sure. If it shows the available command lines, it means Ethminer is installed in the system successfully, otherwise repeat these previous steps at the outset until it’s sorted out.
15. Additionally, to find out the performance of the available hardware adapter, use one of the following commands. The OpenCL one is for measuring the performance of AMD adapters, and CUDA one is for measuring the performance of NVidia adapters.
- OpenCL Benchmark
ethminer -G –M
- CUDA Benchmark
ethminer -U -M
How to Configure Ethminer to Mine Ether
Once Ethminer is installed on the system, the remaining part is configuring it so it’s ready to be used to mine Ether. First of all, before initiating the mining, it’s important to get a valid Ethereum address which is used to retrieve mined Ether. This address is a public; hence it’s shareable, however the given private key is supposed to be kept hidden.
- Visit the following web URL https://www.myetherwallet.com
- Type a valid password and create a wallet to store Ether.
- Now save the given Keystore file which contains relevant information of the wallet.
- After it’s downloaded, proceed by clicking “I understand, Continue” button.
- Save the Private Key. The Website lets users to print it on a paper too. Once the address is saved, proceed by clicking “Save Your Address” button.
- Then it will ask how would you like to access to your wallet, what it means how to retrieve information related to the account. This basically contains “Account Address”, “Account Balance in ETH”, “Transaction History”, “Private Key”, “Public Ethereum Address”.
- Use the following command in Terminal window after filing stated placeholders. HashRate is calculated at the 15th step of the previous segment, use that retrieved value here, Ethereum Address is the public address created with previous steps, RigName is the name of the machine, which is optional, and thus can be omitted if desired. Any custom name can be used there.
ethminer -G -F
http://ethereumpool.co/?miner=<HashRate>@<EtherumAddress>@<RigName>
How to Tweak the Performance?
Performance of mining can be improved in multiple ways, but this is only relevant for CUDA enabled graphics adapters. Use the following flags when benchmarking and then use the returned hash value at the previous segment’s 8th step in HashRate placeholder along with the flags. The hash value is generated at 15th step of segment before the previous segment.
–cuda-block-size: A block is a group of threads which can be executed parallelly, by increasing the block size the application can make use of many threads at the same time. But according to this report after the block size 16,32 depending on the CUDA enabled adapter, the performance gain goes downhill as the time increases. The recommended values are 16,32,64.
–cuda-grid-size: Grid is a group of blocks, as previously, increasing the grid size increases the performance. The recommended values are 8192, 16384, 32768, 65536.
–cuda-parallel-hash: Is a variable parameter which assists in increasing the performance. The recommended values are 8,16.
–cuda-streams: In CUDA stream means a sequence of operations which are executed as they are issued on the video adapter. Here operations mean the mathematical calculations performed by GPU. In both Bitcoins and Ethereum mining, mining means basically solving complex mathematical problems; hence having a higher stream value improves the performance, but there is a limit depending on the model of the graphics adapter. The recommended values are 16,32.
Conclusion
Ethereum is a rising star in the cryptocurrency ecosystem, which plans to lead the information technology to the decentralized way. In Ethereum system, ether is a token which fuels the ecosystem, which can also be traded just as Bitcoins. Ether can be mined with modern graphics adapters just as Bitcoins used to be. The popular selections for this purpose are Nvidia and AMD. Nvidia uses CUDA, whereas AMD uses OpenCL. The Ethminer slightly favors Nvidia GPUs by providing more flags for CUDA APIs, and thus it’s expected that Nvidia GPUs will out perform others. Since contemporary Nvidia graphics adapters are extremely power efficient, it’s more beneficial to use Nvidia graphics adapters compared to AMD which is still popular among Bitcoin miners. Either way Ether is an important part of the future of cryptocurrency, and will probably coexist with Bitcoins instead of replacing it altogether.